Abstract
Buckwheat is a key crop in Japanese agriculture, with notable regional variations in harvest volume, cultivation area, and yield per 10 ares. As of 2022, the nationwide harvest volume peaked at 40,000 tons, reflecting stable demand for this versatile crop. The total cultivation area reached 65,600 hectares, with larger regions playing a significant role in production. Despite these broad contributions, Saga Prefecture stands out for its exceptional yield per 10 ares, achieving 89 kg, the highest in Japan. This highlights the region’s effective cultivation techniques and favorable growing conditions. Over the years, trends show increasing efforts to optimize yields, particularly in high-performing areas, while addressing challenges like aging farmers and climatic fluctuations.
Buckwheat harvest volume (main data).
Buckwheat has played a vital role in Japanese agriculture, but its production has seen significant changes over time. Nationwide harvest yields peaked at 154,000 tons in 1914, reflecting its historical importance as a staple crop. However, as of 2022, yields have declined to 26% of that peak, highlighting a long-term downward trend. This shift is attributed to factors such as dietary diversification, declining farmland use, and aging farming populations. Despite the decrease, buckwheat remains culturally significant, with efforts focusing on sustaining production through improved farming techniques and regional branding. High-yield regions, like Saga, showcase potential for innovation in this enduring crop.


The maximum is 154kt[1914] of Japan, and the current value is about 26%
Buckwheat harvest volume (by prefecture).
Buckwheat production in Japan shows strong regional concentration, with Hokkaido leading as the top producer. In 2022, Hokkaido achieved a harvest yield of 18,300 tons, the highest nationwide, reflecting its favorable climate, expansive farmland, and efficient farming practices. This dominance underscores the region’s critical role in sustaining Japan’s buckwheat supply. Nationally, production levels have declined compared to historical peaks, influenced by shrinking farmland and an aging workforce. Despite this, efforts to enhance productivity and regional branding continue. Hokkaido’s success demonstrates the potential for optimizing cultivation in suitable regions, ensuring buckwheat remains a vital crop in Japan’s agricultural landscape.


The maximum is 18.3kt of Hokkaido, the average is 869t, and the total is 40kt
Buckwheat cultivation area (main data).
The land area used for buckwheat cultivation in Japan has seen a significant reduction over time. In 1898, the cultivated area reached its historical peak of 179,000 hectares, reflecting buckwheat’s importance as a staple crop in traditional agriculture. However, by 2022, this figure had dropped to just 36.8% of its peak, highlighting a long-term decline. Contributing factors include changes in dietary habits, urbanization, and the aging farming population, leading to reduced farmland usage. Despite this, buckwheat retains cultural and culinary significance, driving regional efforts to sustain cultivation. Targeted measures, including improved farming practices and regional branding, aim to preserve this traditional crop.


The maximum is 179kha[1898] of Japan, and the current value is about 36.8%
Buckwheat cultivation area (by prefecture).
Hokkaido leads Japan in buckwheat cultivation, with 24,000 hectares dedicated to the crop in 2022, making it the largest contributor nationwide. This dominance is attributed to the region’s favorable climate, expansive farmland, and efficient agricultural practices. Nationally, the cultivation area has declined significantly from historical highs, reflecting shifts in dietary preferences, urbanization, and the aging farming population. Despite this trend, buckwheat remains a culturally significant crop, particularly for traditional dishes like soba. Hokkaido’s consistent leadership highlights its vital role in sustaining buckwheat production and driving innovation in cultivation practices to preserve this agricultural heritage.


The maximum is 24kha of Hokkaido, the average is 1.43kha, and the total is 65.6kha
Buckwheat yield per 10a (by prefecture).
Buckwheat yields in Japan show notable regional disparities, with Saga achieving the highest yield per 10 ares in 2022 at 89 kg, far exceeding the national average of 49.1 kg. This highlights the effectiveness of Saga’s farming techniques and favorable conditions. The total nationwide yield stands at 2.31 tons, reflecting steady but localized production in regions with optimal environments. Over time, average yields have improved due to advancements in cultivation practices and crop management. However, challenges such as an aging farming population and climate variability continue to impact consistency. Regional efforts to boost efficiency are key to sustaining this culturally significant crop.
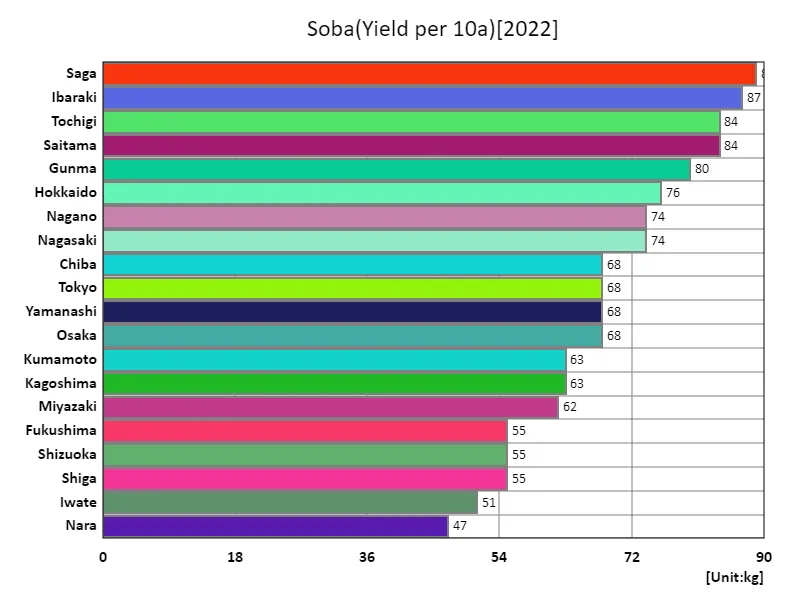

The maximum is 89kg of Saga, the average is 49.1kg, and the total is 2.31t



Comments