Abstract
In Japan’s peach farming, the national harvest volume in 2022 is expected to be 117kt, a relatively stable level. In the same year, the area of fruit-bearing trees nationwide was 9.31 kha, which is slightly less than the harvest volume, but the introduction of efficient cultivation techniques has made it possible to produce a high harvest. Yamanashi had the largest shipping volume at 33.7kt, indicating that this region is one of the main peach producing areas. Based on past trends, peach farming has seen stable harvests thanks to technological innovation and improvements in efficiency, with Yamanashi in particular attracting attention as a center of this trend.
Peach harvest volume (main data).
In Japanese peach farming, the peak harvest volume recorded nationwide was 281kt in 1973, and has since shown a downward trend. The 2022 harvest is expected to be only 41.5% of its peak, which may be due to structural changes in agriculture in general and changing economic conditions. Additionally, factors such as urbanization and labor shortages are also thought to be affecting agricultural production. Although technological innovation and agricultural policy reforms have improved production efficiency, the effects of changes in demand and domestic and international competition must also be taken into account. Therefore, although peach farming is on the decline, there is a need to establish a sustainable production system and develop strategies that meet market needs.
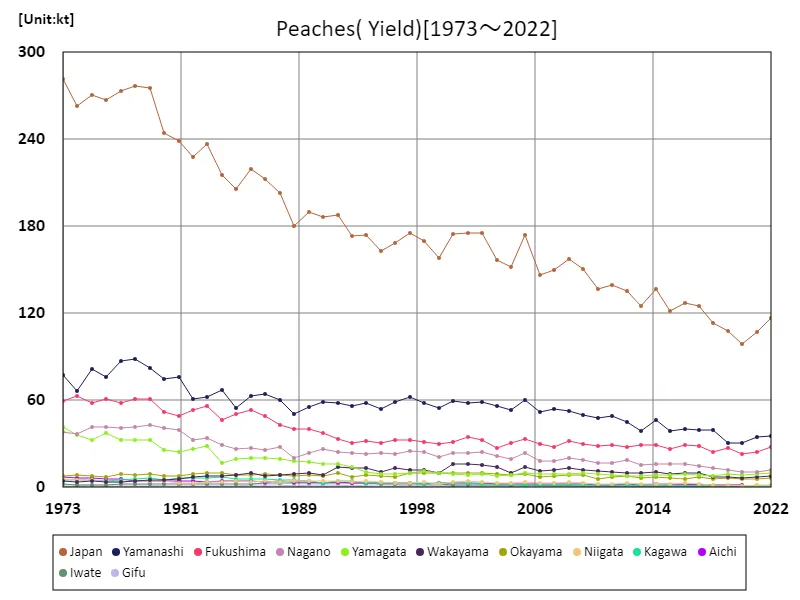

The maximum is 281kt[1973] of Japan, and the current value is about 41.5%
Peach harvest volume (by prefecture).
In Japanese agriculture, peach harvest yields show different characteristics depending on the prefecture. According to data for 2022, Yamanashi recorded the highest overall harvest of 35.7kt, topping the national total. Yamanashi is one of the main peach producing areas, and advances in climatic conditions and cultivation techniques have made it possible to produce high yields. On the other hand, harvest yields in other prefectures tend to be lower than in Yamanashi. This is thought to be due to differences in climate, soil conditions, and cultivation techniques from region to region. In addition, fluctuations in harvest yields by prefecture are also greatly influenced by annual weather conditions and agricultural policies. Changes in demand and domestic and international competition also affect agricultural yields, and producers and other stakeholders need to take these factors into account when making production plans. Generally speaking, while peach harvest volumes vary from region to region, a notable feature is that high production volumes are maintained, especially in Yamanashi.
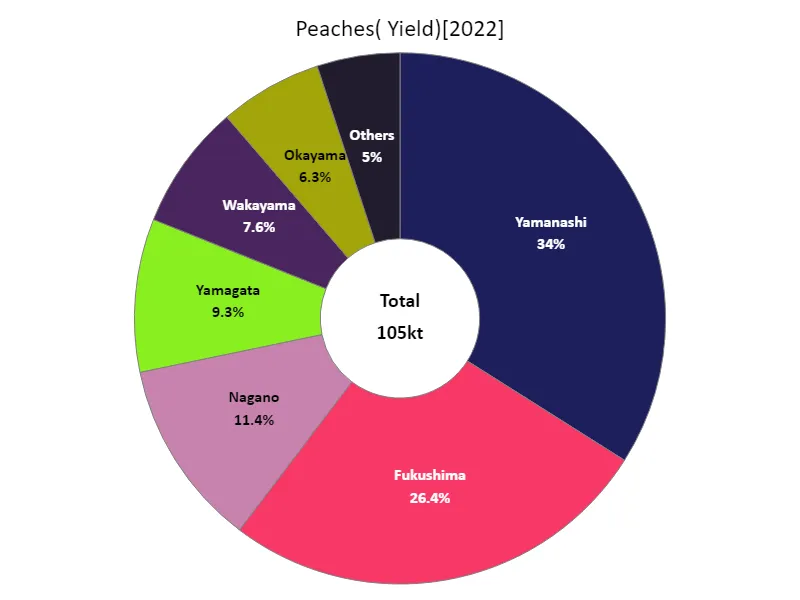

The maximum is 35.7kt of Yamanashi, the average is 9.55kt, and the total is 105kt
Peach bearing tree area (main data).
In Japanese peach farming, the peak area of fruiting trees recorded nationwide was 17 kha in 1973, and has been declining since then. According to 2022 data, the national area of fruiting trees remains at 54.8% of its peak level, indicating a long-term trend of decline. The reasons for this decline include urbanization, conversion of agricultural land to other uses, and labor shortages. Changes in agricultural structure and economic factors are also thought to be influencing the situation. On the other hand, there are cases where technological innovation and efficiency efforts have led to increased yields per unit area. The variation in fruiting tree area varies from region to region, influenced by differences in climatic conditions and land use. Different agricultural policies and support measures in each prefecture may also affect the area of fruiting trees. In general, the area of peach fruiting trees is showing a long-term downward trend, and in order to address this, it is necessary to establish sustainable agricultural management and introduce efficient production methods.
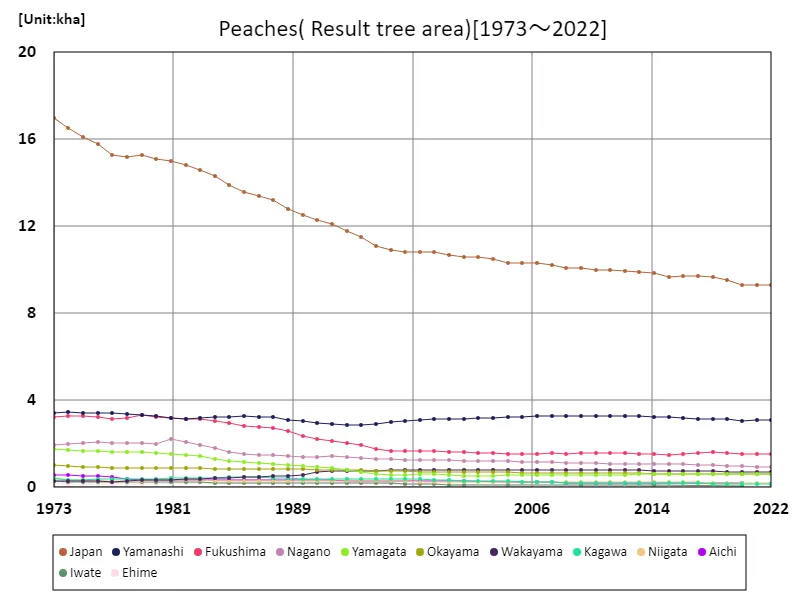

The maximum is 17kha[1973] of Japan, and the current value is about 54.8%
Peach bearing tree area (by prefecture).
According to data from 2022, Yamanashi recorded the largest area of peach bearing trees in Japanese agriculture overall at 3.1 kha, which is currently the highest. Yamanashi is one of the major peach producing areas, and the increase in the area of fruiting trees is thought to be due to the characteristics of the region and the efforts of producers. On the other hand, the area of fruiting trees in other prefectures tends to be lower than that of Yamanashi. This is due to regional factors such as climatic conditions, soil, and water resources, and agriculture is developed according to the characteristics of each region. In addition, agricultural policies and support measures may also be influencing the expansion of fruiting tree area, and it is possible that different policies and initiatives are being applied in different regions. In general, the area of peach fruiting trees varies by region, but one notable feature is that it shows a tendency for it to expand, especially in Yamanashi. It is expected that sustainable peach farming will continue to develop by making the most of local resources.
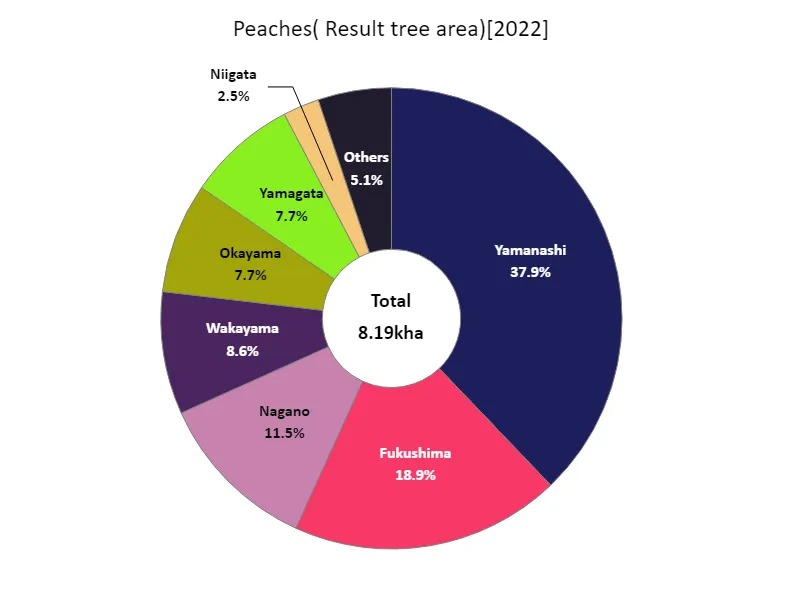

The maximum is 3.1kha of Yamanashi, the average is 744ha, and the total is 8.19kha
Peach shipment volume.
In Japanese agriculture, Yamanashi recorded the highest peach shipment volume of 33.7kt in 2022, which is a notable feature. The average shipping volume was 8.88kt, suggesting that there are disparities in shipping volumes between regions. The reasons why Yamanashi’s shipping volume is so much higher than other regions include its excellent cultivation techniques, well-established production systems, and the region’s unique climatic conditions. Furthermore, with a total shipping volume of 97.7kt, peaches are one of Japan’s major fruits and occupy an important position in the agricultural economy. Increases and decreases in shipping volumes are also greatly influenced by seasons and weather conditions, so producers need to make production plans taking these factors into account. Additionally, changes in demand and maintaining market competitiveness are also important issues, which require quality control and diversification of sales channels. Generally speaking, peach shipping volumes vary depending on the characteristics and technological level of each region, but one feature of the region is that stable production is maintained throughout Japan, with Yamanashi at the center.
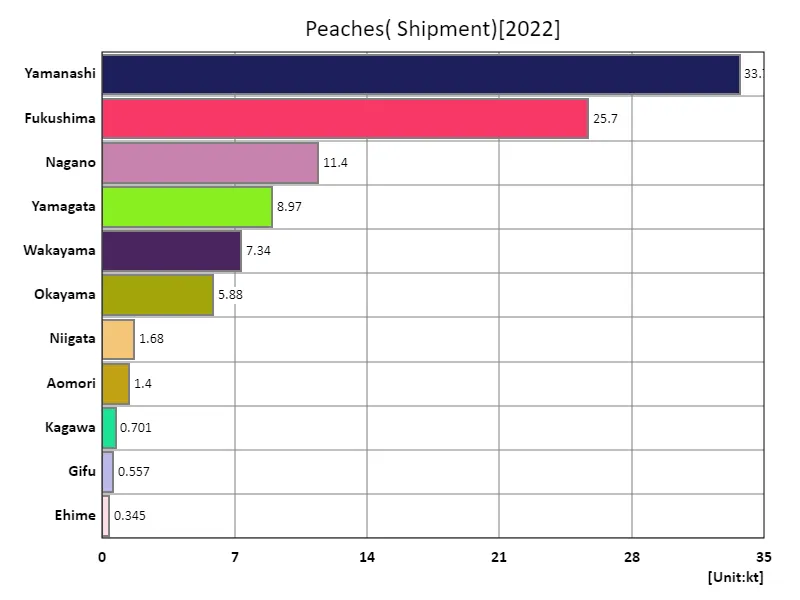

The maximum is 33.7kt of Yamanashi, the average is 8.88kt, and the total is 97.7kt



Comments