Abstract
There is growing interest in fruit vegetables, especially bell peppers, in Japanese agriculture. In 2022, the harvest volume across the country reached up to 150kt and the area planted reached up to 3.17kha. These figures indicate the adoption of efficient production technologies and the modernization of agriculture. Meanwhile, Ibaraki recorded the highest shipping volume at 31.5kt. Since Ibaraki ranked first in terms of shipping volume, it is possible that there are differences in production characteristics and demand from region to region. These data show that bell pepper cultivation is an important industry throughout Japan, with particular attention being paid to technological innovation and the utilization of regional characteristics.
Bell pepper harvest yield (main data).
Bell pepper yields in Japanese agriculture have undergone various changes between 1973 and 2022. The peak harvest volume nationwide was recorded at 182kt in 1989, and has been declining since then. The current harvest yield is 82.2% of the peak. The reasons behind this decline include increased productivity through agricultural modernization and technological innovation, as well as a decrease in farmland. Changes in demand and domestic and international competitive conditions may also be having an impact. On the other hand, the importance of sustainable agriculture and regional brands has recently been recognized, and bell pepper cultivation as a regional specialty product has been attracting attention. Given this background, in the future it will be necessary to establish a production system that can adapt to changes in demand and technological innovation.
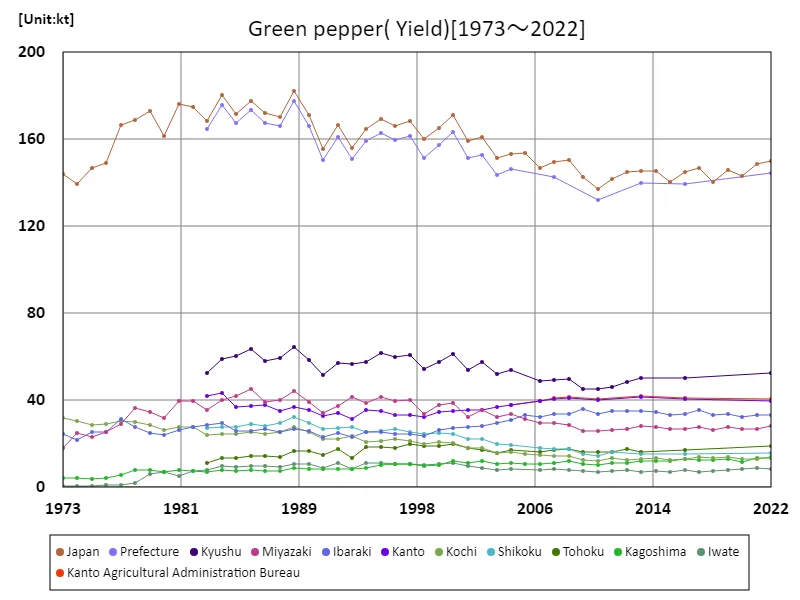

The maximum is 182kt[1989] of Japan, and the current value is about 82.2%
Bell pepper harvest volume (by prefecture).
Looking at data for fruit vegetable harvests in Japanese agriculture by prefecture in 2022, Ibaraki recorded the highest overall yield of 33.3 kt, the highest level to date. This is a result that reflects Ibaraki’s regional characteristics and advances in agricultural technology, and suggests that the prefecture is a major producer of fruit and vegetables. As a general trend, harvest yields vary from region to region due to differences in climate, soil conditions, and the level of agricultural development from prefecture to prefecture. In addition, as demand for fruit vegetables increases, efficient production systems and quality control are becoming more important, and producers are working to meet these demands. Furthermore, the importance of sustainable agriculture and local brands is being recognized, and local varieties and cultivation techniques are attracting attention. In the future, it will be necessary to produce fruit and vegetables that take advantage of the characteristics of each region while also responding to changes in demand and the effects of climate change.
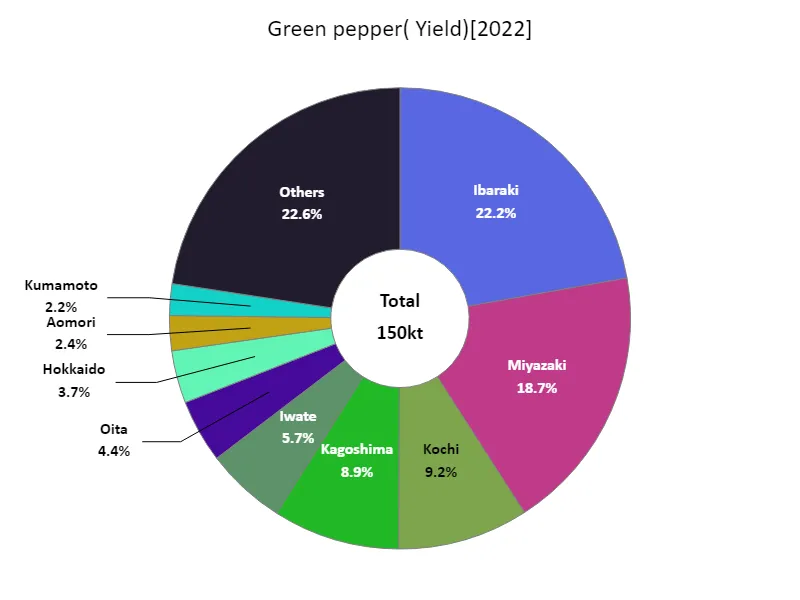

The maximum is 33.3kt of Ibaraki, the average is 3.19kt, and the total is 150kt
Area cultivated with bell peppers (main data).
The area of land cultivated with bell peppers in Japanese agriculture has undergone changes between 1973 and 2022. The peak cultivated area nationwide was 4.8 kha in 1982, but has been declining since then, and the current cultivated area is only 66% of the peak. Possible reasons for this decline include structural changes in agriculture, changes in market demand, and labor shortages. In particular, economic growth and urbanization are contributing to a decrease in farmland and the number of people working in agriculture. On the other hand, recently, due to growing health consciousness and an emphasis on local production and consumption, there have been efforts to develop regional brands and high added value, and in some regions production is taking advantage of specific varieties and cultivation techniques. In the future, as sustainable agriculture and the use of local resources become even more important, there will be a demand for efficient production systems and stronger quality control that matches demand.
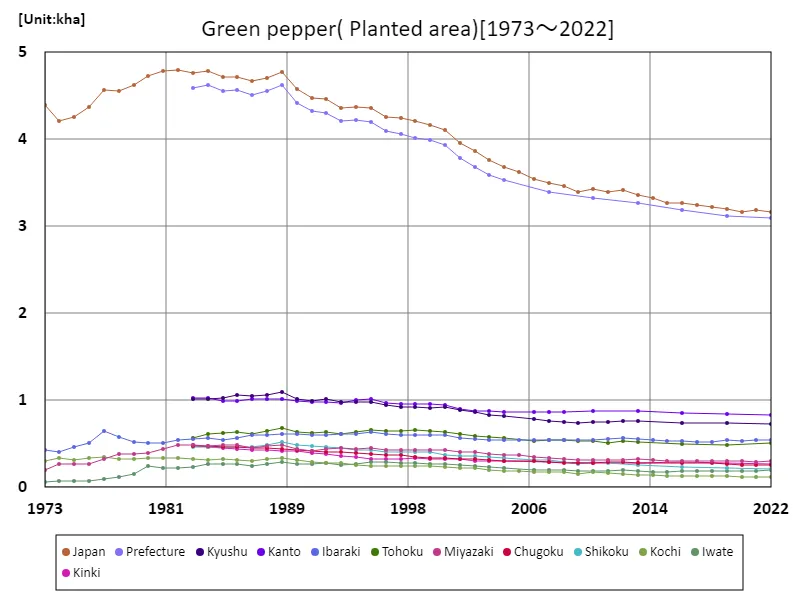

The maximum is 4.8kha[1982] of Japan, and the current value is about 66%
Area cultivated with bell peppers (by prefecture).
Looking at data by prefecture for 2022 on the area of fruit and vegetable cultivation in Japanese agriculture, Ibaraki recorded the highest total of 539 hectares, the highest level to date. This is a result that reflects Ibaraki’s regional characteristics and advances in agricultural technology, and suggests that the prefecture is a major producer of fruit and vegetables. In addition, fruit vegetable cultivation is also being actively carried out in other regions, which is thought to be due to increasing demand and improved productivity as a result of agricultural modernization. In particular, demand is growing for regional brands and high-quality fruit and vegetable products, and producers are working to improve varieties and cultivation techniques to meet this demand. Furthermore, as the promotion of sustainable agriculture and local production for local consumption progresses, attention is being paid to utilizing local resources and developing regional varieties. In the future, it is expected that fruit and vegetable production will continue to take advantage of the characteristics of each region, while also responding to changes in demand and the effects of climate change.
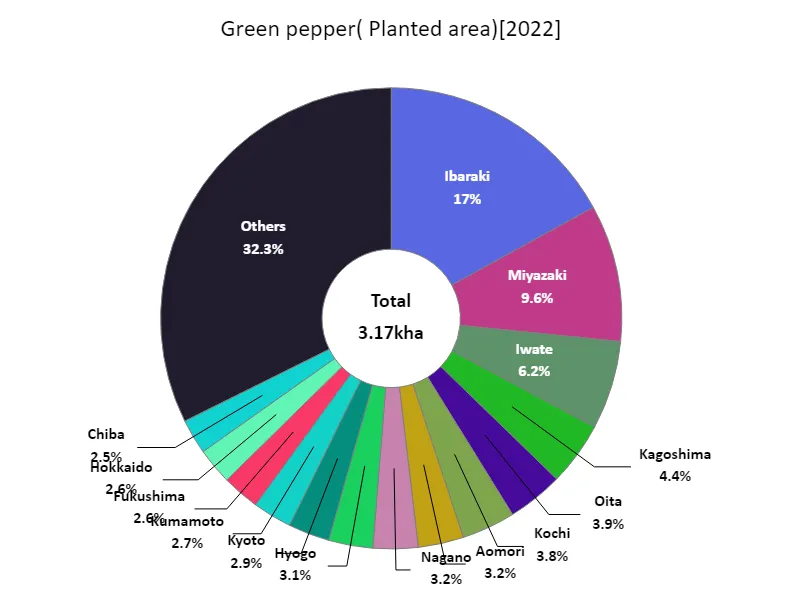

The maximum is 539ha of Ibaraki, the average is 67.4ha, and the total is 3.17kha
The volume of green peppers shipped.
In 2022, Ibaraki Prefecture recorded the highest overall shipment volume of bell peppers in Japanese agriculture, reaching 31.5kt. This shows that Ibaraki Prefecture is a major producer of bell peppers. The overall average shipment was 2.85kt, bringing the total to 134kt. These figures show that while bell pepper production is widespread throughout Japan, Ibaraki Prefecture is at the center of it. Bell pepper shipment volumes tend to fluctuate depending on demand and the season. Demand increases especially during the summer, and so do shipping volumes. Additionally, demand for bell peppers is thought to be expanding in recent years due to growing health consciousness and diversifying cuisine. In response to this, producers are working to improve quality control and production techniques. Furthermore, as the emphasis on regional brands and local production for local consumption increases, pepper producing areas such as Ibaraki Prefecture are producing bell peppers that make use of regional varieties and cultivation methods. These efforts play a key role in gaining consumer trust. Looking to the future, there will be a demand for sustainable agriculture and the utilization of local resources, so it will be important to maintain the production volume and quality of bell peppers. Efforts are needed to ensure a stable supply while responding flexibly to changes in demand and the effects of climate change.
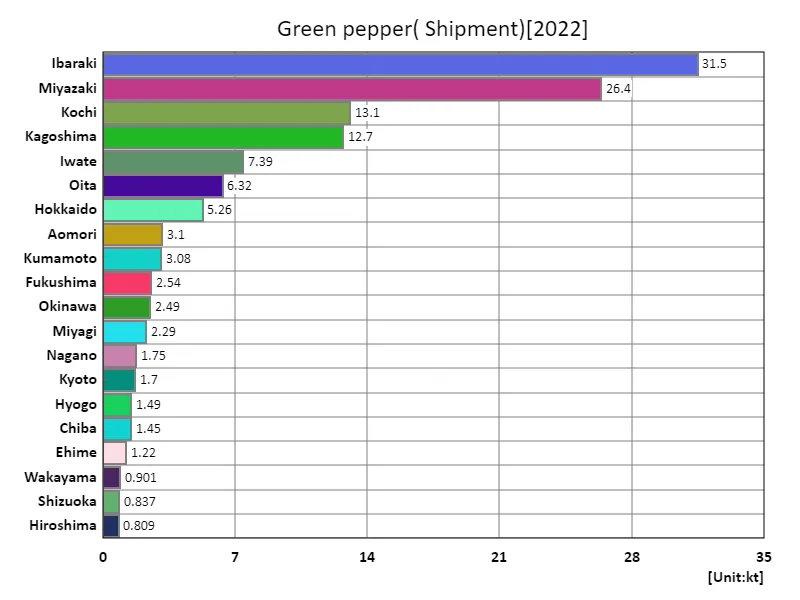

The maximum is 31.5kt of Ibaraki, the average is 2.85kt, and the total is 134kt



Comments