Abstract
Annual yields of hay and cotton in the United States vary widely depending on region and climatic conditions. Hay production is concentrated primarily in the Western and Midwestern states, with Alaska’s production at 450 USD/t being an exception. Hay is primarily used as livestock feed, so areas with high production volumes are impacted by high demand for livestock. Cotton is primarily produced in the South and Southwest, with Texas being the largest producer. Cotton yields are highly dependent on weather conditions and do best in dry climates. Historically, hay and cotton production has been strongly linked to local climate and demand, with climatic and market forces influencing yields.
Average price (Hey)
The annual U.S. hay harvest has varied over time with regional variations in production. Looking back at data from 1866 to 2023, hay production has been on the rise, primarily in the Western and Midwestern states. In recent years, Alaska has recorded the highest yield at 450 USD/t. Alaska is a relatively new growing region and is experiencing rapid growth compared to other states, but yields remain stable compared to their peak. Historical data shows that climate change and changes in market demand have affected production volumes. Yields vary depending on local climate, advances in agricultural technology, and economic factors, but recent trends show a trend towards more efficient cultivation techniques and optimizing production in response to high demand.
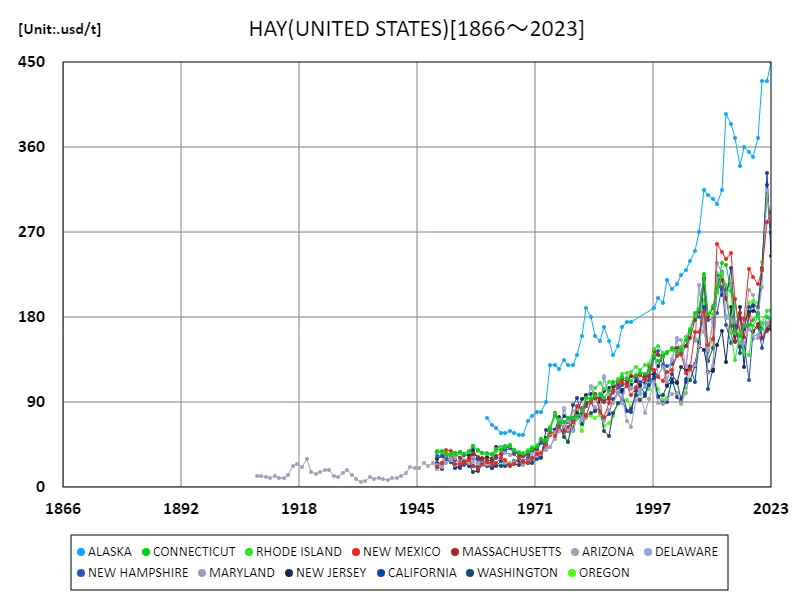

The maximum is the latest one, 450usd/t of ALASKA
Average price (Hey, latest year)
Data on the US annual hay harvest for 2023 showed Alaska recording the highest yield at 450 usd/t. Alaska peaked this year and has been holding steady at 100% yield. Historically, hay production in the United States has taken place primarily in the West and Midwest, but Alaska’s growth reflects evolving climatic conditions and agricultural techniques. Alaska’s production increase is due to more efficient growing practices and increased demand. Overall, U.S. hay production is driven by regional characteristics and market forces, but has recently been marked by the adoption of new technologies and environmentally friendly approaches.
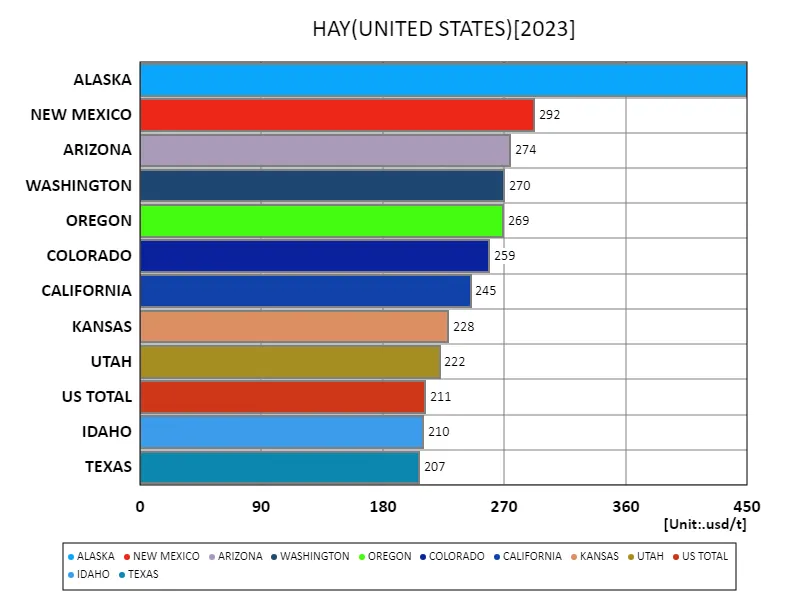

The maximum is 450usd/t of ALASKA, the average is 186usd/t, and the total is 9.29kusd/t
Average price (cotton)
According to data for 2023, California recorded the highest annual yield for US field cotton at 381 USD/t. The overall average price was 243 usd/t with a total yield of 4.13 kusd/t. These figures reflect regional variations in cotton production and market price fluctuations. Most cotton in the United States is produced in the South and Southwest, with Texas being the largest producer, but California also has an important production base. California’s high yields are a testament to advanced agricultural techniques and high production efficiency. Historically, cotton production has tended to favour dry climates, so it has been mainly produced in the dry regions of the south. As climate change and water constraints affect production, modern agricultural technologies and sustainable practices are being adopted. Overall, U.S. cotton production is subject to regional characteristics and market price fluctuations, but high harvesting efficiency and technological innovations help maintain a stable supply.
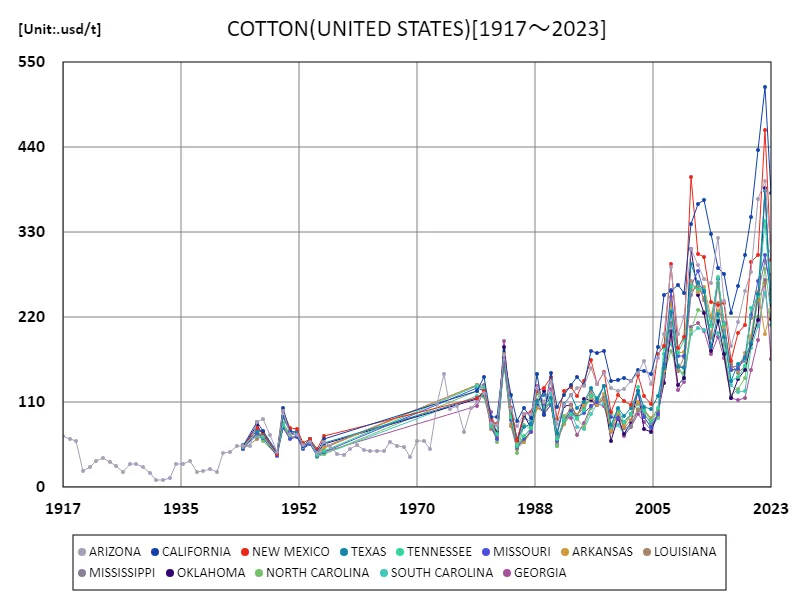

The maximum is 518usd/t[2022] of CALIFORNIA, and the current value is about 73.6%
Average price (Cotton, latest year)
Cotton production in the United States has undergone significant change between 1909 and 2023. Of particular note is the highest cotton price recorded by California in 2022 at $518/t. This peak demonstrates that California has advanced agricultural technology and an efficient production system. However, current prices are only 73.6% of their peak price, indicating that market fluctuations and changes in production conditions are having an impact. Cotton production occurs primarily in the South and Southwest, with Texas being the largest producer. California was a relatively latecomer to cotton production and has played a key role in recent years in both production and price. From the early 1900s to the present, cotton production has undergone significant advances due to climate change, technological innovation, and water management. In particular, the latest technology and improved varieties have enabled increased yields and stable quality. Overall, U.S. cotton production is influenced by regional characteristics and market trends, but continues to grow sustainably through technological innovation and efficient production management.
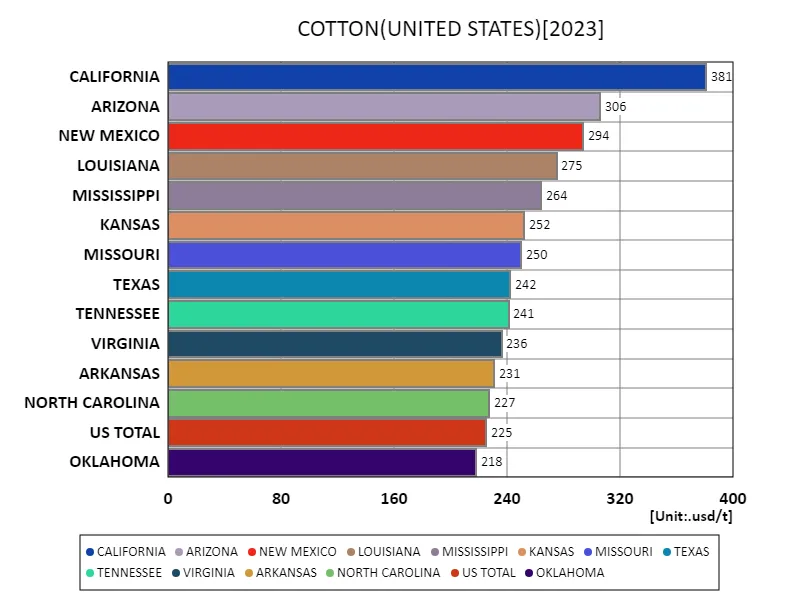

The maximum is 381usd/t of CALIFORNIA, the average is 229usd/t, and the total is 4.35kusd/t
Main data
| HAY(ALL CLASSES, ALL PRODUCTION PRACTICES, ALL UTILIZATION PRACTICES, PRICE RECEIVED, UNITED STATES) [usd/t] | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALASKA | NEW MEXICO | ARIZONA | WASHINGTON | OREGON | COLORADO | CALIFORNIA | KANSAS | UTAH | US TOTAL | |
| 2023 | 450 | 292 | 274 | 270 | 269 | 259 | 245 | 228 | 222 | 211 |
| 2022 | 430 | 281 | 315 | 320 | 305 | 245 | 333 | 211 | 294 | 239 |
| 2021 | 430 | 230 | 212 | 232 | 239 | 224 | 230 | 158 | 233 | 193 |
| 2020 | 370 | 215 | 183 | 191 | 195 | 212 | 180 | 128 | 181 | 156 |
| 2019 | 350 | 223 | 204 | 193 | 197 | 231 | 192 | 127 | 181 | 168 |
| 2018 | 355 | 231 | 209 | 186 | 195 | 220 | 191 | 153 | 171 | 159 |
| 2017 | 360 | 178 | 172 | 172 | 170 | 172 | 168 | 111 | 134 | 137 |
| 2016 | 340 | 162 | 153 | 142 | 164 | 151 | 149 | 90.5 | 127 | 132 |
| 2015 | 370 | 199 | 163 | 174 | 192 | 179 | 172 | 106 | 162 | 151 |
| 2014 | 385 | 248 | 218 | 217 | 219 | 206 | 232 | 152 | 188 | 175 |
| 2013 | 395 | 242 | 201 | 209 | 200 | 236 | 199 | 164 | 182 | 183 |
| 2012 | 315 | 249 | 222 | 228 | 210 | 237 | 204 | 196 | 189 | 184 |
| 2011 | 300 | 258 | 222 | 212 | 227 | 204 | 224 | 169 | 185 | 178 |
| 2010 | 305 | 157 | 128 | 147 | 157 | 127 | 125 | 102 | 106 | 114 |
| 2009 | 310 | 151 | 121 | 134 | 143 | 134 | 104 | 101 | 102 | 117 |
| 2008 | 315 | 186 | 184 | 222 | 198 | 161 | 191 | 116 | 167 | 148 |
| 2007 | 270 | 164 | 150 | 149 | 157 | 138 | 154 | 99.5 | 129 | 127 |
| 2006 | 250 | 164 | 130 | 128 | 130 | 131 | 111 | 103 | 99.5 | 105 |
| 2005 | 240 | 125 | 124 | 114 | 114 | 101 | 128 | 70 | 94.5 | 96.3 |
| 2004 | 230 | 121 | 99.5 | 111 | 105 | 84 | 115 | 68 | 88.5 | 89.5 |
| 2003 | 225 | 142 | 89 | 93.5 | 88.5 | 86 | 90.5 | 68.5 | 81.5 | 88.8 |
| 2002 | 215 | 140 | 99.5 | 111 | 100 | 116 | 95.5 | 87.5 | 94.5 | 92.4 |
| 2001 | 210 | 124 | 99 | 120 | 112 | 101 | 115 | 89 | 95 | 96.5 |
| 2000 | 220 | 122 | 94 | 107 | 94.5 | 85.5 | 90.5 | 77 | 78.5 | 80.4 |
| 1999 | 195 | 113 | 88.5 | 98 | 92 | 69 | 89 | 65 | 71.5 | 76.9 |
| 1998 | 200 | 117 | 89.5 | 97 | 104 | 92 | 96 | 72.5 | 76 | 89.7 |
| 1997 | 190 | 124 | 111 | 115 | 117 | 101 | 117 | 84 | 84 | 100 |
| 1996 | 128 | 94 | 115 | 104 | 98 | 108 | 83 | 72 | 88.9 | |
| 1995 | 114 | 78.5 | 97 | 99.5 | 88.5 | 98.5 | 75 | 66 | 82.2 | |
| 1994 | 120 | 100 | 92.5 | 99 | 91 | 107 | 73 | 79.5 | 86.7 | |
| 1993 | 105 | 92.5 | 98 | 97.5 | 77 | 102 | 71 | 65 | 84.7 | |
| 1992 | 175 | 97.5 | 63.5 | 82.5 | 85 | 64.5 | 79.5 | 65.5 | 61 | 74.3 |
| 1991 | 175 | 107 | 70.5 | 80.5 | 92.5 | 70.5 | 80.5 | 63.5 | 56 | 71.2 |
| 1990 | 170 | 111 | 96 | 91 | 92 | 80.5 | 101 | 61 | 79.5 | 80.6 |
| 1989 | 150 | 110 | 98.5 | 89.5 | 88.5 | 91.5 | 100 | 72 | 82.5 | 85.4 |
| 1988 | 140 | 102 | 89.5 | 78.5 | 76 | 82 | 94 | 77 | 76 | 85.2 |
| 1987 | 155 | 89 | 81.5 | 54.5 | 68 | 62 | 77.5 | 58.5 | 67 | 65 |
| 1986 | 170 | 74.5 | 70.5 | 60 | 65 | 58 | 72.5 | 43 | 62.5 | 59.8 |
| 1985 | 155 | 80 | 79.5 | 84.5 | 76.5 | 57.5 | 83 | 48 | 67 | 67.6 |
| 1984 | 160 | 99 | 84.5 | 80.5 | 73 | 72 | 80.5 | 73 | 70.5 | 74 |
| 1983 | 180 | 90 | 93 | 78.5 | 75 | 68.5 | 90.5 | 74 | 77 | 75.8 |
| 1982 | 190 | 75 | 73.5 | 77 | 75 | 66 | 86.5 | 57 | 66 | 69.3 |
| 1981 | 160 | 84 | 74 | 67 | 60 | 65 | 76 | 58.5 | 59.5 | 67.3 |
| 1980 | 140 | 86.5 | 82.5 | 82.5 | 79.5 | 64.5 | 95 | 62 | 70 | 71 |
| 1979 | 130 | 69 | 81 | 73.5 | 64 | 53 | 87 | 48.5 | 55 | 59.4 |
| 1978 | 130 | 64 | 60.5 | 47.5 | 49 | 50 | 60 | 45 | 47 | 49.8 |
| 1977 | 135 | 58.5 | 65 | 53.5 | 56.5 | 56 | 60 | 43 | 58 | 53.7 |
| 1976 | 125 | 63.5 | 68.5 | 66 | 63.5 | 56 | 74.5 | 53 | 53.5 | 60.2 |
| 1975 | 130 | 54 | 59 | 58.5 | 59.5 | 54 | 61 | 48 | 52.5 | 52.1 |
| 1974 | 130 | 58.5 | 56 | 58 | 57.5 | 52 | 63 | 46 | 46.5 | 50.9 |
| 1973 | 90 | 45 | 43 | 60.5 | 52.5 | 45 | 50 | 38.5 | 38.5 | 41.6 |
| 1972 | 80 | 36.5 | 35 | 31.5 | 33.5 | 40 | 34.5 | 26.5 | 35 | 31.3 |
| 1971 | 80 | 35 | 33 | 29.5 | 31 | 30.5 | 31.5 | 24 | 29.5 | 28.1 |
| 1970 | 75 | 31.5 | 31.5 | 25.5 | 26 | 25.5 | 30 | 24.5 | 25 | 26.1 |
| 1969 | 70 | 27 | 28 | 26 | 26 | 25.5 | 27.5 | 21 | 24 | 24.7 |
| 1968 | 55 | 26.5 | 24 | 26 | 25.5 | 27 | 25 | 21 | 22 | 23.6 |
| 1967 | 55 | 30.5 | 30.5 | 23.5 | 24 | 27 | 28 | 20.5 | 23.5 | 24.5 |
| 1966 | 58 | 25 | 26.5 | 24.5 | 27 | 26 | 27.5 | 23.5 | 26.5 | 25 |
| 1965 | 60 | 23.2 | 24.9 | 22.8 | 25.8 | 24.9 | 23.5 | 18.2 | 23 | 23.2 |
| 1964 | 58 | 28.5 | 25.3 | 23 | 25.7 | 27.6 | 24.3 | 21.8 | 21.6 | 23.9 |
| 1963 | 58 | 31 | 30.7 | 22.7 | 23.9 | 27.5 | 27.5 | 22.6 | 20.4 | 24.6 |
| 1962 | 63 | 25.3 | 26.1 | 23.5 | 23.1 | 21.6 | 22.6 | 18.2 | 20.1 | 21.8 |
| 1961 | 66 | 24.1 | 23.2 | 20.6 | 21.9 | 21.7 | 20.3 | 17.2 | 25 | 20.7 |
| 1960 | 73.5 | 26.3 | 25.1 | 22.1 | 23.1 | 24.1 | 23.9 | 17.7 | 26.4 | 21.7 |
| 1959 | 24.3 | 25.7 | 23.5 | 25.5 | 22 | 25.5 | 16.3 | 22.9 | 22.3 | |
| 1958 | 19.5 | 24.6 | 17.7 | 18.1 | 15.6 | 22.6 | 11.6 | 16.2 | 18.8 | |
| 1957 | 23 | 26.5 | 15.8 | 16 | 17.9 | 22.4 | 15.4 | 17.1 | 19.3 | |
| 1956 | 28.4 | 25.9 | 24.7 | 23.2 | 25.2 | 22.9 | 25.4 | 21.1 | 22.2 | |
| 1955 | 26.1 | 28.2 | 27 | 26.6 | 22.4 | 25.7 | 20.3 | 22.4 | 22.5 | |
| 1954 | 24.3 | 25.6 | 22.1 | 21.4 | 26.3 | 20.4 | 23 | 21.6 | 21.9 | |
| 1953 | 24.9 | 23.1 | 20.3 | 20.2 | 20.9 | 21.1 | 25.6 | 19.5 | 21.9 | |
| 1952 | 38 | 31 | 27.2 | 27.9 | 30.2 | 30.6 | 31.4 | 25.1 | 26.9 | |
| 1951 | 39.3 | 34.4 | 28 | 28.4 | 32.6 | 29.8 | 23.7 | 30.3 | 25.7 | |
| 1950 | 25.9 | 21 | 26.1 | 25 | 27.3 | 19.5 | 18.2 | 22.2 | 21.1 | |
| 1949 | 21.6 | 19.7 | 25.7 | 26 | 20.3 | 22.2 | 15.5 | 20.8 | 21.1 | |
| 1948 | 26.2 | 24.3 | ||||||||
| 1947 | 23 | 22.9 | ||||||||
| 1946 | 25.6 | 22.7 | ||||||||
| 1945 | 20.2 | 20.3 | ||||||||
| 1944 | 20.1 | 21.4 | ||||||||
| 1943 | 21.4 | 19.9 | ||||||||
| 1942 | 15.6 | 14.6 | ||||||||
| 1941 | 11.7 | 12.3 | ||||||||
| 1940 | 9.9 | 9.78 | ||||||||
| 1939 | 9.9 | 10.3 | ||||||||
| 1938 | 7.4 | 7 | ||||||||
| 1937 | 9.3 | 9 | ||||||||
| 1936 | 9.4 | 10.5 | ||||||||
| 1935 | 8.6 | 7.6 | ||||||||
| 1934 | 10.5 | 11.7 | ||||||||
| 1933 | 6.8 | 7.7 | ||||||||
| 1932 | 6.1 | 6 | ||||||||
| 1931 | 8.6 | 8.6 | ||||||||
| 1930 | 13.2 | 11 | ||||||||
| 1929 | 18.7 | 11.4 | ||||||||
| 1928 | 15.5 | 11.4 | ||||||||
| 1927 | 10.6 | 10.3 | ||||||||
| 1926 | 11.5 | 12.6 | ||||||||
| 1925 | 18.8 | 12.9 | ||||||||
| 1924 | 18 | 12.9 | ||||||||
| 1923 | 16.1 | 12.9 | ||||||||
| 1922 | 14.2 | 11.6 | ||||||||
| 1921 | 16 | 10.9 | ||||||||
| 1920 | 29.8 | 16.4 | ||||||||
| 1919 | 21.4 | 21 | ||||||||
| 1918 | 24.9 | 19.8 | ||||||||
| 1917 | 22.7 | 17 | ||||||||
| 1916 | 12.8 | 11.3 | ||||||||
| 1915 | 10.2 | 10 | ||||||||
| 1914 | 10.2 | 10.4 | ||||||||
| 1913 | 11.5 | 11.3 | ||||||||
| 1912 | 9.9 | 10.6 | ||||||||
| 1911 | 10.8 | 13.3 | ||||||||
| 1910 | 12.2 | 11.4 | ||||||||
| 1909 | 12.4 | 10.2 | ||||||||
| 1908 | 9.08 | |||||||||
| 1907 | 11.6 | |||||||||
| 1906 | 10.4 | |||||||||
| 1905 | 8.49 | |||||||||
| 1904 | 8.82 | |||||||||
| 1903 | 9.18 | |||||||||
| 1902 | 9.05 | |||||||||
| 1901 | 9.88 | |||||||||
| 1900 | 9.78 | |||||||||
| 1899 | 8.2 | |||||||||
| 1898 | 6.52 | |||||||||
| 1897 | 7.21 | |||||||||
| 1896 | 7.6 | |||||||||
| 1895 | 9.63 | |||||||||
| 1894 | 8.98 | |||||||||
| 1893 | 9.48 | |||||||||
| 1892 | 8.78 | |||||||||
| 1891 | 8.65 | |||||||||
| 1890 | 8.11 | |||||||||
| 1889 | 7.74 | |||||||||
| 1888 | 9.24 | |||||||||
| 1887 | 10.09 | |||||||||
| 1886 | 8.72 | |||||||||
| 1885 | 10.07 | |||||||||
| 1884 | 8.99 | |||||||||
| 1883 | 8.77 | |||||||||
| 1882 | 9.99 | |||||||||
| 1881 | 12.23 | |||||||||
| 1880 | 11.82 | |||||||||
| 1879 | 9.63 | |||||||||
| 1878 | 7.32 | |||||||||
| 1877 | 8.72 | |||||||||
| 1876 | 9.8 | |||||||||
| 1875 | 12.75 | |||||||||
| 1874 | 13.85 | |||||||||
| 1873 | 14.4 | |||||||||
| 1872 | 15.35 | |||||||||
| 1871 | 16.57 | |||||||||
| 1870 | 14.45 | |||||||||
| 1869 | 12.76 | |||||||||
| 1868 | 13.9 | |||||||||
| 1867 | 14.3 | |||||||||
| 1866 | 14.48 | |||||||||



Comments