Abstract
In recent years, Fuji apple production in Japan has demonstrated notable trends. As of 2022, national harvest volume peaked at 378,000 tons, with bearing tree area reaching 17,800 hectares. Aomori Prefecture leads in shipping, handling 197,000 tons of Fuji apples. Historically, Fuji apples have been prized for their crisp texture and sweetness, making them a significant crop in Japan. Aomori’s prominence reflects its favorable climate and soil conditions, contributing to its high production and shipping volumes. This regional dominance underscores Aomori’s critical role in Japan’s apple industry.
Fuji apple harvest volume (main data).
Since the peak harvest of 538,000 tons in 1992, Japan’s Fuji apple production has fluctuated. As of 2022, national harvest levels are at 70.2% of that historic high, reflecting a decline over the decades. Despite this decrease, Fuji apples remain a staple due to their exceptional sweetness and crisp texture. Factors such as changing agricultural practices and climate conditions have influenced these trends. Although current yields are lower, Fuji apples continue to be a vital crop, with significant regional production contributing to Japan’s apple industry.
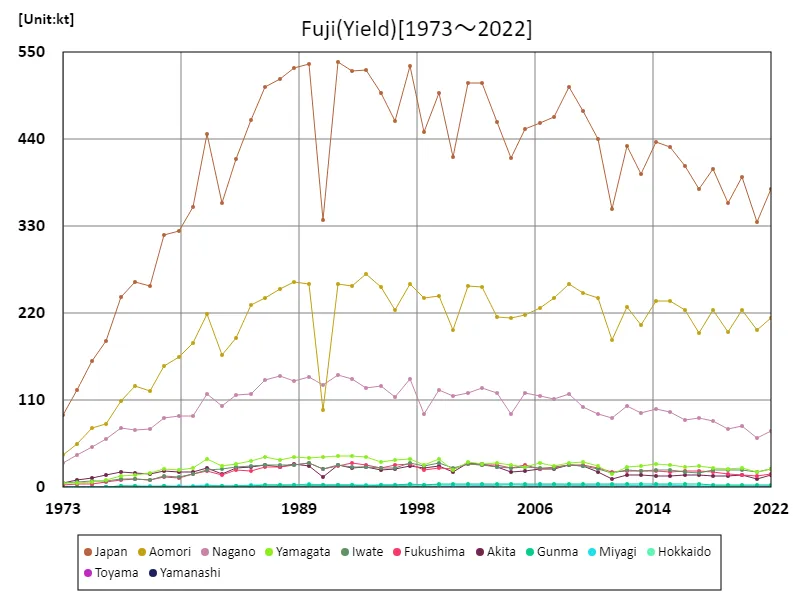

The maximum is 538kt[1992] of Japan, and the current value is about 70.2%
Fuji apple harvest volume (by prefecture).
As of 2022, Aomori Prefecture leads Japan in apple harvest yields, with a record 215,000 tons. This peak highlights Aomori’s dominant position in the industry, driven by its ideal climate and soil for apple cultivation. Historically, Aomori has been a major producer, with its high production volumes reflecting a consistent trend of excellence. While national figures have seen fluctuations, Aomori’s significant contribution underscores its role as a key player in Japan’s apple sector, maintaining high standards and substantial output amid changing agricultural conditions.
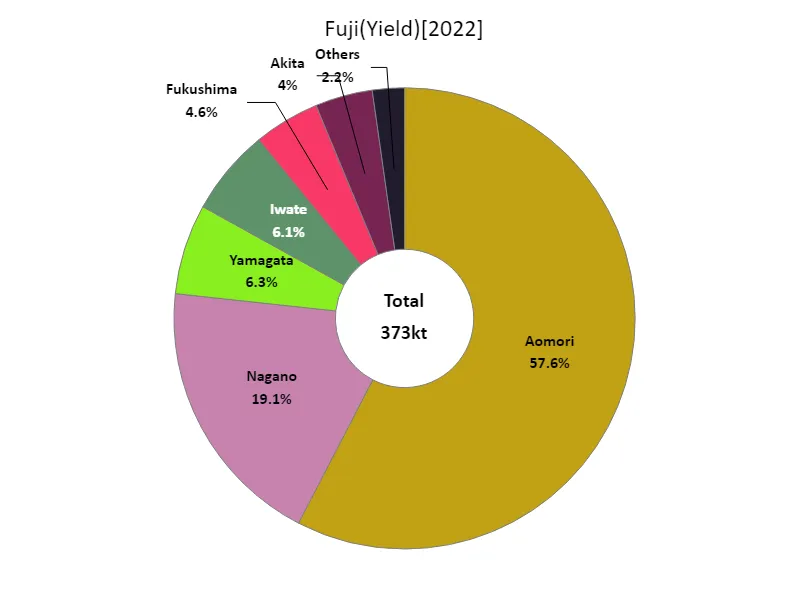

The maximum is 215kt of Aomori, the average is 28.7kt, and the total is 373kt
Fuji fruit tree area (main data).
When examining the area of fruiting Fuji apple trees in Japanese agriculture based on data from 1973 to 2022, some interesting trends can be seen. The national area of fruiting trees peaked at 23.2 kha in 1994 and has been declining since then. The current fruiting tree area is only 76.7% of its peak. This decline is due to factors such as structural changes in agriculture, changes in market demand, and changes in local environmental conditions. Changes in technology and growing methods for Fuji apple cultivation may also be a factor. On the other hand, it is also possible that yields per unit area have increased due to improved varieties and cultivation techniques. In order to respond to agricultural policies and consumer demand, it is becoming increasingly important to build efficient production systems and utilize local resources. Taking into account changes over the years, the area of fruiting Fuji apple trees is on a downward trend, but there is a need to establish a sustainable production system that meets demand.
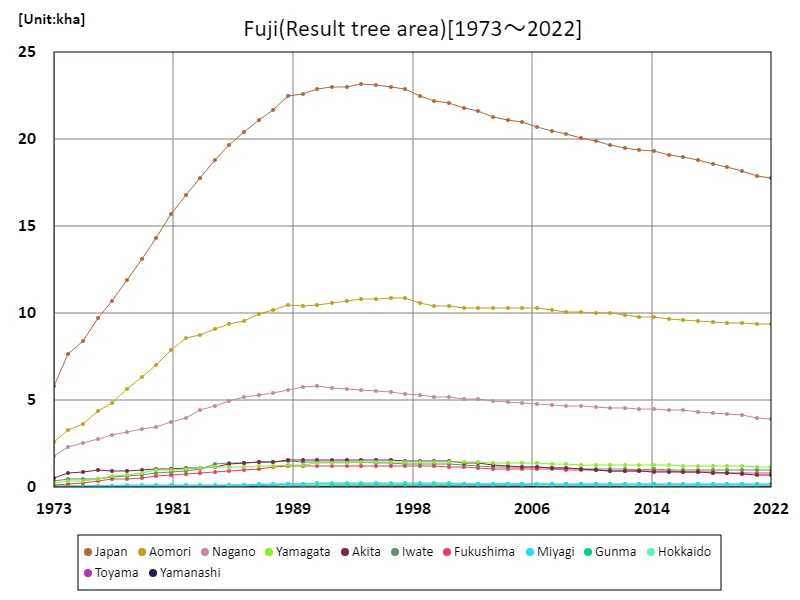

The maximum is 23.2kha[1994] of Japan, and the current value is about 76.7%
Fuji fruit tree area (by prefecture).
When examining the area of apple bearing trees in Japanese agriculture based on data by prefecture in 2022, some interesting characteristics become apparent. The largest total bearing tree area is 9.37kha in Aomori, which is currently the largest. Aomori’s long history and rich natural environment make it well suited to apple cultivation, and these geographical characteristics have led to the largest area of fruiting trees in the country. Meanwhile, the area of fruiting trees is also increasing in other regions, and each region is now producing distinctive apples. For example, Hokkaido and Nagano Prefecture are also major apple producing areas, and each region produces apples using its own unique varieties and cultivation techniques. In recent years, the area of fruiting trees has been expanding due to technological innovations in agriculture and the spread of sustainable cultivation methods. In addition, demand for apples is expanding both domestically and overseas due to consumers becoming more health-conscious and more aware of local production and consumption. Due to these factors, Japanese apple farming is evolving towards creating a sustainable production system while taking advantage of the characteristics of each region.
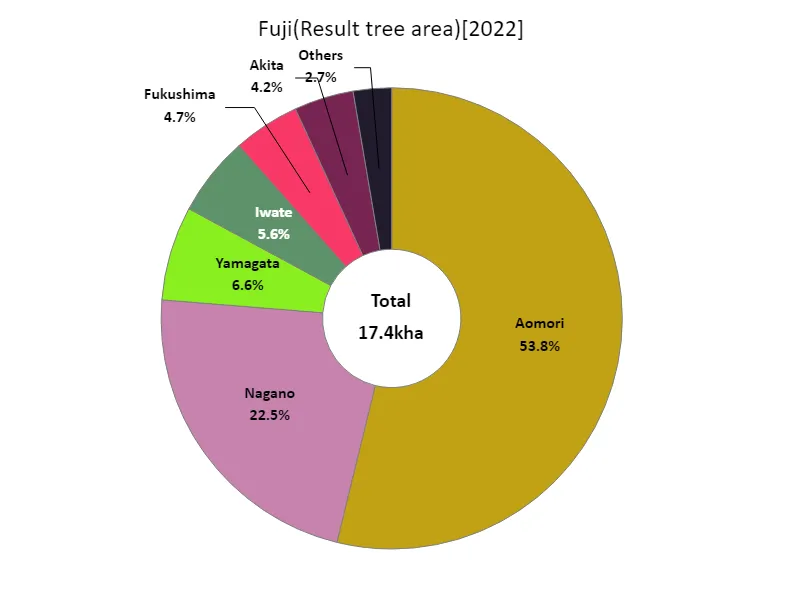

The maximum is 9.37kha of Aomori, the average is 1.34kha, and the total is 17.4kha
Fuji apple shipment volume.
In 2022, Aomori Prefecture led Japan in Fuji apple shipping volumes, handling 197,000 tons. This figure highlights Aomori’s pivotal role in the industry, driven by its substantial production capacity. Nationwide, the average shipping volume for Fuji apples was 26,300 tons, with a total of 341,000 tons shipped across Japan. These numbers reflect the ongoing prominence of Fuji apples, known for their superior taste and quality. Aomori’s significant share underscores its critical position in meeting domestic and regional demand, reinforcing its status as Japan’s primary apple-producing area.
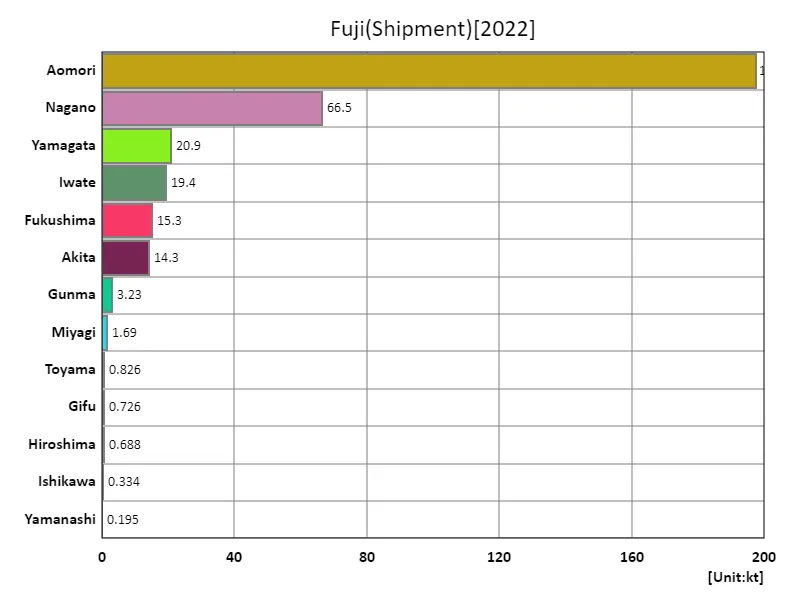

The maximum is 197kt of Aomori, the average is 26.3kt, and the total is 341kt



Comments