Abstract
In adzuki bean agriculture in Japan, based on data from 2022, the national harvest was 42.1kt and the cultivated area was 23.2kha. In addition, the yield per 10a in Hokkaido is 206kg. These figures show that adzuki bean farming in Japan is stable overall, with Hokkaido in particular boasting high yields. Hokkaido’s climate and land conditions may be suitable for growing adzuki beans. The relatively large cultivated area across the country indicates that adzuki beans are one of the important crops in Japan. Harvest volume and yield may continue to fluctuate in the future due to factors such as climate change and advances in agricultural technology, but at present there appears to be a stable trend.
Adzuki bean harvest volume (main data).
The adzuki bean harvest in Japan has undergone various changes between 1883 and 2022. In particular, harvest volumes peaked in 1961 at 185kt, but have declined in the decades since. The current harvest is only about 22.8% of the peak yield, reflecting the impact of various factors on azuki bean demand and production. Based on past trends, factors affecting adzuki bean demand and production include climate change, changes in agricultural policies, economic fluctuations, and advances in agricultural technology. Additionally, changes in food culture and demand both at home and abroad may also be affecting harvest yields. Taking these factors into account, it is important to make predictions and develop strategies for future adzuki bean yields.
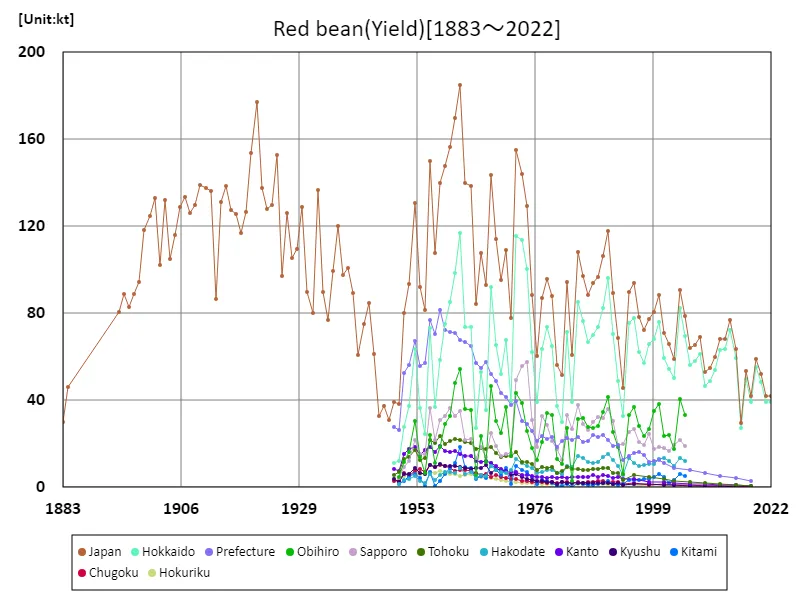

The maximum is 185kt[1961] of Japan, and the current value is about 22.8%
Adzuki bean harvest volume (by prefecture).
According to the latest data for 2022, Hokkaido has the highest adzuki bean harvest in Japan, at 39.3kt. This is the largest amount ever recorded, suggesting that Hokkaido is a major region for azuki bean production. Hokkaido’s vast land area and favorable climatic conditions make it ideal for cultivating adzuki beans, resulting in high yields. On the other hand, harvest yields in other regions tend to be lower than in Hokkaido. This may be due to differences in climate and land conditions from region to region, as well as differences in agricultural techniques. Azuki beans are a traditional food ingredient in Japan, and as demand is relatively stable, production in each region plays an important role. In the future, it is expected that the production volume of adzuki beans in each region will continue to be adjusted according to the characteristics of each region and changes in demand.


The maximum is 39.3kt of Hokkaido, the average is 13.3kt, and the total is 39.8kt
Area cultivated with adzuki beans (main data).
The area of adzuki bean cultivation in Japan has undergone various changes between 1883 and 2022. In particular, the peak of 176kha nationwide was recorded in 1931, and has been declining since then. The current cultivated area is only about 13.2% of the peak area, which is thought to be due to changes in demand for adzuki beans and the agricultural structure. Factors such as urbanization of farmland and modernization of agriculture may have influenced the cultivation of adzuki beans. Additionally, changes in agricultural policies and fluctuations in demand both at home and abroad were also factors that influenced the area planted. On the other hand, since adzuki beans are a traditional Japanese food ingredient and demand is relatively stable, a certain amount of land area is being cultivated for them. Future planted area is expected to be influenced by factors such as changes in demand, trends in agricultural policy, and climate change. Farmers and governments need to consider these factors and develop strategies to promote sustainable azuki bean cultivation.


The maximum is 176kha[1931] of Japan, and the current value is about 13.2%
Adzuki bean cultivation area (by prefecture).
According to data from 2022, Hokkaido has the largest area cultivated with adzuki beans in Japan, at 19.1kha. This is the largest amount ever recorded, suggesting that Hokkaido is a major region for azuki bean production. Hokkaido has a large area of land and favorable climatic conditions that make it suitable for growing adzuki beans. On the other hand, the cultivated area in other regions tends to be smaller than that of Hokkaido. This may be due to differences in climate and land conditions from region to region, as well as differences in agricultural policies. Azuki beans are a traditional food ingredient in Japan, and as demand is relatively stable, production in each region plays an important role. It is expected that the area of land area planted with adzuki beans in each region will continue to be adjusted in the future according to the characteristics of each region and changes in demand.


The maximum is 19.1kha of Hokkaido, the average is 6.57kha, and the total is 19.7kha
Azuki bean yield per 10ares (by prefecture).
According to data from 2022, Hokkaido has the highest yield of adzuki beans per 10a in Japan. The yield per 10 ares in Hokkaido is 206 kg, which is extremely high compared to other regions. On the other hand, the overall average yield was 125 kg, indicating that Hokkaido’s yield was above average. Hokkaido’s vast land area and favorable climatic conditions make it ideal for growing azuki beans, resulting in high yields. Generally, areas with high yields per 10 ares have a combination of good soil and water conditions and appropriate agricultural techniques. In contrast, other areas may experience below average yields. This may be due to differences in climate and land conditions from region to region, as well as differences in agricultural techniques. The yield per 10 ares of adzuki beans can be improved through efforts by producers in agricultural practices, including optimizing harvesting techniques and fertilizer use, so local efforts and technological innovation will remain important in the future.


The maximum is 206kg of Hokkaido, the average is 125kg, and the total is 375kg



Comments