Abstract
Russia leads the world in currant production, recording 510kt in 2022. This figure reflects the previous trend and indicates that Russian currant production is stable. Other countries also produce, but their scale is smaller than Russia’s and their influence is limited. This trend is shaped by factors such as climatic conditions, soil adaptability, and agricultural policies. In addition, the growing demand for currants also contributes to the increase in production. While Russia is the global leader, other countries also have their own peculiarities and competitiveness in currant production, but their scale tends to be relatively small.
Currant production (Worldwide)
Looking at the production data for currants from 1961 to 2022, Russia achieved a record production of 510kt in 2022, which is 100% of the peak, and Russian currant production is growing steadily. The reasons for this growth include the suitability of Russia’s climatic conditions and soil, as well as improved agricultural techniques. Meanwhile, currant production in other countries remains relatively stable, and while Russia is the global leader, other countries continue to produce at their own scale. In addition, the increasing demand for currants also contributes to the increase in production. Generally speaking, Russian currant production accounts for the majority of the market share, while other countries also produce according to their region and demand, while maintaining their inherent competitiveness.
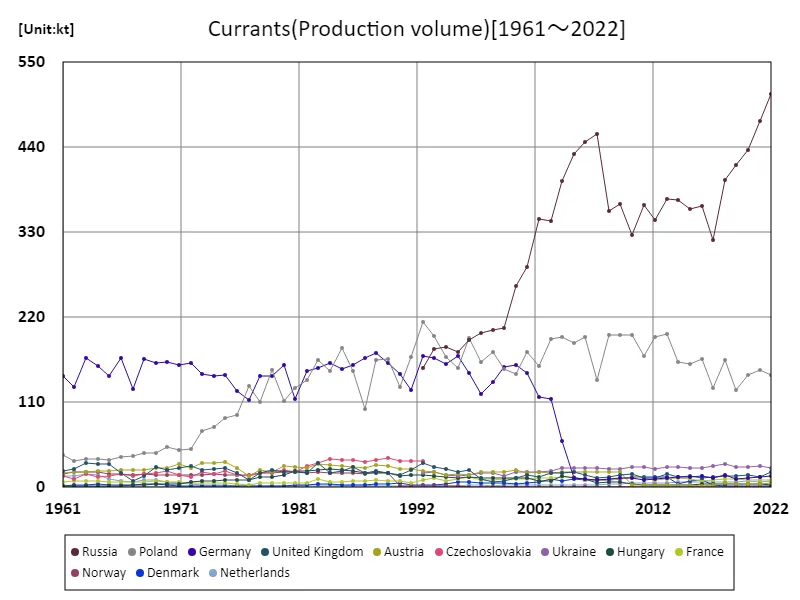

The maximum is the latest one, 510kt of Russia
Currant production (latest year, worldwide)
Looking at the 2022 production data for the agricultural crop currant, Russia recorded an astounding figure of 510kt. This is equivalent to about two-thirds of the total, overwhelming the production of other countries. This trend is likely due to Russia’s vast land area, suitable climatic conditions, and development of agricultural technology. Meanwhile, the average production of other countries remains at a relatively low level of 18.6kt. This suggests that currant production varies by region. In addition, the total production of 764kt indicates that currant is a relatively niche crop. While demand is increasing, production is still limited and competition in the market may become fierce. Overall, while Russia’s production is overwhelming, other countries also meet the global demand for currants while having their own characteristics and competitiveness.
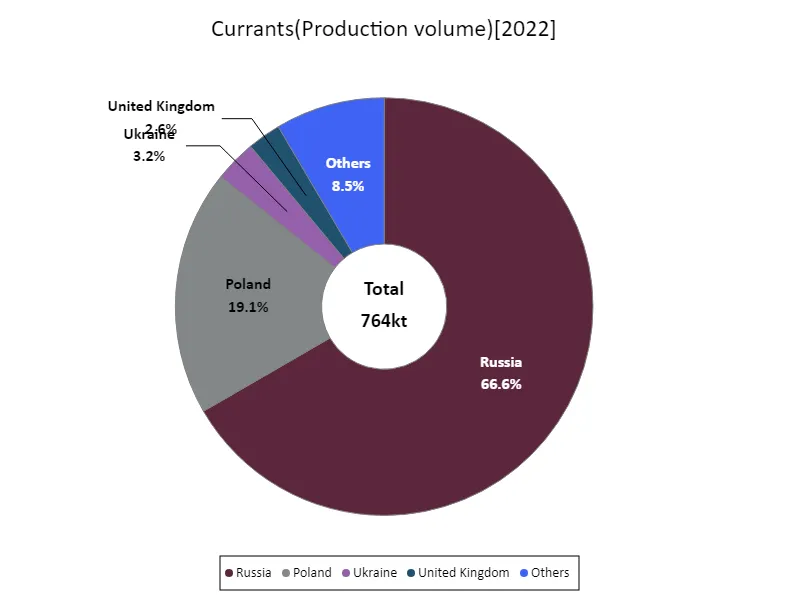

The maximum is 510kt of Russia, the average is 18.6kt, and the total is 764kt
Currant production (continent)
Looking at the 2022 production data for the agricultural crop currant, Europe recorded the largest production of 769kt. This is the highest value ever, indicating that European currant production is steadily growing. This growth is likely due to Europe’s climatic conditions, advances in agricultural technology, and support from agricultural policies. Meanwhile, currant production in other regions is relatively low, with Europe having an overwhelming market share. This is presumably due to the fact that Europe’s land and climate are suitable for currant cultivation and the high demand for currants in the region. In addition, the concentration of currant production in Europe plays an important role in the region’s agricultural economy. Overall, while Europe is the world leader in currant production, other regions also meet the demand for currants while having their own characteristics and competitiveness.
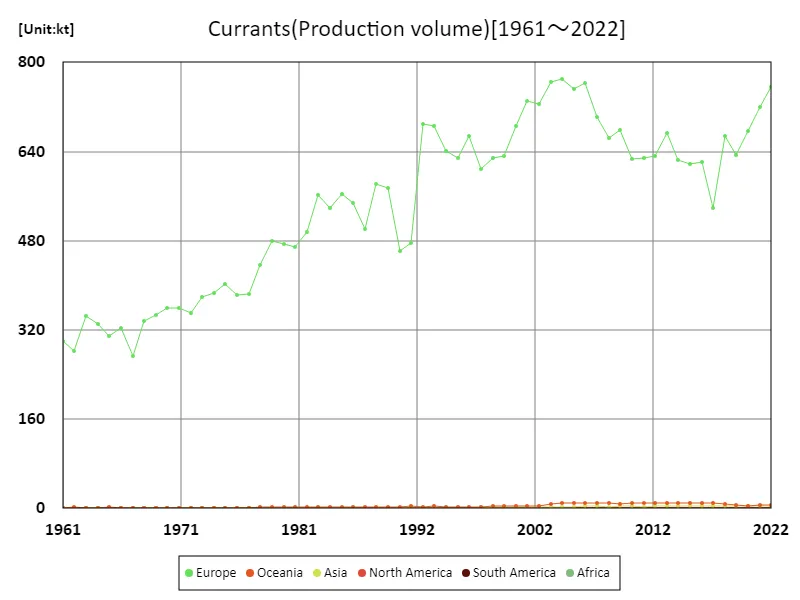

The maximum is 769kt[2004] of Europe, and the current value is about 98.1%
Currant production (latest year, continent)
Looking at the 2022 production data for the agricultural crop currant, Europe recorded the largest production of 755kt. This figure is significantly higher than the average production of other regions, indicating that Europe is the major producer of currants. One of the reasons why Europe’s currant production is overwhelmingly larger than other regions is the suitability of the region’s climatic conditions and soil. In addition to this, the development of agricultural technology and improved efficiency in Europe, as well as the support of agricultural policies, also contribute to the increase in production. On the other hand, the relatively low average production in other regions suggests that currant cultivation is not necessarily suitable in some regions. In addition, the overall production figure of 764kt means that currants are a relatively niche crop. While demand is increasing, production is still limited and competition in the market may be intense. Overall, Europe is the global currant production leader, and other regions also meet the demand for currants while having their own characteristics and competitiveness.
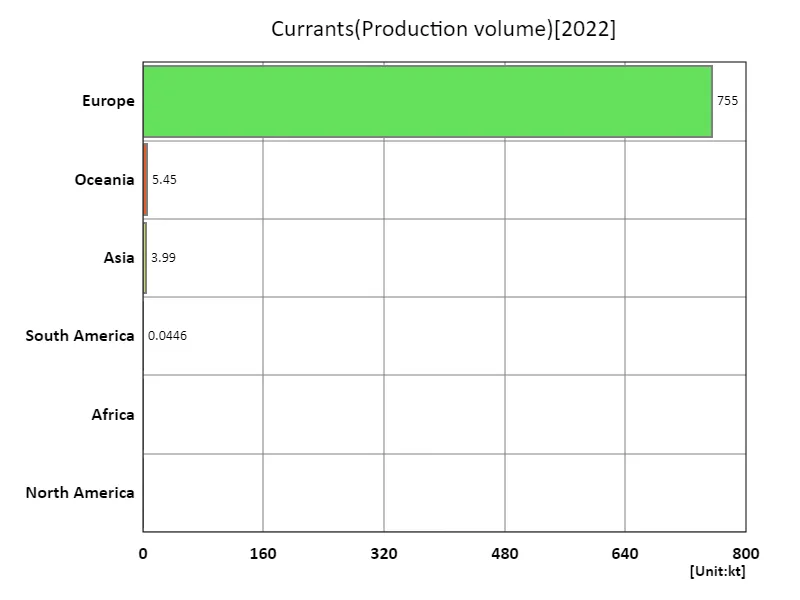

The maximum is 755kt of Europe, the average is 191kt, and the total is 764kt



Comments