Abstract
Eggplant cultivation has seen significant global trends, with China consistently leading in production and land use. In 2022, China had the largest area dedicated to eggplant cultivation, covering 818,000 hectares (kha), far outpacing other countries. Historically, eggplant farming has been concentrated in Asia, particularly in countries like India and Bangladesh, with China also holding a dominant share. Over the years, global production has shifted towards intensifying yields through better farming practices and increased demand in both domestic and export markets. Other key producers, including Turkey, Indonesia, and Egypt, have also expanded their cultivation areas.
Eggplant land use (Worldwide)
Eggplant cultivation has experienced notable trends over the past six decades, with China consistently being the largest producer. The highest recorded land use for eggplants was 982,000 hectares (kha) in 2006, after which the area began to decline. As of 2022, China’s eggplant cultivation stands at 818,000 kha, about 83.3% of its peak. This decline may be attributed to shifts in agricultural priorities, land use changes, and possibly competition from other crops. Despite this, China remains the dominant producer, while other countries like India and Turkey continue to expand their cultivation areas.


The maximum is 3.19Mt[2016] of Canada, and the current value is about 72%
Eggplant land use (latest year, worldwide)
Eggplant cultivation globally in 2022 shows China as the dominant producer, with 818,000 hectares (kha), far surpassing other nations. The total global land area for eggplant cultivation was 1.89 million hectares (mha), with the average area per country being 19.5 kha. China’s substantial share highlights its central role in global eggplant production, while other countries have smaller contributions. Over time, eggplant farming has become more concentrated in Asia, with countries like India, Turkey, and Egypt also playing significant roles. The overall trend reflects increased specialization and productivity in major producing regions.


The maximum is 2.3Mt of Canada, the average is 145kt, and the total is 6.66Mt
Eggplant land use (continent)
In 2022, Asia dominated global eggplant cultivation, with the region covering a maximum of 1.81 million hectares (mha), reflecting its central role in production. The majority of eggplant farming is concentrated in countries like China, India, and Turkey, which have historically led production. Over time, eggplant farming has remained heavily concentrated in Asia due to favorable climates and high domestic demand. Other regions have seen smaller areas dedicated to eggplant cultivation, with global production focusing on meeting both local consumption and export needs, particularly in Asia’s growing markets.


The maximum is 3.78Mt[2016] of North America, and the current value is about 67.8%
Nasu land use (latest year, continent)
In 2022, Asia remained the dominant region for eggplant cultivation, covering 1.75 million hectares (mha) of the global total of 1.89 mha. The average land area for eggplant farming per country stood at 315,000 hectares. The trend reflects Asia’s historical and ongoing centrality in eggplant production, driven by high domestic consumption, favorable climates, and established farming practices. China, India, and Turkey are major contributors, while other regions have relatively smaller cultivation areas. Overall, eggplant farming continues to be highly concentrated in Asia, with gradual growth in other regions.
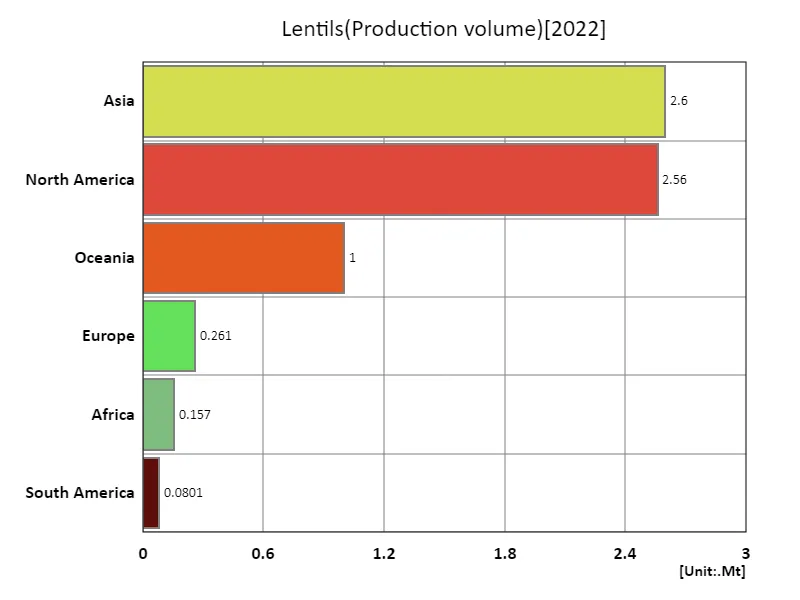

The maximum is 2.6Mt of Asia, the average is 1.11Mt, and the total is 6.66Mt



Comments