Abstract
As of December 2022, the price of beef cattle in Japan, specifically for a castrated Japanese steer for fattening, reached up to 675,000 yen. Historically, livestock prices in Japan have fluctuated due to factors like feed costs, labor expenses, and market demand. Over recent years, prices have generally risen due to increased feed and production costs, alongside growing consumer demand for high-quality beef. This trend reflects broader agricultural challenges, including fluctuating input costs and evolving market conditions.
General agricultural production materials (livestock animals)
From January 2020 to December 2022, the price of beef cattle in Japan has shown significant variation. The peak was 822,000 yen in April 2021 for a castrated Wagyu beef steer. As of the latest data, prices are at 82.1% of this peak. This decline reflects the broader trend of fluctuating input costs and market adjustments. Prices spiked due to high demand and increased feed costs, but they have since moderated. The overall trend highlights the volatility in agricultural markets influenced by both economic conditions and supply chain dynamics.
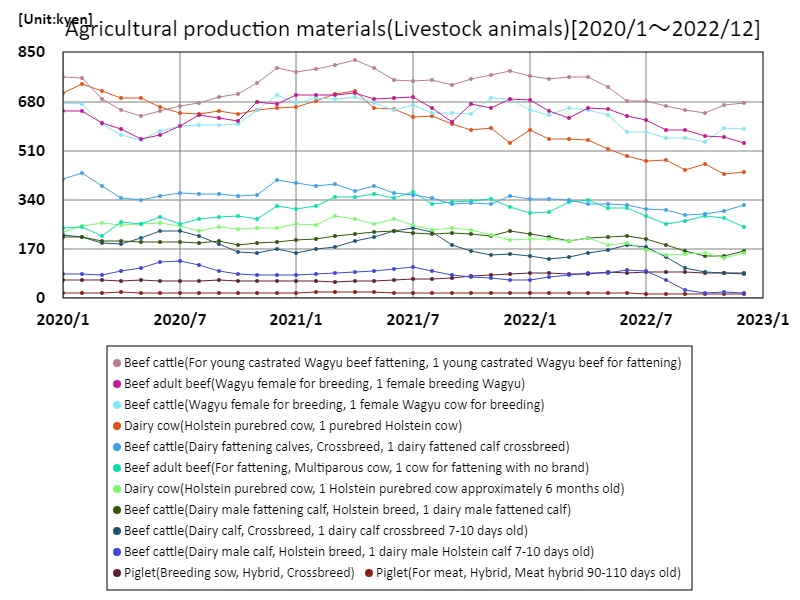

The maximum is 822kyen[2021年4月] of Beef cattle(For young castrated Wagyu beef fattening, 1 young castrated Wagyu beef for fattening), and the current value is about 82.1%
General agricultural production materials (feed)
From January 2020 to December 2022, the price of compound feed in Japan peaked at 123,000 yen in October 2022 for 1 ton of loose feed for young dairy and rearing cattle. The current price remains at this peak level, indicating persistent high costs. This trend reflects ongoing inflation in feed prices driven by global supply chain issues and increased production costs. The stability at peak prices suggests that feed costs are a significant burden for farmers, influencing overall agricultural production expenses.
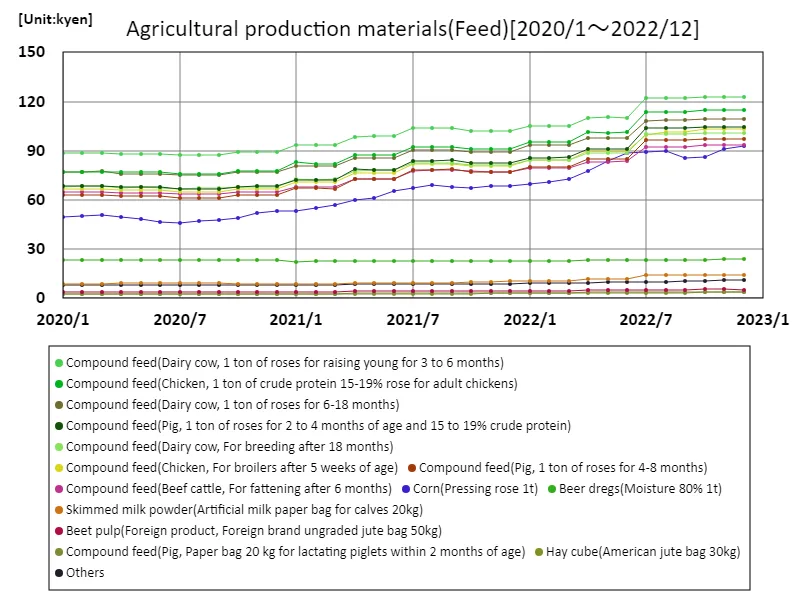

The maximum is 123kyen[2022年10月] of Compound feed(Dairy cow, 1 ton of roses for raising young for 3 to 6 months), and the current value is about 100%
General agricultural production materials (heat, light, and power)
As of January 2020, agricultural production input prices in Japan have shown notable variance. Heavy oil, a key energy input, peaked at 22,300 yen for 200 liters, with an average price of 7,080 yen. This significant fluctuation reflects broader trends in energy costs, influenced by global oil market volatility and domestic supply issues. The high peak underscores the financial pressure on farmers due to rising energy costs, impacting overall agricultural expenses. The overall trend highlights the sensitivity of agricultural inputs to global economic shifts and energy price instability.
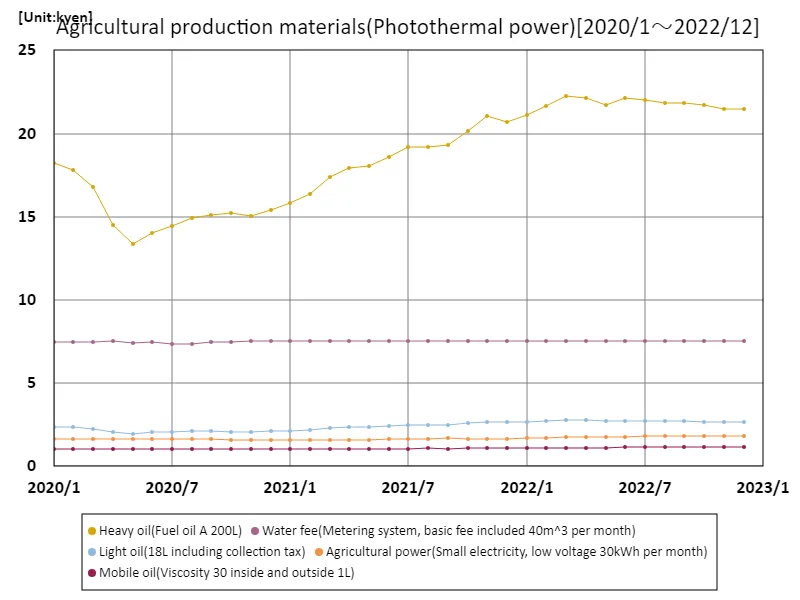

The maximum is 22.3kyen[2022年3月] of Heavy oil(Fuel oil A 200L), and the current value is about 96.5%
General agricultural production materials (construction materials)
As of January 2020, construction material prices in Japanese agriculture have seen significant highs, with steel shutters (approximately 3m x 2.5m) reaching 195,000 yen, the highest recorded price. This peak reflects the increased cost of construction materials, driven by rising steel prices and supply chain disruptions. The persistent high price of shutters highlights the broader trend of escalating costs in agricultural infrastructure, impacting farmers’ capital expenditures. Overall, these trends underscore the ongoing challenges in managing construction expenses within the agricultural sector.
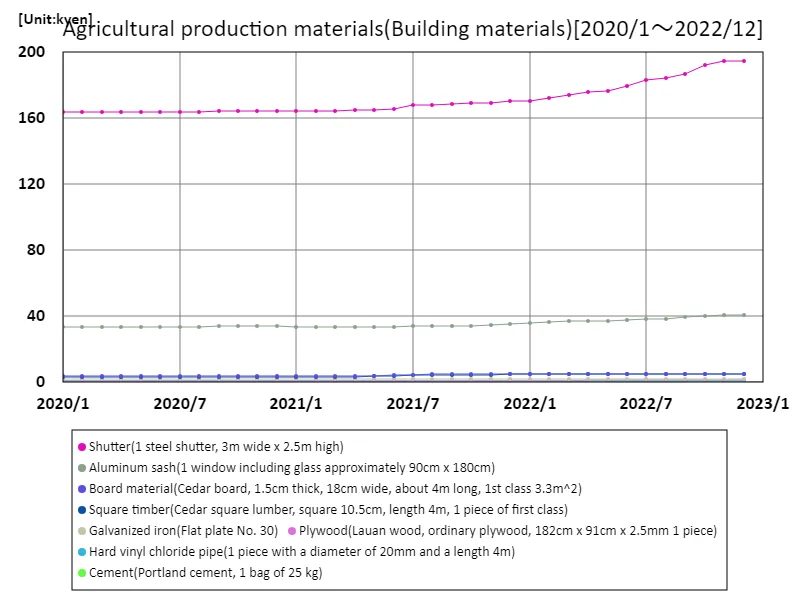

The maximum is the latest one, 195kyen of Shutter(1 steel shutter, 3m wide x 2.5m high)



Comments