Abstract
Based on data on fruit vegetables in Japanese agriculture, particularly summer and autumn peppers, the national harvest volume in 2022 will be 71.2kt, with the maximum cultivated area being 2.42kha. The largest shipping volume was in Ibaraki Prefecture, at 12.1kt. These figures indicate that production of summer and autumn bell peppers in Japan is relatively large-scale, with Ibaraki Prefecture being one of the centers in particular. Based on past trends, demand for summer/fall peppers is stable and production may be increasing. Changes in agricultural technology and demand are likely to lead to increases in production and shipments in the future.
Summer/autumn pepper harvest yields (main data).
Japan’s summer/autumn pepper harvest has fluctuated between 1973 and 2022. The peak was recorded in 1984 at 105 kt nationwide, and while it has fluctuated since then, it has generally been on a downward trend. As of 2022, overall harvest volumes are approximately 67.6% of their peak. Behind this trend are changes in cultivated area and production volume, as well as changes in demand, as agriculture becomes more mechanized and efficient. Climate change and changes in agricultural policy may also be playing a role. In the future, changes in demand, technological innovations, and fluctuations in weather conditions are likely to affect harvest yields.
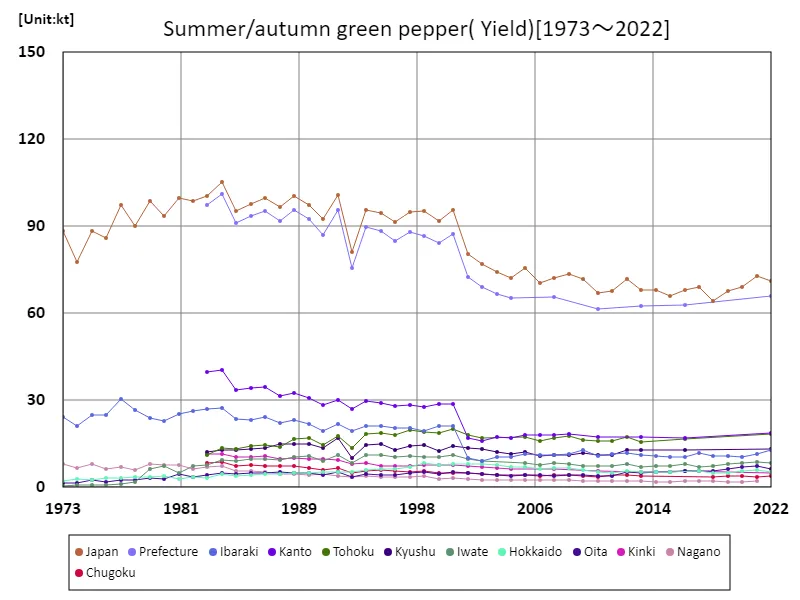

The maximum is 105kt[1984] of Japan, and the current value is about 67.6%
Summer and autumn bell pepper harvest volumes (by prefecture).
Data for 2022 on fruit and vegetable harvests in Japan shows that Ibaraki Prefecture recorded the highest yield in the country at 12.7kt, which is currently the highest. Considering the characteristics and trends so far, it is suggested that Ibaraki Prefecture is an important region for fruit and vegetable production. Ibaraki Prefecture has fertile land and abundant water sources, making it an ideal environment for agriculture. It is also possible that improvements in agricultural techniques and cultivation methods are increasing yields. Ibaraki Prefecture is the largest producer of fruit and vegetables in the country, making the region a leader in fruit and vegetable production and exerting a great influence. There is a possibility that fruit and vegetable production in Ibaraki Prefecture will continue to increase, and it is predicted that it will play an important role in the local economy and food supply.
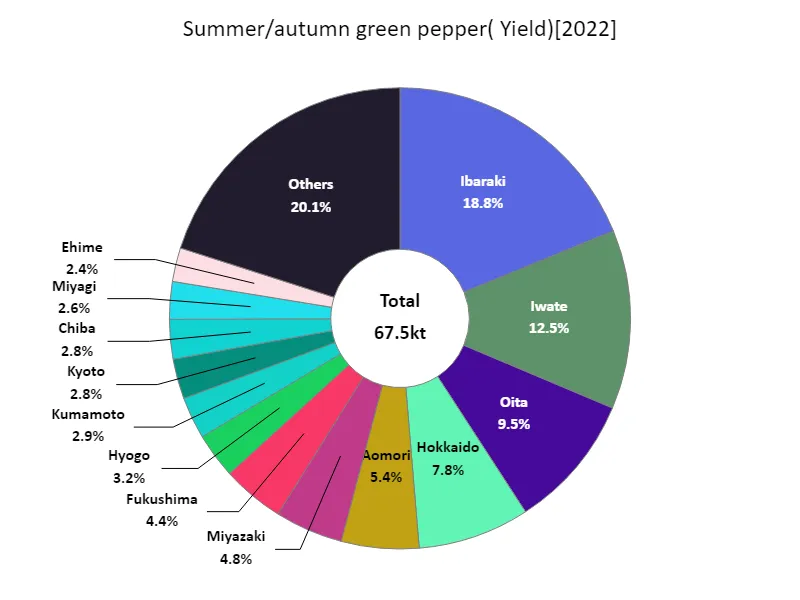

The maximum is 12.7kt of Ibaraki, the average is 1.61kt, and the total is 67.5kt
Planted area for summer/autumn bell peppers (main data).
As can be seen from data from 1973 to 2022, the area planted to summer/autumn peppers in Japan has fluctuated. The peak was recorded in 1981 at 3.94 kha nationwide, and has been declining since then. As of 2022, the total cultivated area is approximately 61.4% of its peak. The background to this trend includes changes in agricultural structure, fluctuations in demand, and changes in agricultural policies. For example, it is possible that the area under cultivation is shrinking due to mechanization and increased efficiency in agriculture. Additionally, changes in demand and the competitive environment both domestically and internationally will also have an impact on the area planted. In the future, changes in demand, technological innovations, and fluctuations in weather conditions may affect the area planted. In addition, from the perspective of promoting sustainable agriculture and food security, policies and initiatives regarding the area planted with summer/autumn bell peppers will attract attention.
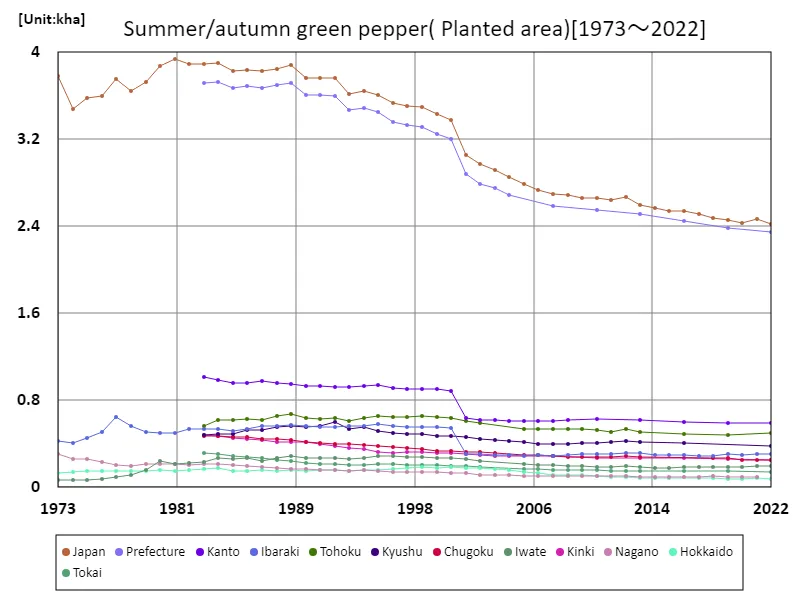

The maximum is 3.94kha[1981] of Japan, and the current value is about 61.4%
Areas planted for summer and autumn bell peppers (by prefecture).
According to data from 2022, the largest area cultivated with fruit vegetables in Japan is Ibaraki Prefecture at 303 hectares, which is the current high. Considering the characteristics and trends thus far, it is suggested that Ibaraki Prefecture is an important region for fruit vegetable cultivation. Ibaraki Prefecture has fertile farmland and favorable climatic conditions, making it an ideal environment for cultivating fruit and vegetables. It is also possible that improvements in agricultural technology and cultivation methods have led to an increase in the area under cultivation. Ibaraki Prefecture has the largest area of land devoted to fruit and vegetable cultivation in the country, so it can be said that this region plays a central role in fruit and vegetable production. It is predicted that fruit and vegetable cultivation in Ibaraki Prefecture will continue to increase and play an important role in the local economy and food supply. From the perspective of agricultural policy and environmental protection, the introduction of sustainable cultivation methods and agricultural diversification will be required.
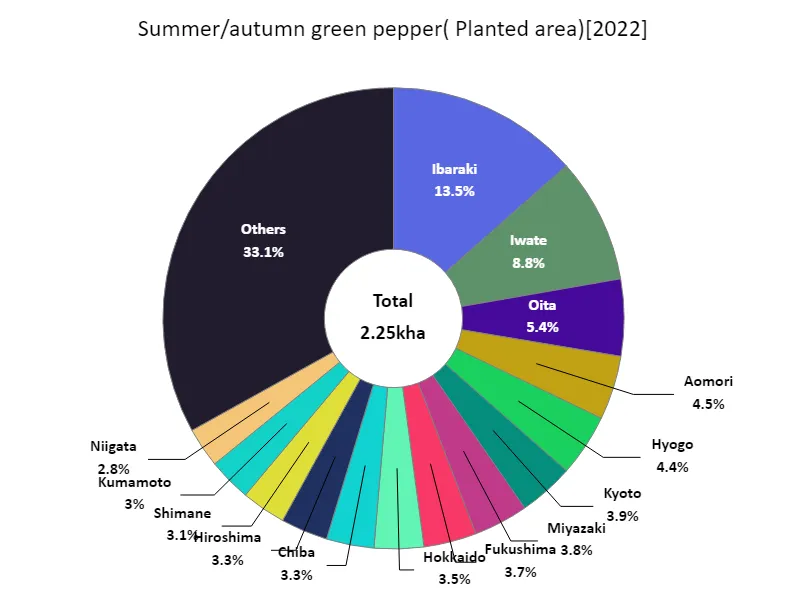

The maximum is 303ha of Ibaraki, the average is 53.5ha, and the total is 2.25kha
Summer and autumn bell pepper shipment volumes.
According to data for 2022, Ibaraki Prefecture had the highest shipment volume of summer and autumn peppers in Japan at 12.1kt, with an overall average of 1.35kt and a total of 56.8kt. Considering the characteristics and trends so far, it is suggested that Ibaraki Prefecture plays a central role in the shipping volume of summer and autumn bell peppers. Ibaraki Prefecture has favorable climatic conditions and fertile soil, making it an ideal region for producing fruit vegetables, so high shipping volumes are a natural result. Also, since the overall average is 1.35kt, it can be seen that the production volume of summer and autumn peppers varies by region. Furthermore, the total of 56.8kt indicates that the production volume of summer and autumn peppers in Japan as a whole is at a certain scale. Changes in demand and weather conditions may affect shipping volumes, and appropriate measures to deal with these factors will be necessary in the future.
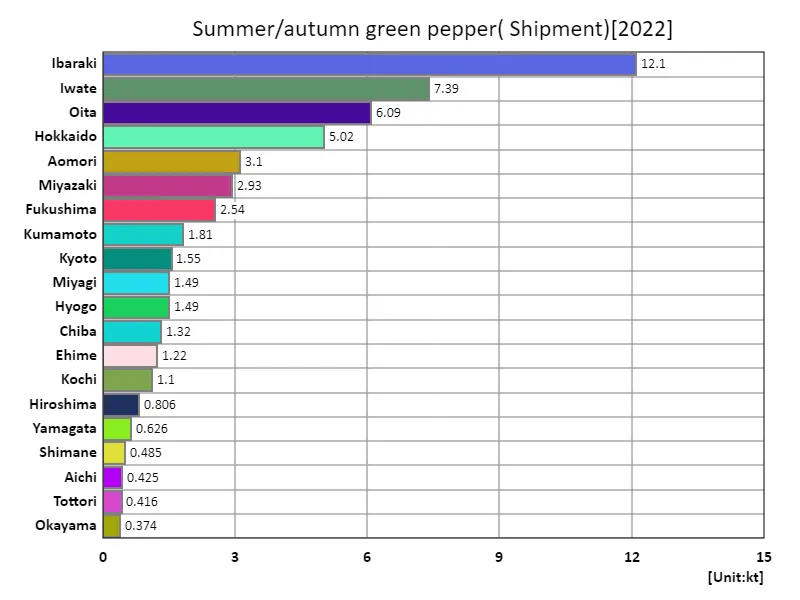

The maximum is 12.1kt of Ibaraki, the average is 1.35kt, and the total is 56.8kt



Comments