Abstract
China has an overwhelming leadership in vegetable production in global agriculture. According to data for 2022, China’s vegetable production has reached 619 Mt, far exceeding other countries. This figure shows that China is actively promoting vegetable production by taking advantage of its vast land area and diverse climatic conditions. China is known as a major vegetable producer, and by supplying a wide variety of vegetables, it contributes not only to domestic demand but also to the international market. Meanwhile, other countries are also focusing on vegetable production, and are producing on a scale second only to China. Based on past trends, the demand for vegetables is increasing worldwide, and production is also on the rise accordingly. As various countries work to introduce agricultural technologies and sustainable production methods, vegetable production is expected to continue to grow in the future.
Vegetable production (worldwide)
Vegetable production in global agriculture has undergone significant changes over the past 60 years. China’s vegetable production has increased rapidly from 1961 to 2022, reaching an astounding figure of 619 Mt in 2022. China’s rapid economic growth and urbanization have led to increased food demand and expanded agricultural production. China’s peak production reaching 100% shows the magnitude of its growth. Meanwhile, other countries also play an important role in vegetable production. Countries such as India, the United States, and Brazil in particular are contributing to global supply through diversification and technological innovation in agricultural production. However, they face various challenges, including rapid population growth and the effects of climate change. A feature so far is that while production continues to increase due to advances in agricultural technology and improvements in production methods, there are also increasing efforts toward sustainable agriculture. In the future, it will be necessary to build more efficient and sustainable agricultural systems.
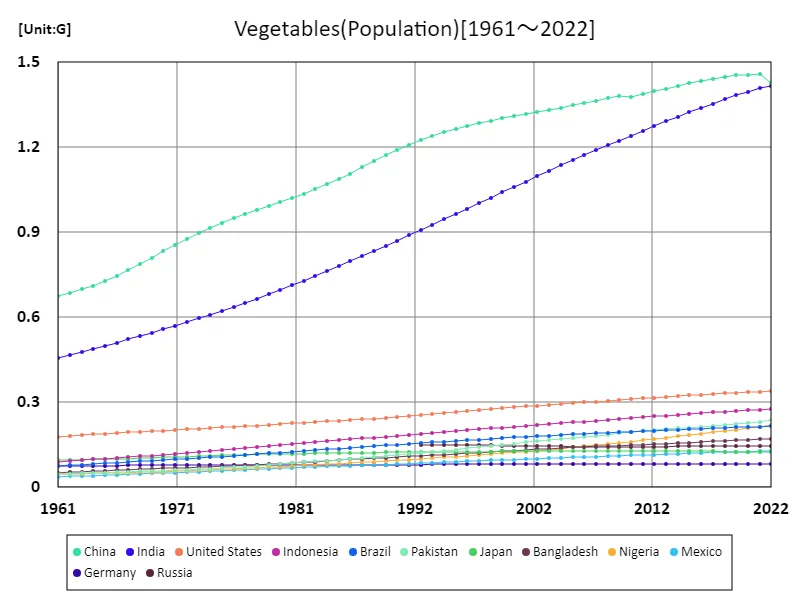

The maximum is 1.46G[2021] of China, and the current value is about 97.8%
Vegetable production (latest year, countries around the world)
From the 2022 data on the production of agricultural vegetables, China boasts an overwhelming leadership. China’s production volume is 619 Mt, which is significantly higher than the overall average. This shows that China is actively engaged in vegetable production, taking advantage of its vast land area and diverse climatic conditions. Other countries have also entered the vegetable production, with a total production volume reaching 1.17 gt. A trend to date is the increasing demand for vegetables worldwide. Due to the growing health consciousness and population growth, the demand for vegetables is expanding, and production volume is also increasing accordingly. There is also increasing interest in sustainable agriculture and quality control, which has led to improvements in production methods and technologies. In the future, along with further increases in production volume, environmental considerations and efforts to ensure food safety will be important.
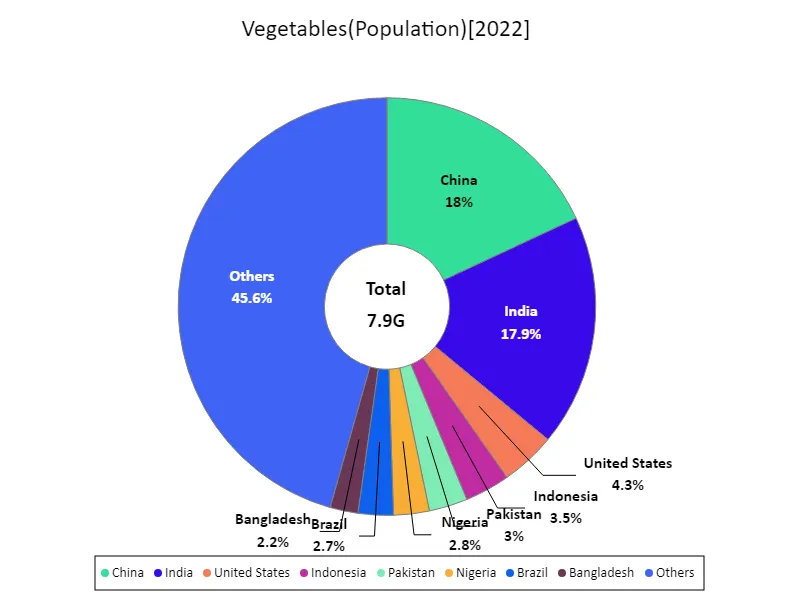

全体の最大はChinaの1.43Gで、平均は41.6M、Totalは7.9G
Vegetable production (continent)
The 2022 data on the production of agricultural vegetables reveals that Asia is the overwhelming leader. The production volume of 927 Mt shows that the Asian region plays a leading role in global vegetable production. This reflects the active promotion of vegetable production by Asian countries, taking advantage of diverse climatic conditions and agricultural technologies. Large Asian countries, especially China, are using their vast farmland and efficient production methods to supply large quantities of vegetables to the global market. On the other hand, other continents and regions also play an important role in vegetable production, but it is noteworthy that Asia boasts the largest production volume. A notable feature so far is the increasing demand for vegetables worldwide. Due to the growing population and increasing health consciousness, the demand for vegetables is expanding, and production is increasing accordingly. In the future, it is expected that production volume, mainly in Asia, will further increase, contributing to global food security.
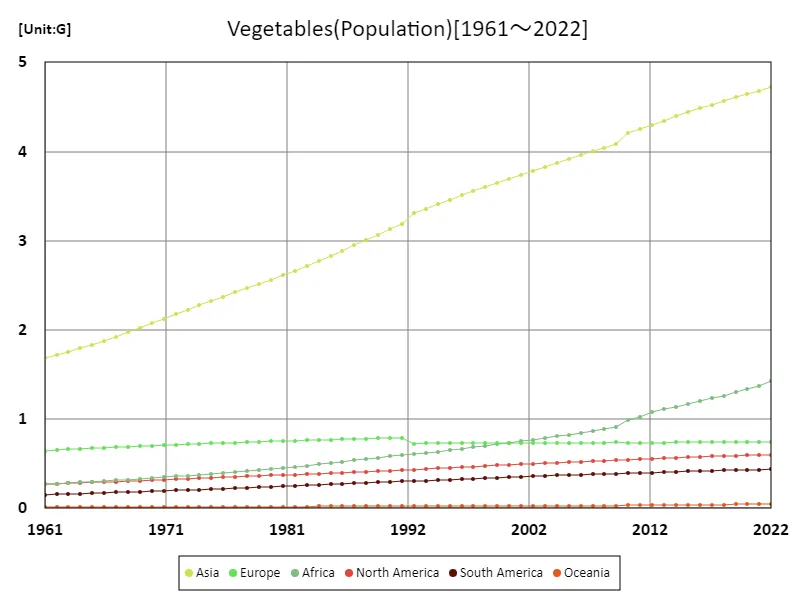

The maximum is the latest one, 4.72G of Asia
Vegetable production (latest year, continent)
From the 2022 data on the production of agricultural vegetables, it is clear that Asia is the largest overall. The production of 927 Mt shows that the Asian region plays a leading role in global vegetable production. Asia’s diverse climatic conditions and advances in agricultural technology contribute to these overwhelming production volumes. Other regions also play an important role, with an average of 196 Mt, but Asia’s production significantly boosts this. A trend to date is the increasing demand for vegetables worldwide. Due to population growth and growing health consciousness, the demand for vegetables is expanding, and production is increasing accordingly. In particular, the Asian region is focusing on vegetable production from the perspective of food security. In the future, it is expected that the global vegetable production will further increase and efforts to ensure sustainable agriculture and food safety will be strengthened.
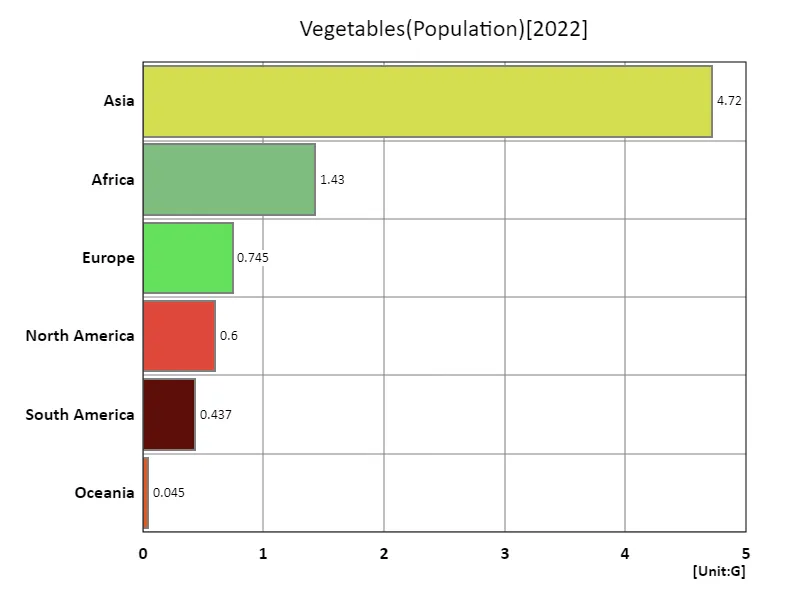

The maximum is 4.72G of Asia, the average is 1.33G, and the total is 7.98G
Main data
| Others(Vegetables, Population) [G] | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| World | Asia | Lower-middle-income countries | Upper-middle-income countries | Africa | China | India | High-income countries | Europe | Low-income countries | |
| 2022 | 7.98 | 4.72 | 3.45 | 2.56 | 1.43 | 1.43 | 1.42 | 1.22 | 0.74 | 0.72 |
| 2021 | 7.91 | 4.68 | 3.41 | 2.55 | 1.37 | 1.46 | 1.41 | 1.22 | 0.74 | 0.7 |
| 2020 | 7.84 | 4.65 | 3.37 | 2.54 | 1.34 | 1.46 | 1.4 | 1.22 | 0.74 | 0.68 |
| 2019 | 7.76 | 4.61 | 3.33 | 2.53 | 1.3 | 1.45 | 1.38 | 1.21 | 0.74 | 0.66 |
| 2018 | 7.68 | 4.57 | 3.28 | 2.52 | 1.26 | 1.45 | 1.37 | 1.21 | 0.74 | 0.64 |
| 2017 | 7.6 | 4.53 | 3.24 | 2.5 | 1.23 | 1.44 | 1.35 | 1.2 | 0.74 | 0.63 |
| 2016 | 7.51 | 4.48 | 3.19 | 2.48 | 1.2 | 1.43 | 1.34 | 1.2 | 0.74 | 0.61 |
| 2015 | 7.43 | 4.44 | 3.14 | 2.46 | 1.17 | 1.43 | 1.32 | 1.19 | 0.74 | 0.59 |
| 2014 | 7.34 | 4.39 | 3.1 | 2.44 | 1.14 | 1.42 | 1.31 | 1.18 | 0.74 | 0.58 |
| 2013 | 7.25 | 4.35 | 3.05 | 2.42 | 1.11 | 1.41 | 1.29 | 1.18 | 0.74 | 0.56 |
| 2012 | 7.16 | 4.3 | 3.01 | 2.4 | 1.08 | 1.4 | 1.27 | 1.17 | 0.74 | 0.55 |
| 2011 | 7.07 | 4.25 | 2.96 | 2.38 | 1.02 | 1.39 | 1.26 | 1.16 | 0.73 | 0.54 |
| 2010 | 6.99 | 4.2 | 2.91 | 2.36 | 0.99 | 1.38 | 1.24 | 1.15 | 0.73 | 0.52 |
| 2009 | 6.9 | 4.09 | 2.87 | 2.35 | 0.91 | 1.38 | 1.22 | 1.15 | 0.74 | 0.51 |
| 2008 | 6.81 | 4.04 | 2.82 | 2.33 | 0.89 | 1.37 | 1.21 | 1.14 | 0.74 | 0.49 |
| 2007 | 6.73 | 4 | 2.78 | 2.31 | 0.87 | 1.36 | 1.19 | 1.13 | 0.74 | 0.48 |
| 2006 | 6.64 | 3.96 | 2.74 | 2.29 | 0.85 | 1.36 | 1.17 | 1.12 | 0.73 | 0.46 |
| 2005 | 6.56 | 3.91 | 2.69 | 2.28 | 0.83 | 1.35 | 1.15 | 1.11 | 0.73 | 0.45 |
| 2004 | 6.48 | 3.87 | 2.65 | 2.26 | 0.81 | 1.34 | 1.14 | 1.1 | 0.73 | 0.44 |
| 2003 | 6.39 | 3.83 | 2.6 | 2.24 | 0.79 | 1.33 | 1.12 | 1.09 | 0.73 | 0.43 |
| 2002 | 6.31 | 3.78 | 2.56 | 2.23 | 0.77 | 1.32 | 1.1 | 1.09 | 0.73 | 0.41 |
| 2001 | 6.23 | 3.74 | 2.51 | 2.21 | 0.75 | 1.32 | 1.08 | 1.08 | 0.73 | 0.4 |
| 2000 | 6.15 | 3.69 | 2.47 | 2.19 | 0.74 | 1.31 | 1.06 | 1.07 | 0.73 | 0.39 |
| 1999 | 6.07 | 3.65 | 2.42 | 2.17 | 0.72 | 1.3 | 1.04 | 1.07 | 0.73 | 0.38 |
| 1998 | 5.99 | 3.6 | 2.38 | 2.16 | 0.7 | 1.29 | 1.02 | 1.06 | 0.73 | 0.37 |
| 1997 | 5.91 | 3.56 | 2.33 | 2.14 | 0.68 | 1.29 | 1 | 1.05 | 0.73 | 0.36 |
| 1996 | 5.83 | 3.51 | 2.29 | 2.12 | 0.67 | 1.28 | 0.98 | 1.05 | 0.73 | 0.35 |
| 1995 | 5.74 | 3.46 | 2.24 | 2.1 | 0.65 | 1.27 | 0.96 | 1.04 | 0.73 | 0.34 |
| 1994 | 5.66 | 3.41 | 2.2 | 2.08 | 0.64 | 1.25 | 0.95 | 1.03 | 0.73 | 0.33 |
| 1993 | 5.58 | 3.36 | 2.15 | 2.05 | 0.62 | 1.24 | 0.93 | 1.02 | 0.73 | 0.32 |
| 1992 | 5.49 | 3.31 | 2.11 | 2.03 | 0.61 | 1.23 | 0.91 | 1.02 | 0.73 | 0.31 |
| 1991 | 5.41 | 3.18 | 2.07 | 2.01 | 0.6 | 1.21 | 0.89 | 1.01 | 0.79 | 0.3 |
| 1990 | 5.32 | 3.13 | 2.02 | 1.98 | 0.58 | 1.19 | 0.87 | 1 | 0.79 | 0.3 |
| 1989 | 5.22 | 3.07 | 1.98 | 1.95 | 0.57 | 1.17 | 0.85 | 0.99 | 0.79 | 0.29 |
| 1988 | 5.13 | 3.01 | 1.93 | 1.92 | 0.55 | 1.15 | 0.83 | 0.99 | 0.78 | 0.28 |
| 1987 | 5.04 | 2.95 | 1.89 | 1.88 | 0.54 | 1.13 | 0.82 | 0.98 | 0.78 | 0.27 |
| 1986 | 4.95 | 2.89 | 1.84 | 1.85 | 0.52 | 1.11 | 0.8 | 0.97 | 0.77 | 0.27 |
| 1985 | 4.86 | 2.83 | 1.8 | 1.82 | 0.51 | 1.09 | 0.78 | 0.96 | 0.77 | 0.26 |
| 1984 | 4.78 | 2.77 | 1.76 | 1.79 | 0.49 | 1.07 | 0.76 | 0.96 | 0.77 | 0.25 |
| 1983 | 4.69 | 2.72 | 1.72 | 1.76 | 0.48 | 1.05 | 0.75 | 0.95 | 0.76 | 0.25 |
| 1982 | 4.61 | 2.67 | 1.67 | 1.73 | 0.47 | 1.04 | 0.73 | 0.94 | 0.76 | 0.24 |
| 1981 | 4.52 | 2.61 | 1.63 | 1.71 | 0.45 | 1.02 | 0.71 | 0.94 | 0.75 | 0.23 |
| 1980 | 4.44 | 2.56 | 1.59 | 1.68 | 0.44 | 1.01 | 0.7 | 0.93 | 0.75 | 0.23 |
| 1979 | 4.37 | 2.51 | 1.55 | 1.65 | 0.43 | 0.99 | 0.68 | 0.92 | 0.75 | 0.23 |
| 1978 | 4.29 | 2.47 | 1.51 | 1.63 | 0.42 | 0.98 | 0.67 | 0.91 | 0.74 | 0.22 |
| 1977 | 4.22 | 2.42 | 1.48 | 1.6 | 0.41 | 0.97 | 0.65 | 0.9 | 0.74 | 0.21 |
| 1976 | 4.14 | 2.37 | 1.44 | 1.58 | 0.4 | 0.95 | 0.64 | 0.9 | 0.73 | 0.21 |
| 1975 | 4.07 | 2.32 | 1.41 | 1.55 | 0.39 | 0.93 | 0.62 | 0.89 | 0.73 | 0.2 |
| 1974 | 4 | 2.27 | 1.38 | 1.52 | 0.38 | 0.92 | 0.61 | 0.88 | 0.72 | 0.2 |
| 1973 | 3.92 | 2.22 | 1.35 | 1.49 | 0.37 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.87 | 0.72 | 0.19 |
| 1972 | 3.84 | 2.17 | 1.32 | 1.46 | 0.36 | 0.88 | 0.58 | 0.87 | 0.71 | 0.19 |
| 1971 | 3.77 | 2.12 | 1.29 | 1.43 | 0.35 | 0.85 | 0.57 | 0.86 | 0.71 | 0.18 |
| 1970 | 3.7 | 2.07 | 1.26 | 1.4 | 0.34 | 0.83 | 0.56 | 0.85 | 0.7 | 0.18 |
| 1969 | 3.62 | 2.02 | 1.23 | 1.37 | 0.33 | 0.81 | 0.55 | 0.84 | 0.7 | 0.17 |
| 1968 | 3.55 | 1.97 | 1.2 | 1.34 | 0.32 | 0.79 | 0.53 | 0.83 | 0.69 | 0.17 |
| 1967 | 3.48 | 1.92 | 1.17 | 1.31 | 0.31 | 0.77 | 0.52 | 0.82 | 0.69 | 0.16 |
| 1966 | 3.41 | 1.88 | 1.14 | 1.28 | 0.31 | 0.75 | 0.51 | 0.81 | 0.68 | 0.16 |
| 1965 | 3.34 | 1.83 | 1.12 | 1.25 | 0.3 | 0.73 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.68 | 0.16 |
| 1964 | 3.27 | 1.79 | 1.09 | 1.22 | 0.29 | 0.71 | 0.49 | 0.79 | 0.67 | 0.15 |
| 1963 | 3.2 | 1.75 | 1.07 | 1.18 | 0.28 | 0.7 | 0.48 | 0.78 | 0.66 | 0.15 |
| 1962 | 3.13 | 1.72 | 1.04 | 1.15 | 0.28 | 0.69 | 0.47 | 0.78 | 0.65 | 0.15 |
| 1961 | 3.07 | 1.69 | 1.02 | 1.13 | 0.27 | 0.68 | 0.46 | 0.77 | 0.65 | 0.14 |



Comments