- Abstract
- Salad lettuce harvest volume among summer and autumn lettuce (main data).
- Harvest volume of salad greens among summer and autumn lettuce (by prefecture).
- Planted area of salad greens among summer and autumn lettuce (main data).
- The area planted with salad greens among summer and autumn lettuce (by prefecture).
- Shipment volume of salad lettuce among summer and autumn lettuce.
- Reference
Abstract
In recent years, the cultivation of salad greens in Japan has shown notable trends. The maximum harvest yield reached 2.13 kilotons in 2022, indicating a stable production level. The total cultivated area for salad greens peaked at 123 hectares, reflecting efficient land use and an increased focus on high-value crops. Chiba Prefecture led in shipping volume with 540 tons, highlighting its significant role in national production. Traditionally, summer and autumn seasons see higher yields due to favorable growing conditions. Overall, the sector demonstrates resilience, adapting to consumer preferences for fresh produce while facing challenges like climate variability and labor shortages.
Salad lettuce harvest volume among summer and autumn lettuce (main data).
The yield of salad greens in Japanese agriculture has experienced significant fluctuations from 1989 to 2022. The peak production reached 5.75 kilotons in 2021, showcasing the potential for high yields under optimal conditions. However, current yields sit at only 37% of this peak, indicating a notable decline in production levels. Factors contributing to this downturn include climate challenges, changing consumer preferences, and labor shortages. Despite these challenges, the focus on sustainable practices and enhanced cultivation techniques offers potential for recovery. The adaptability of farmers to market demands and environmental conditions will be crucial for revitalizing salad green yields in the coming years.
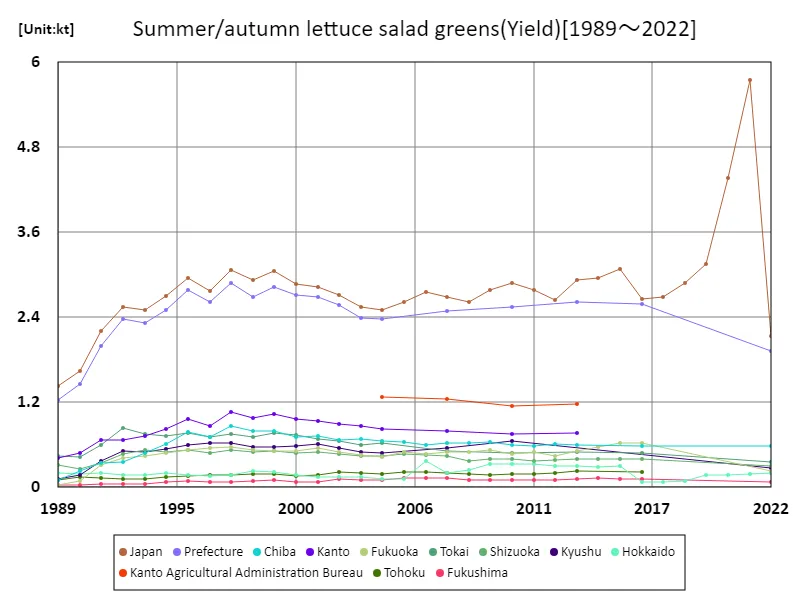

The maximum is 5.75kt[2021] of Japan, and the current value is about 37%
Harvest volume of salad greens among summer and autumn lettuce (by prefecture).
In 2022, the yield of leafy vegetables in Japan showcased regional strengths, with Chiba Prefecture leading at 579 tons. This dominance highlights Chiba’s favorable climate and advanced agricultural practices, positioning it as a key player in the leafy vegetable market. The focus on quality and consistency has contributed to its success, meeting growing consumer demand for fresh produce. Overall, the trend indicates a shift toward optimizing cultivation techniques and sustainable practices across the country. However, challenges such as labor shortages and climate variability persist. Continued investment in innovation and support for farmers will be essential to enhance yields and ensure stability in the leafy vegetable sector.
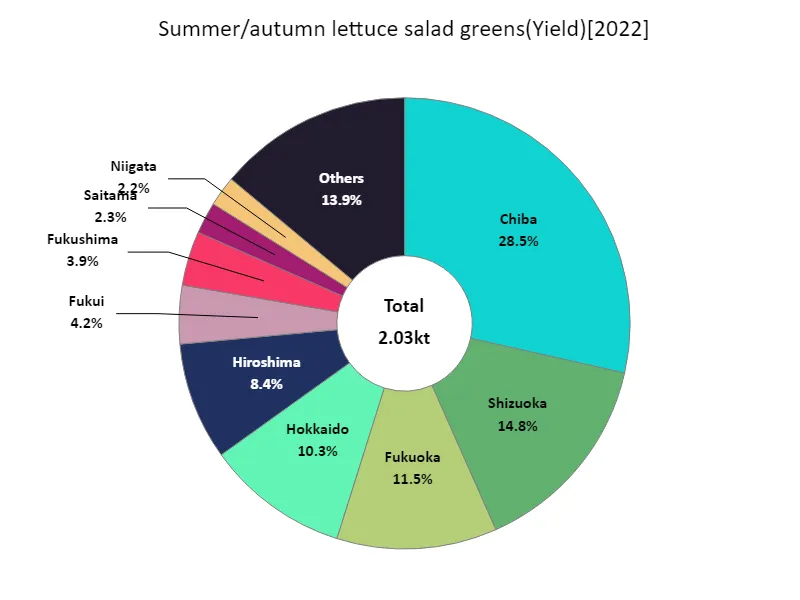

The maximum is 579t of Chiba, the average is 70t, and the total is 2.03kt
Planted area of salad greens among summer and autumn lettuce (main data).
From 1989 to 2022, the area planted for salad greens in Japan has shown significant trends, peaking at 225 hectares in 2021. Currently, the cultivated area is at 54.7% of this peak, indicating a decline that reflects various challenges in the agricultural sector. Factors such as labor shortages, climate variability, and shifting consumer preferences have influenced this reduction. However, the focus on high-quality production and sustainable practices remains strong. Farmers are increasingly adopting innovative cultivation techniques to optimize land use and improve yields. Moving forward, supporting these initiatives will be crucial for revitalizing the planted area and ensuring a stable supply of salad greens in Japan.
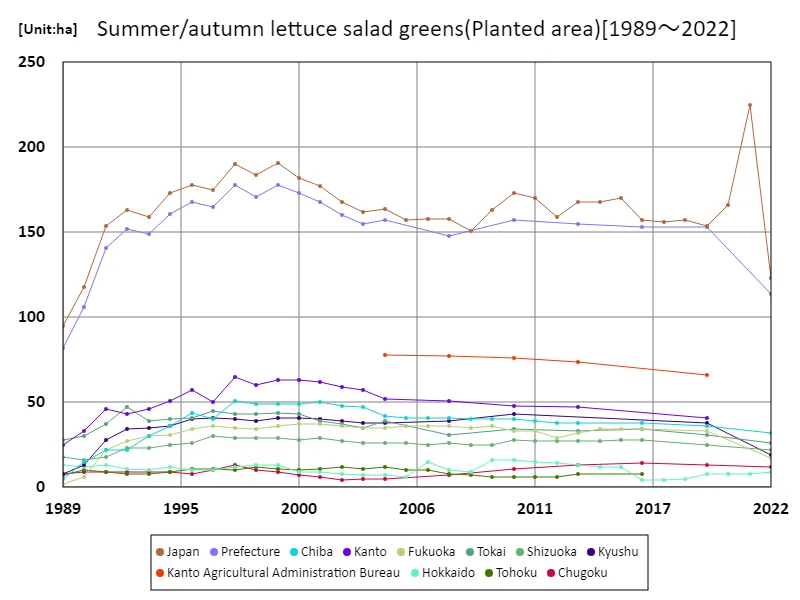

The maximum is 225ha[2021] of Japan, and the current value is about 54.7%
The area planted with salad greens among summer and autumn lettuce (by prefecture).
The 2022 prefecture-by-prefecture data reveals some interesting characteristics regarding the area planted to leafy vegetables in Japanese agriculture. The largest total cultivated area was 32 hectares in Chiba Prefecture, which is currently recorded as the largest amount. This data shows that Chiba Prefecture has demonstrated excellent performance in the cultivation of leafy vegetables. In addition, the area planted with leafy vegetables may show different trends depending on the region. Factors that affect cultivated area include local climatic conditions, land use, and agricultural policies. Additionally, changes in demand and fluctuations in market prices may also affect the area under cultivation. Considering past trends, it is possible that the adoption of efficient production methods and the development of cultivation plans tailored to regional characteristics have contributed to the increase in production area. In the future, cultivation strategies that take into account regional characteristics and market trends will be required.
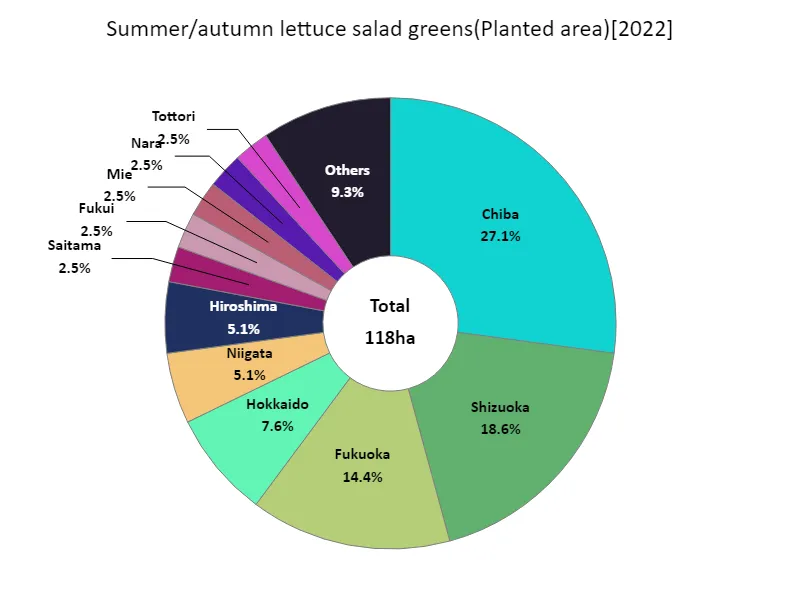

The maximum is 32ha of Chiba, the average is 4.07ha, and the total is 118ha
Shipment volume of salad lettuce among summer and autumn lettuce.
In 2022, the shipping volume of salad greens in Japan revealed significant insights into the leafy stem vegetable market. Chiba Prefecture led with an impressive 540 tons, underscoring its pivotal role in the supply chain. The national average shipping volume was 65.4 tons, with a total of 1.9 kilotons shipped across the country. This distribution indicates a strong regional concentration, with Chiba capitalizing on favorable growing conditions and effective logistics. Trends show increasing consumer demand for fresh, locally sourced produce, pushing farmers to adopt innovative practices. However, challenges like labor shortages and climate variability persist. Continued investment in sustainable farming and infrastructure will be crucial for enhancing future shipping volumes.
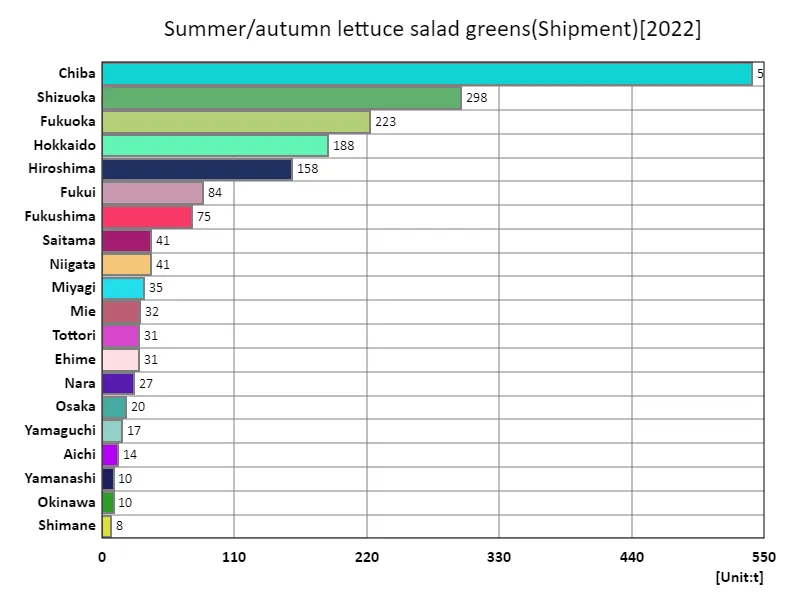

The maximum is 540t of Chiba, the average is 65.4t, and the total is 1.9kt



Comments