Abstract
In Japan’s corn agriculture, the nationwide harvest volume in 2022 was 4.88 Mt, with the cultivated area being 96.3 kha. On the other hand, Gunma Prefecture had the highest yield per 10a, at 5.85t. The trend so far has been a steady increase in harvest volume and cultivated area, with Gunma Prefecture in particular maintaining high yields. This may be due to local climate and soil conditions. Additionally, technological innovation and capital investment in Japanese agriculture as a whole may be leading to the adoption of more efficient cultivation methods. However, differences in production volumes exist between individual prefectures and regions, suggesting the need for regional agricultural policies and support.
Corn yield (main data).
Japan’s corn yield has changed between 1959 and 2022. At its peak in 1990, the national production reached 6.85 Mt, but has been declining since then. The current harvest yield is 71.3% of the peak yield. This trend may be due to changes in agricultural policies, shifts in market demand, and a decline in the agricultural labor force. In recent years, climate change and natural disasters may also be affecting yields. Considering these factors, it may be difficult to expect steady increases in future corn yields.
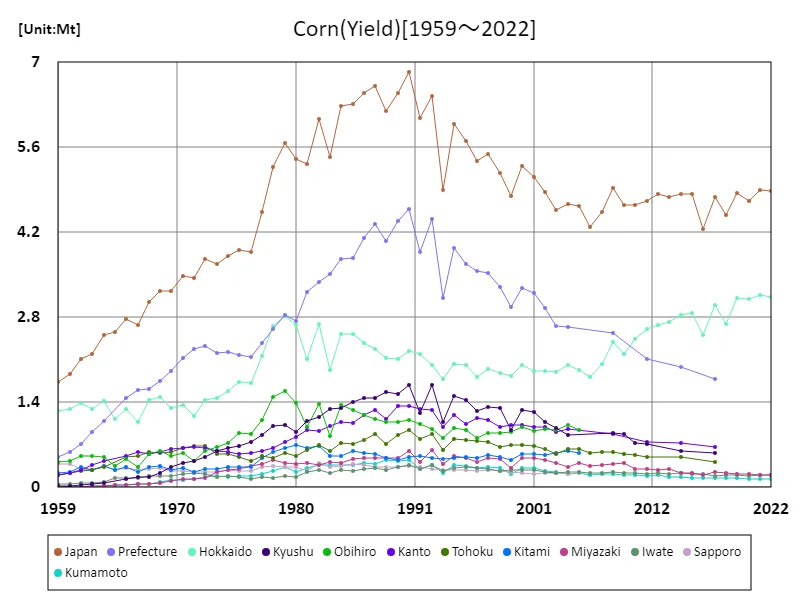

The maximum is 6.85Mt[1990] of Japan, and the current value is about 71.3%
Corn harvest volume (by prefecture).
Regarding Japan’s corn harvest, data for 2022 shows that Hokkaido recorded the highest yield overall at 3.13 Mt, which is the current peak. What has stood out so far is that Hokkaido stands out as a major production area. Hokkaido’s vast farmland and relatively cool climate make it ideal for cultivation, resulting in sustained high yields. Additionally, factors such as technological innovation and investment in facilities may also be contributing to improved yields in Hokkaido. However, other regions are seeing relatively low yields. This may be due to differences in climatic conditions, soil conditions, and agricultural practices. In the future, maintaining and improving an efficient agricultural production system, centered on Hokkaido, will likely remain an important factor in Japan’s corn production.
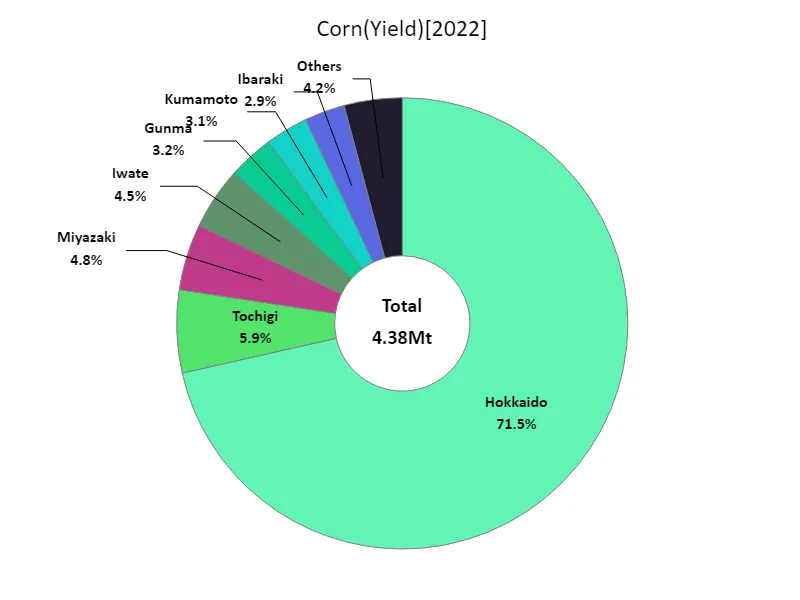

The maximum is 3.13Mt of Hokkaido, the average is 273kt, and the total is 4.38Mt
Corn planted area (main data).
Japan’s corn planting area fluctuates between 1959 and 2022. At its peak in 1987, the total area nationwide was recorded at 127 kha, but has been declining since then. The current area under cultivation is 75.7% of the peak area. Possible factors behind this trend include changes in agricultural structure, changes in market demand, and a decrease in the agricultural labor force. Other factors that are contributing to this include changes in government agricultural policies and subsidy systems, as well as increased competition between regions. Furthermore, growing interest in agricultural sustainability and environmental protection in recent years may also be a factor in the conversion of farmland and a shift to the cultivation of more diverse crops in some areas. Given these factors, future corn acreage will be influenced by agricultural policy, changing demand, and environmental considerations.
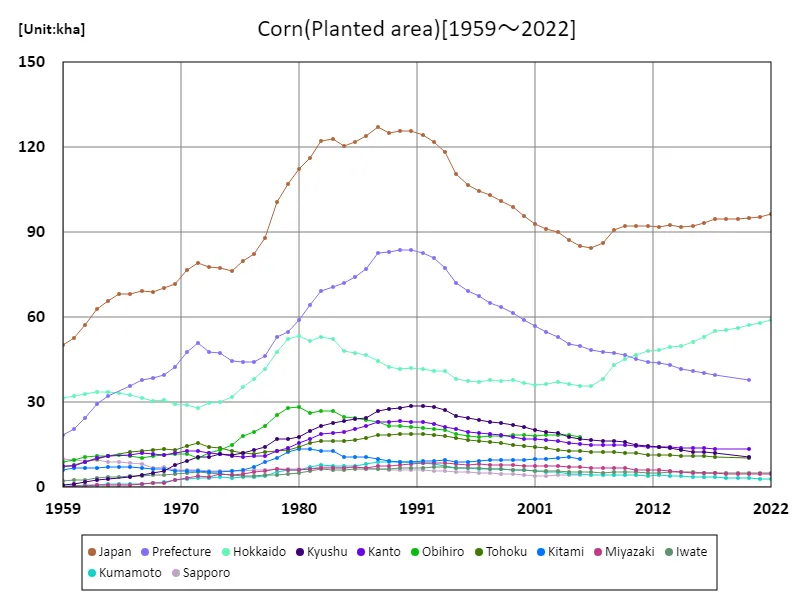

The maximum is 127kha[1987] of Japan, and the current value is about 75.7%
Corn planted area (by prefecture).
According to data for 2022, Japan’s total corn planted area is 59kha, which is the current maximum. What is particularly noteworthy is that Hokkaido recorded the highest total value overall. Hokkaido has vast farmland and cool climate conditions that are ideal for cultivation, resulting in a thriving corn production area. Another factor is that Hokkaido has higher land availability than other regions. Meanwhile, in other regions, the area under cultivation tends to be relatively small. This may be due to climatic conditions, land use constraints, or competition with other crops. In the future, maintaining and improving an efficient agricultural production system, centered on Hokkaido, will likely remain an important factor in Japan’s corn production.
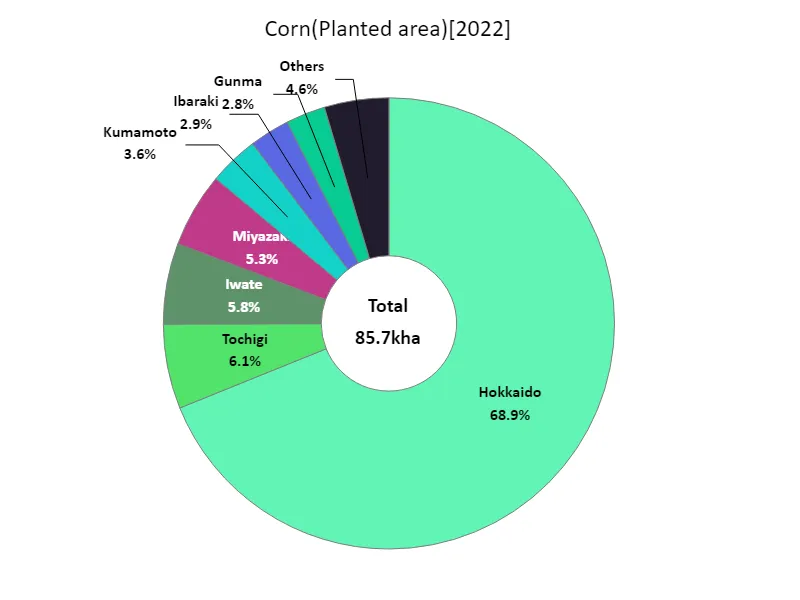

The maximum is 59kha of Hokkaido, the average is 5.35kha, and the total is 85.7kha
Corn yield per 10a (by prefecture).
According to data from 2022, the average corn yield per 10a in Japan is 4.41t overall, with Gunma Prefecture recording the highest yield of 5.85t. This indicates that Gunma Prefecture is maintaining high yields. Gunma Prefecture’s high yields may be due to the local climatic conditions, quality of the soil, and the technical skills of the farmers. Meanwhile, the overall average yield was 4.41t, which represents the midpoint of the yield for Japan as a whole. The data suggests that some regions are producing high yields, while others have room for improvement. In addition, the total overall yield was 70.5 tons, which indicates that corn production throughout Japan is being maintained at a constant level. Going forward, the spread of technology and know-how from high-yield areas such as Gunma Prefecture, as well as improving production efficiency in other regions, will likely remain important issues for Japan’s corn production.
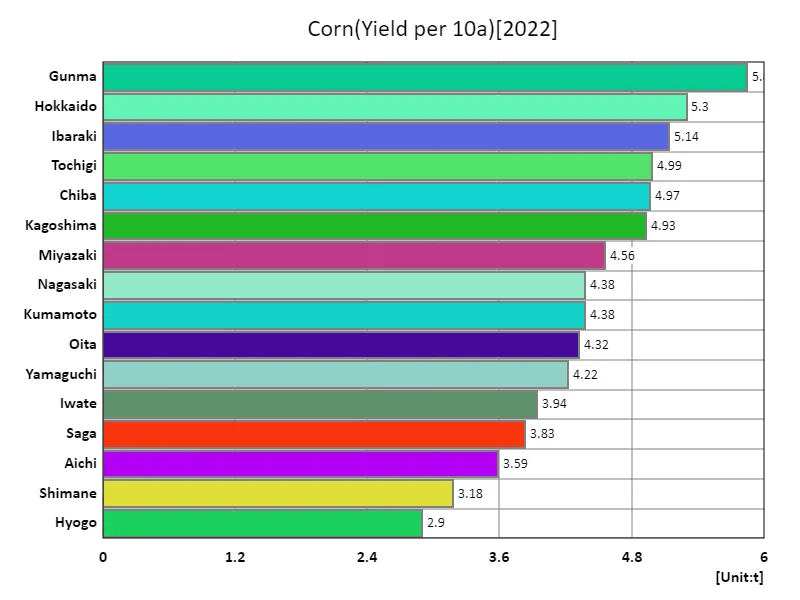

The maximum is 5.85t of Gunma, the average is 4.41t, and the total is 70.5t



Comments