Abstract
When considering Jonagold harvest yields, fruiting tree area, and shipping volumes in Japanese apple farming based on 2022 data, some interesting trends emerge. The national harvest was 45.7kt, indicating stable production. On the other hand, the maximum fruiting tree area is relatively small at 2.34 kha. This suggests that Japanese apple farmers are producing efficiently within their limited land area. The largest shipment volume was Aomori at 33.5kt, reaffirming that Aomori is a major apple producing region in Japan. Additionally, Jonagold is a popular variety and is in high demand. These data indicate that Japanese apple farming is supported by stable production volumes and demand, and that efficient production methods are being adopted.
Jonagold harvest yield (main data).
The Jonagold harvest volume in Japanese apple farming has changed from 1987 to 2022. At its peak in 2002, the nation achieved a record harvest of 88.4kt, but has been declining since then, currently standing at 51.7%. This trend is thought to be due to a variety of factors in agriculture. For example, these include the effects of recent climate change and extreme weather, changes in productivity due to advances in agricultural technology, and changes in consumer demand and preferences. Jonagold is a popular variety and demand remains high, but a number of factors are contributing to the decline in production. Given these trends, Japanese apple farming faces continuing challenges, but it is hoped that improvements in technology and management will help to restore and stabilize production.
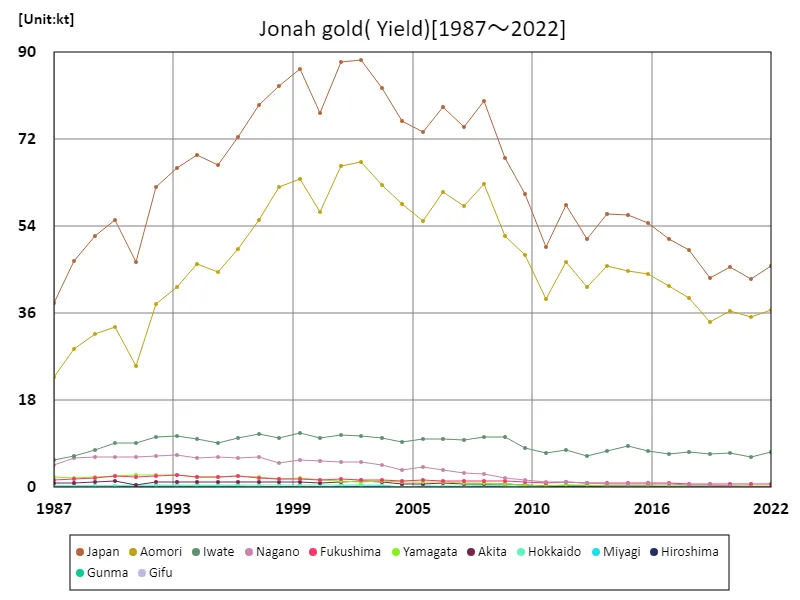

The maximum is 88.4kt[2002] of Japan, and the current value is about 51.7%
Jonagold harvest volume (by prefecture).
Based on data for 2022, Aomori Prefecture recorded the highest apple harvest in Japan at 36.7kt, making it the top in the country. This trend has continued for many years and shows that Aomori is a major apple producing region in Japan. Due to its climatic conditions and soil characteristics, Aomori Prefecture is known as an area suitable for apple cultivation, and produces high-quality apples. However, apples are also produced in other regions, and apple cultivation has spread throughout Japan. This results in differences in varieties and production volumes from region to region. Furthermore, Japanese apples are not only sold domestically but are also exported overseas, making them competitive in the international market. In this way, Japanese apple farming maintains stable production while taking advantage of the characteristics and competitiveness of each region.
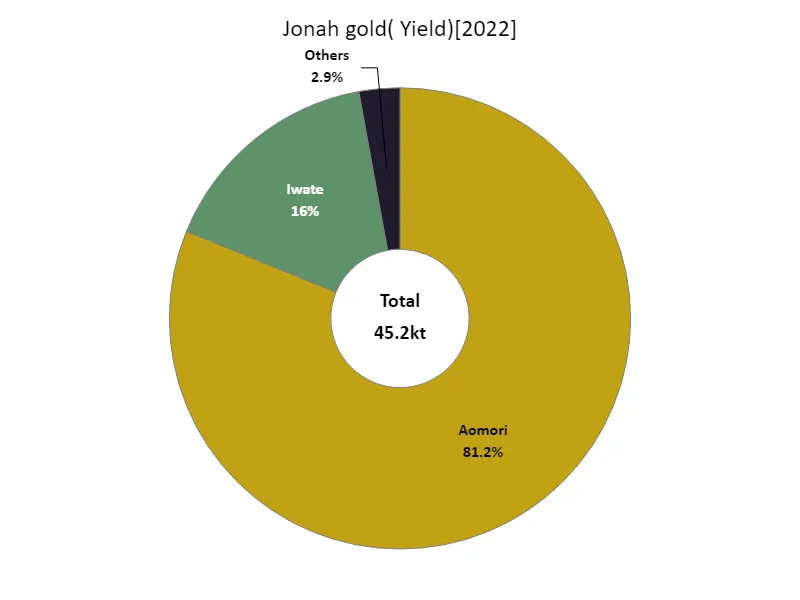

The maximum is 36.7kt of Aomori, the average is 3.77kt, and the total is 45.2kt
Jonagold bearing tree area (main data).
The area of Jonagold bearing trees in Japanese agriculture has changed from 1987 to 2022. In 2000, the country achieved a record-high bearing tree area of 3.72kha, but since then it has been in decline, currently standing at 62.9% of its peak. This trend is believed to be due to a variety of factors. For example, recent structural changes in agriculture, economic conditions, and changes in farmers’ intentions and demand may be influencing this. Advances in agricultural technology may also be a factor, with more efficient cultivation methods being introduced. Jonagold is a popular variety and demand means it may continue to be grown even if production declines. However, agricultural stakeholders and policymakers need to closely monitor this trend as the decline in fruit-bearing tree area could have an impact on production volume and quality.
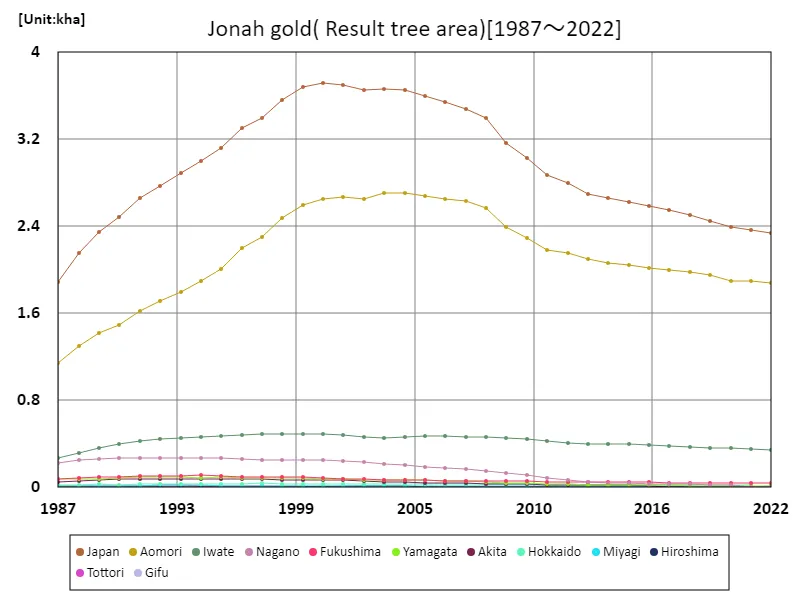

The maximum is 3.72kha[2000] of Japan, and the current value is about 62.9%
Jonagold fruiting tree area (by prefecture).
According to 2022 data, the largest area of apple bearing trees in Japanese agriculture is 1.88kha in Aomori Prefecture. This figure is the current highest and reaffirms Aomori’s position as a major apple producing region in Japan. Due to its climatic conditions and soil characteristics, Aomori Prefecture is known as an area suitable for apple cultivation, and produces high-quality apples. On the other hand, although production is also carried out in other regions, the area of fruiting trees tends to be significantly smaller than that of Aomori. This suggests that Aomori’s apple production stands out from other regions. Furthermore, Japanese apples are not only sold domestically but are also exported overseas, making them competitive in the international market. The increase in the area of fruiting trees in Aomori Prefecture is the result of local agricultural policies, technological advances, and the efforts of producers, and can be said to be contributing to the sustainable development of Japan’s apple industry.
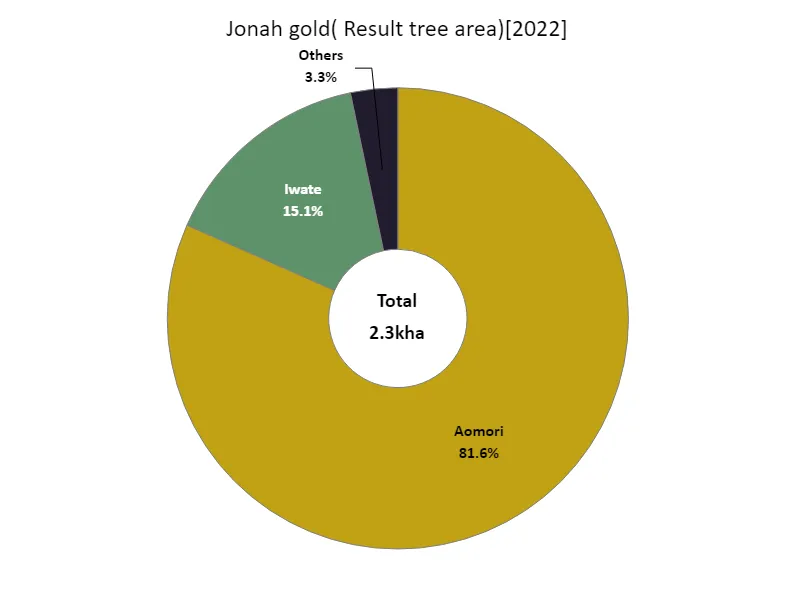

The maximum is 1.88kha of Aomori, the average is 192ha, and the total is 2.3kha
Jonagold shipping volume.
Based on data for 2022, the overall volume of Jonagold shipments in Japanese agriculture was highest in Aomori Prefecture at 33.5kt, with an average of 3.41kt and a total of 40.9kt. These figures make it clear that Aomori Prefecture is the main producer of Jonagold in Japan. Due to its climatic conditions and soil characteristics, Aomori Prefecture is known as an area suitable for growing apples, and produces high-quality Jonagold apples. On the other hand, although it is also produced in other regions, the shipping volumes tend to be smaller than those of Aomori Prefecture. This is thought to be due to differences in agricultural structure and demand from region to region. Jonagold is a popular variety and has stable demand, so it is grown not only in Aomori Prefecture but also in other areas. However, it is clear that most of the shipments are supplied from Aomori Prefecture. Japan’s Jonagold production and shipments depend on regional cooperation and adapting to demand, and these data illustrate that trend.
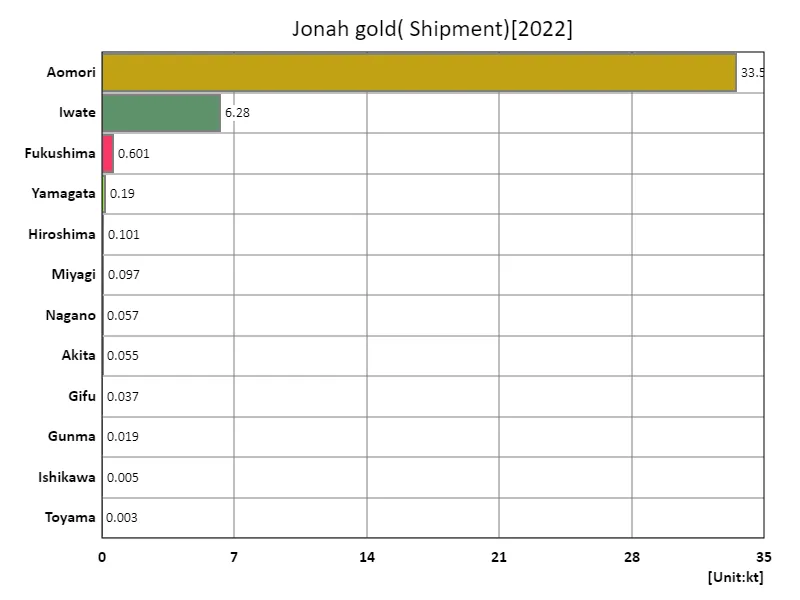

The maximum is 33.5kt of Aomori, the average is 3.41kt, and the total is 40.9kt



Comments