Abstract
In Japan’s marine aquaculture industry, surveys are being conducted on production statistics for total shrimp, spiny lobster, kuruma prawn, and other shrimp species. Data for 2022 shows tillage gauge production at a record 12.9kt. Looking at past trends, marine fisheries occupy an important position in Japan’s fishing industry, with the production of sea bream, spiny lobster, and prawns being particularly prominent. These varieties play an important role in Japan’s food culture and economy, and demand is stable. In addition, as aquaculture technology and management improve, production volumes are also showing a tendency to increase. Furthermore, the importance of sustainable fisheries management is being recognised and environmental considerations are increasing. The marine fisheries production statistics survey is a valuable source of information for industry and governments and is expected to be useful in future fisheries policies and planning.
Total shrimp production
The total production statistics survey of Japan’s marine fisheries includes data from 1956 to 2022. The highest figure was recorded in 1963 at 88.1kt, and looking at the trend since then, there has been a 14.6% decrease from the peak. This decrease can be attributed to a variety of factors. For example, possible influences include a decline in fishing resources, environmental changes, and changes in fishing policies. Economic and social changes are also affecting marine fisheries, with fluctuations in demand and labour also being factors to consider. Under these circumstances, sustainable fisheries management and technological innovation are required. In the future, efforts will be needed to protect and restore fisheries resources.
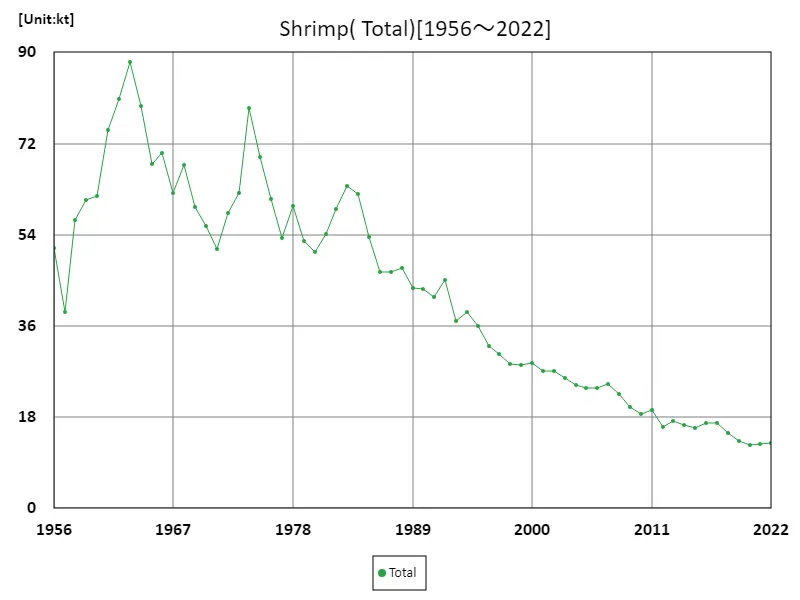

The maximum is 88.1kt[1963] of Total, and the current value is about 14.6%
Lobster production
The production statistics survey of spiny lobster in Japan’s marine fisheries includes data from 1956 to 2022. The highest recorded was 1.85kt in 1964, and looking at the trend since then, there has been a 60.4% decrease compared to the peak. This decline is thought to be due to a combination of factors, including not only fluctuations in catch volumes, but also a decline in fishing resources and environmental changes. In particular, changes in marine ecosystems and climate change may be having an impact. Changing demand and consumption patterns may also be at play. Under these circumstances, sustainable fisheries management and resource conservation are becoming increasingly important. In the future, efforts will be needed to restore and regenerate fisheries resources.
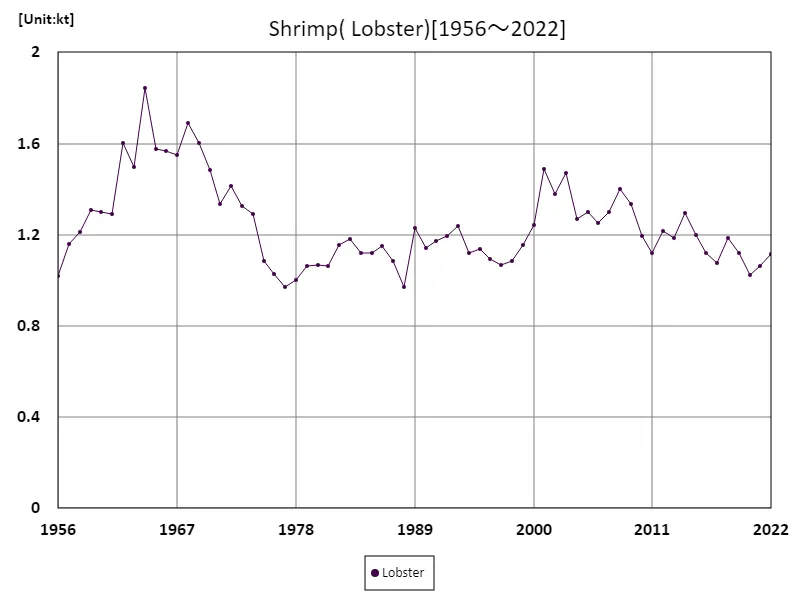

The maximum is 1.85kt[1964] of Lobster, and the current value is about 60.4%
Production of prawns
The latest statistical survey of shrimp production in Japan’s marine fisheries is from 1956, when the overall maximum was 3.77 kt. The average and total value are also 3.77kt. This data suggests that shrimp catches have remained relatively stable. However, the data only covers one year, limiting the ability to grasp long-term trends. Therefore, a more comprehensive analysis using data covering more years is needed. It is also necessary to consider the status and role of the prawn compared to other fishery species. In general, it can be said that the shrimp fishery may have a certain degree of stability, and that sustainable fisheries management and environmental conservation efforts are important to maintain this stability.
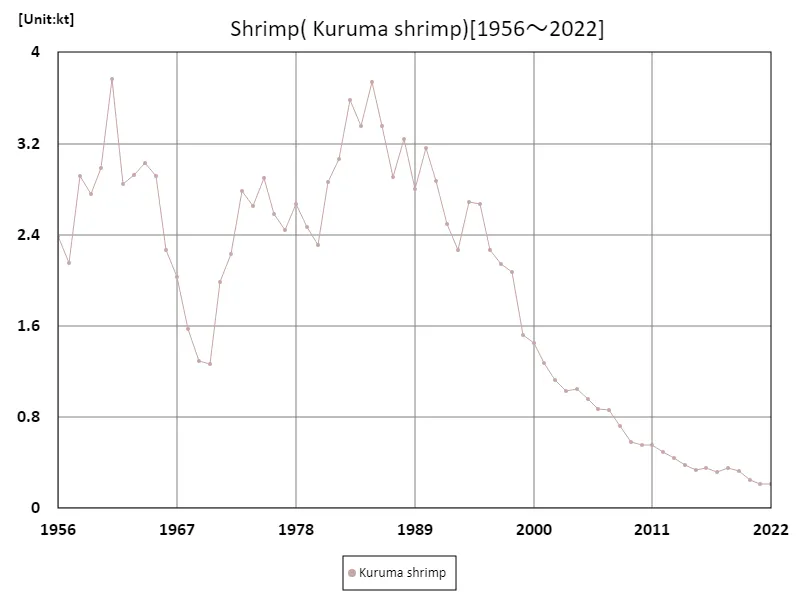

The maximum is 3.77kt[1961] of Kuruma shrimp, and the current value is about 5.68%
Other shrimp production
The production statistics survey of other shrimp species in Japan’s marine fisheries includes data from 1956 to 2022. The highest recorded speed was 83.7kt in 1963, and there has now been a 13.8% decrease from the peak. This decline is thought to be due not only to fluctuations in catch volumes, but also to factors such as a decline in fishing resources and environmental changes. Changing demand and consumption patterns may also be playing a role. Other shrimp species are important ingredients in Japanese food culture, and while demand remains stable, declining catches may be creating supply challenges. Under these circumstances, sustainable fisheries management and resource protection are required. In the future, efforts will be needed to restore and regenerate fisheries resources.
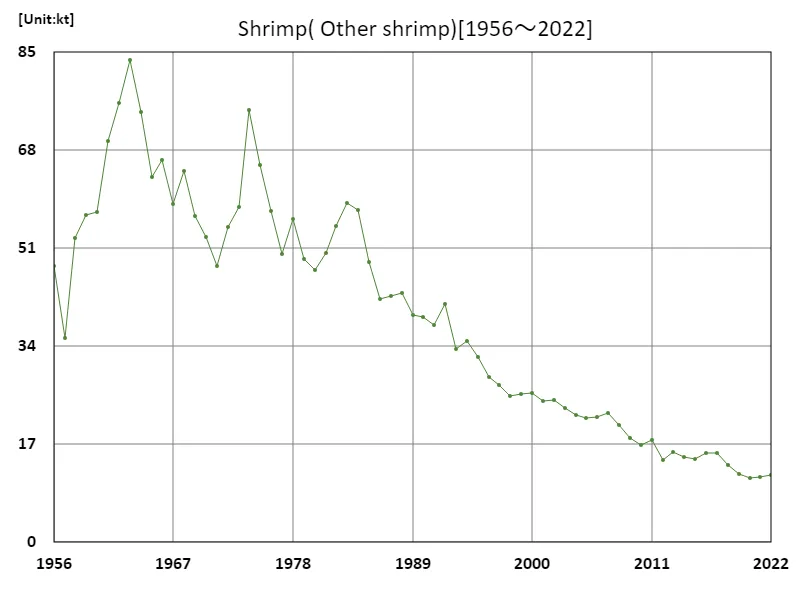

The maximum is 83.7kt[1963] of Other shrimp, and the current value is about 13.8%



Comments