Abstract
The latest trends in wage payments and employment types in agriculture are manifold. According to data from 2022, the salary payment for large-scale vegetable growers operating more than 30.0 hectares can reach up to 67.2 million yen. These figures indicate that agricultural management has rapidly become more sophisticated and expanded in recent years. While the proportion of permanent employees and full-time staff among agricultural workers is increasing and there is a movement towards a stable employment environment, the proportion of non-permanent employees remains high. As technological innovation and efforts toward sustainability advance, there are also increasing demands for the expertise and experience of agricultural workers. As such, the agricultural labor market is becoming more diverse and sophisticated, and information on wage levels and employment types is attracting attention as a factor contributing to the development of the industry as a whole.
Salary payment amount
Looking at trends in agricultural wage payments from 2019 to 2022, we can see that wages have increased significantly, especially for large-scale vegetable growers. In 2022, operators with 30.0 hectares or more of vegetables can expect to earn up to 67.2 million yen, the highest figure yet. This increase is likely due to technological innovation and efficiency improvements in agriculture, as well as increased compensation for large-scale operators in particular. On the other hand, although the proportion of regular employment has increased slightly across the labor market, the presence of non-regular employees remains large. In particular, the proportion of seasonal and temporary workers is high, and disparities in wage levels have also been pointed out as an issue. Furthermore, as sustainability efforts intensify, there is a growing demand for the skills and expertise of agricultural workers. For example, there is an increasing demand for workers with the skills to farm organically and reduce pesticides. While rising wages and diversifying employment types suggest the maturity and development of the agricultural labor market, the reality is that challenges remain depending on the region and crop. In the future, technological advances and policy support are expected to play an important role in improving the treatment of agricultural workers and creating a stable employment environment.
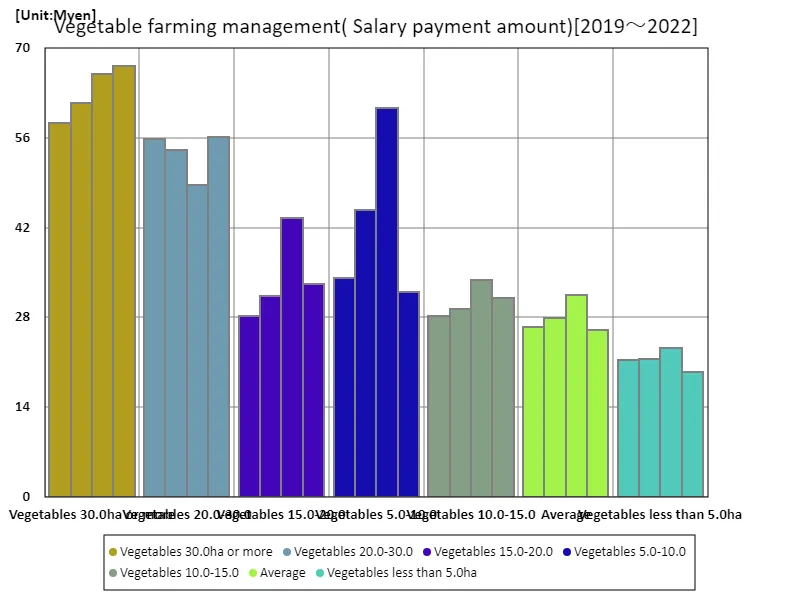

The maximum is the latest one, 67.2Myen of Vegetables 30.0ha or more
Owner/paid officer
The latest data on salaries for agricultural business owners and paid officers shows that overall salary levels for 2022 are as follows: In vegetable cultivation, if one operates 30.0 hectares or more, the maximum salary is 19.7 million yen, the average salary is 11.5 million yen, and the total salary is 80.3 million yen. These figures suggest that remuneration for agricultural owners and paid officers has remained stable at a certain level, while larger scale operators are paying relatively higher salaries. This trend reflects the fact that agricultural management has become more sophisticated through technological innovation and efficiency, and that the value of specialized knowledge and experience required of managers and executives is increasing. In addition, while there is a trend in the agricultural labor market toward an increasing proportion of regular employees, non-regular employees still exist, and there is a need for balance in working conditions. In particular, the proportion of seasonal and temporary workers is high, which could lead to imbalances in wage levels. From the perspective of sustainability, the role of managers and paid officers is becoming more important as the technical level of agricultural workers improves and environmentally friendly agricultural techniques are introduced. It has been shown that improving wage levels and working conditions are important issues for the development of agriculture and the stability of the labor market.
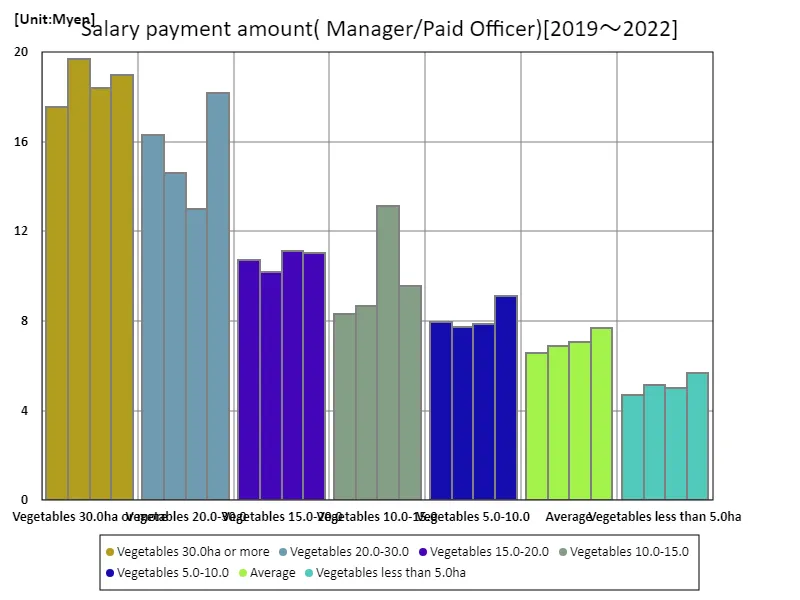

The maximum is 19.7Myen[2020] of Vegetables 30.0ha or more, and the current value is about 96.3%
Full-time employee/permanent staff
The latest data on salaries for full-time and permanent employees in agriculture shows that the maximum salary in 2022 was recorded at 38.1 million yen for an owner of a 5.0-10.0 hectare vegetable farm. This figure is the highest ever and indicates that compensation for farmers has increased in recent years. Generally, if you work in agriculture as a full-time employee, you can expect a stable employment environment and social security. In recent years, the proportion of full-time employees in the agricultural labor market has increased slightly, and there is an increasing demand for workers with advanced specialized knowledge and experience, especially as technological innovation and efforts to improve productivity continue. However, the agricultural labor market still has a high proportion of non-regular and seasonal workers, and challenges remain in stabilizing and balancing working conditions. Economic uncertainty is a challenge among workers, especially on small farms and in primary industries. With growing awareness of sustainability and environmental protection, education and technical training for agricultural workers is becoming increasingly important. Agricultural workers who work as permanent employees are expected to provide leadership and expertise to meet these challenges, and as a result, their remuneration is expected to increase. Going forward, it will be important to improve the labor market so that managers and workers can grow together and contribute to the sustainable development of agriculture.
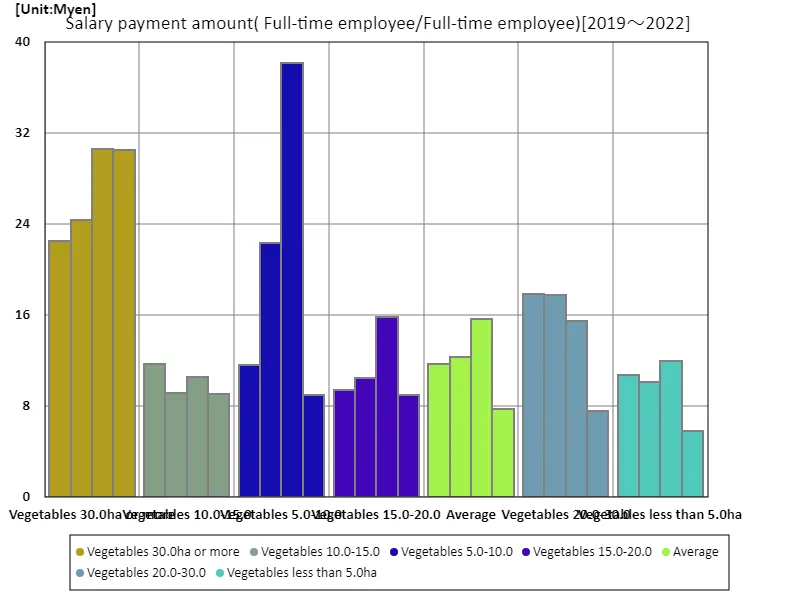

The maximum is 38.1Myen[2021] of Vegetables 5.0-10.0, and the current value is about 23.5%
Non-permanent employees and full-time employees
The latest data on full-time and non-full-time employment in agriculture shows salary levels in 2022 as follows: The maximum salary for managers of vegetable farms operating between 20.0 and 30.0 hectares was 30.4 million yen, the average salary was 14 million yen, and the total salary amounted to 98.3 million yen. In the agricultural labour market, the predominant forms of employment other than full-time and permanent employees are generally seasonal or temporary employment. There is a large number of temporary workers, especially in response to the seasonal nature of agricultural work and demand during peak production periods. While this type of employment ensures flexibility in the agricultural labor supply, it also faces challenges such as unstable working conditions and equilibrium in wage levels. In recent years, technological innovation and automation in agriculture have led to the mechanization of some tasks, while the structure of the labor market is also changing. This has led to an increased demand for workers with specific skills and expertise, which in turn has tended to drive up wage levels. For example, this includes operating and maintaining agricultural machinery and using IT technology. As sustainability efforts intensify, there is a need to improve the skills of agricultural workers and ensure stable working conditions. Non-regular workers are also important members of agricultural management, and it is necessary to improve their skills through appropriate education and training and create an environment in which they can work comfortably. In the future, it is expected that wage levels and working conditions for agricultural workers as a whole will improve in line with technological advances and labor market needs. This will in turn promote sustainable agricultural development and labor market stability.
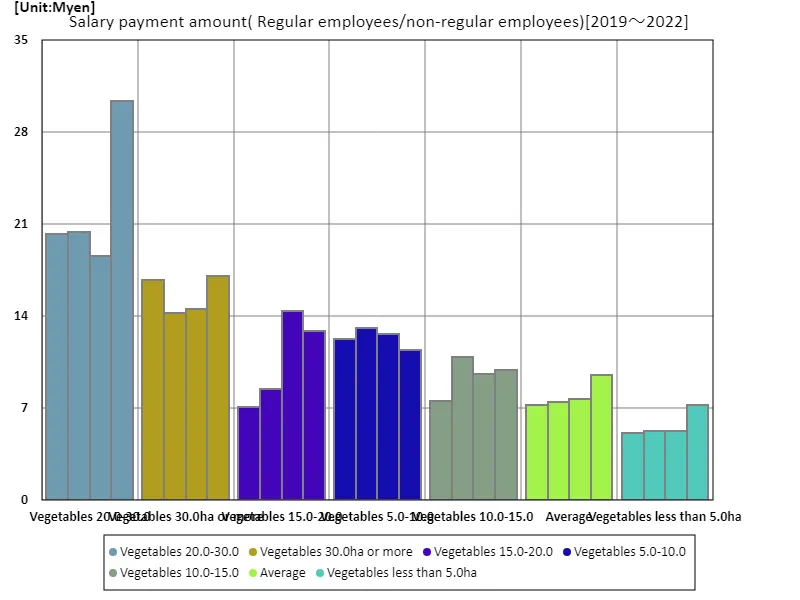

The maximum is the latest one, 30.4Myen of Vegetables 20.0-30.0



Comments