- Abstract
- Among tomatoes, the harvest volume of tomatoes for processing (main data).
- The harvest volume of tomatoes for processing (by prefecture).
- Among tomatoes, the area cultivated for processing tomatoes (main data).
- The area of tomatoes cultivated for processing (by prefecture).
- The amount of tomatoes shipped for processing.
- Reference
Abstract
When viewed from the perspectives of yield, cultivated area, and shipping volume, processing tomato agriculture in Japan exhibits some interesting characteristics. The 2022 harvest is expected to be up to 24.7kt nationwide, indicating some stability. The cultivated area in that year was the largest in the country at 435 hectares, indicating high productivity. In terms of shipping volume, Ibaraki had the highest volume at 10.9 kt, showing a bias in production between regions. Based on past trends, production of tomatoes for processing has been stable, with Ibaraki in particular standing out as one of the centers. Given this characteristic, appropriate measures will be required in response to fluctuations in production capacity and demand in each region.
Among tomatoes, the harvest volume of tomatoes for processing (main data).
The harvest volume of tomatoes for processing in Japan reached a national peak of 85.6kt in 1989, but has been on a downward trend since then. As of 2022, that figure has fallen to 28.9%. Possible reasons for this decrease include changes in agricultural structure and fluctuations in demand. The modernization of agriculture and urbanization are resulting in a decrease in farmland and an aging farming population, which is affecting the production of tomatoes for processing. Changing consumer tastes and competition from foreign products may also be playing a role. Under these circumstances, it is necessary to establish a sustainable production system and adjust production to meet demand. The decline in processing tomato harvests is one of the challenges facing Japanese agriculture, and support from the government and related organizations, as well as the efforts of farmers, are essential.
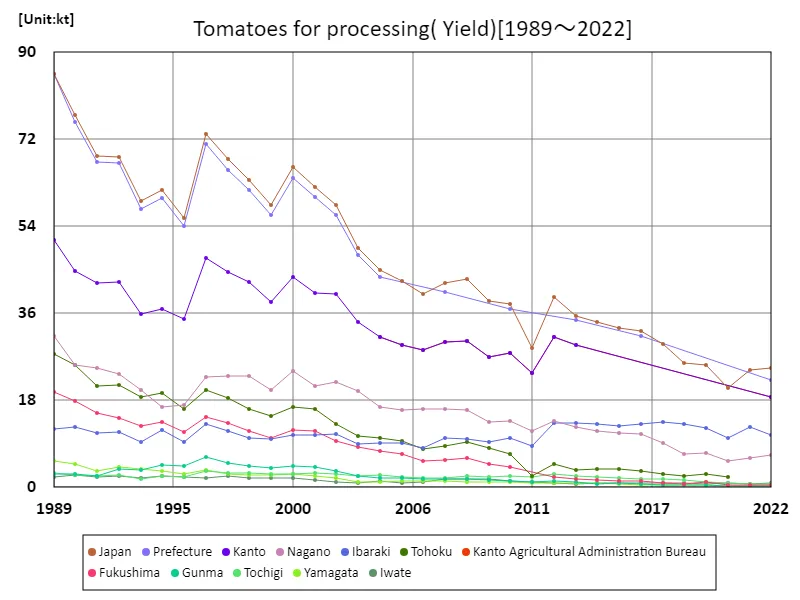

The maximum is 85.6kt[1989] of Japan, and the current value is about 28.9%
The harvest volume of tomatoes for processing (by prefecture).
The latest data for 2022 on fruit and vegetable harvests in Japan shows that Ibaraki Prefecture recorded the largest yield overall at 10.9kt, which is the highest yield to date. Ibaraki Prefecture has long been known as one of the agricultural centers of Japan, with its fertile soil and proactive agricultural policies contributing to the production of fruit and vegetables. On the other hand, fruit and vegetable production is also thriving in other regions, and depending on the region, differences in climatic conditions and soil tend to place more importance on certain items. The increase or decrease in fruit and vegetable harvest volume varies depending on the season and climate change, but in recent years, technological innovation and improvements in agricultural policies have raised hopes for stable production. On the other hand, there are concerns that a decrease in farmland and labor shortages due to population decline and urbanization will have an impact on future fruit and vegetable harvests. To address these challenges, it is important to build sustainable agricultural systems and support farmers.
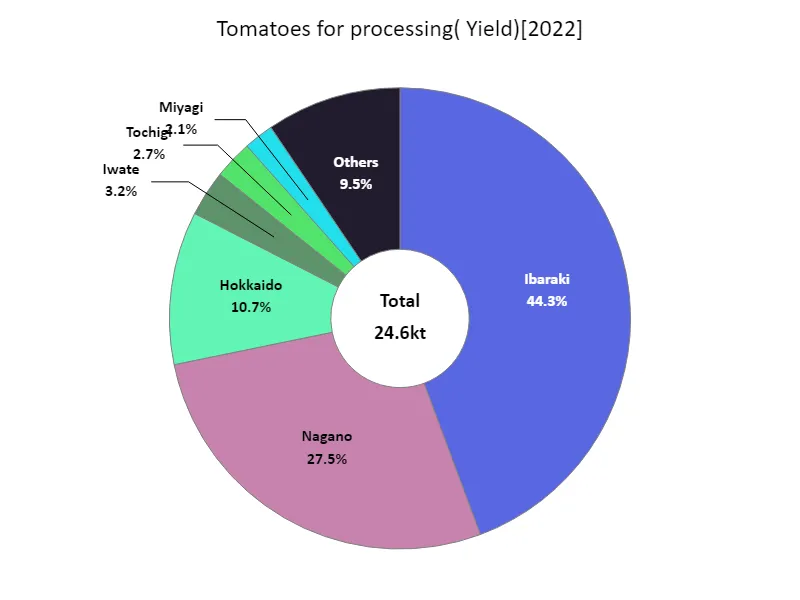

The maximum is 10.9kt of Ibaraki, the average is 1.37kt, and the total is 24.6kt
Among tomatoes, the area cultivated for processing tomatoes (main data).
The area cultivated for processing tomatoes in Japan peaked at 1.28 kha nationwide in 1989, but has been on a downward trend since then. As of 2022, it has fallen to 34% of its peak. Possible reasons for this decrease include changes in agricultural structure and fluctuations in demand. The modernization of agriculture and urbanization are resulting in a decrease in farmland and an aging farming population, which is affecting the area planted for tomatoes for processing. There may also have been a decline in demand for tomatoes for processing. Changing consumer tastes and competition from foreign products may also be contributing to the decline in acreage. Under these circumstances, it is necessary to establish a sustainable production system and adjust cultivated areas to match demand. The decline in the area planted with processing tomatoes is one of the challenges facing Japanese agriculture, and support from the government and related organizations, as well as the efforts of farmers, are essential.
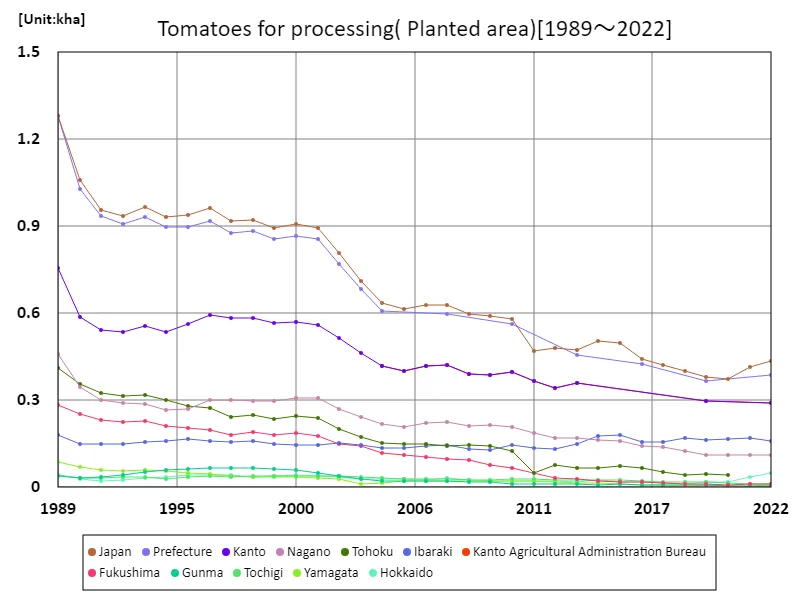

The maximum is 1.28kha[1989] of Japan, and the current value is about 34%
The area of tomatoes cultivated for processing (by prefecture).
Looking at the data on the area of land cultivated with fruit and vegetables in Japan in 2022, Ibaraki Prefecture boasts the largest area overall, with a record of 160 hectares. Supported by its rich agricultural areas and proactive agricultural policies, Ibaraki Prefecture maintains a certain leadership position in fruit and vegetable production. In general, the area planted to fruit vegetables varies from region to region and is influenced by climatic conditions and soil suitability. Consumer demand and market trends also influence acreage. Recent trends include ensuring supplies to urban areas and a shift towards high value-added crops. In addition, the promotion of sustainable agriculture and strengthening of cooperation between regions are contributing to the stabilization of fruit and vegetable production area. On the other hand, challenges such as population decline and agricultural labor shortages exist, and policies to address these are needed. Data on the area planted to fruit and vegetable crops is an important indicator for assessing the health and sustainability of a region’s agriculture.
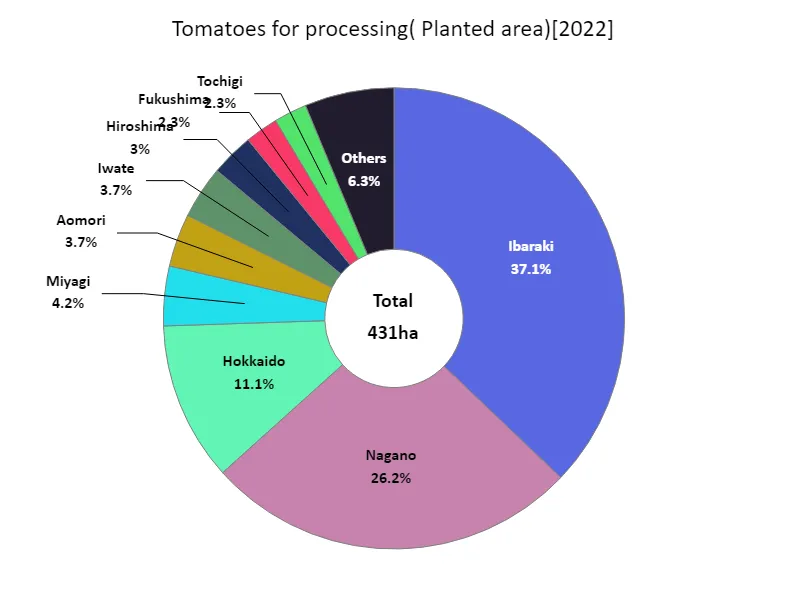

The maximum is 160ha of Ibaraki, the average is 23.9ha, and the total is 431ha
The amount of tomatoes shipped for processing.
Japan’s total shipments of tomatoes for processing in 2022 will be 24.5kt, of which Ibaraki Prefecture will account for the largest share at 10.9kt. As this data shows, Ibaraki Prefecture is a major producer of tomatoes for processing, with production volumes far exceeding those of other regions. On the other hand, the overall average shipping volume was 1.36kt, indicating that Ibaraki Prefecture’s production volume had a major impact. The shipping volume of tomatoes for processing is influenced by factors such as the characteristics of the agricultural region, climatic conditions, the technical level of farmers, and market demand. The reason Ibaraki Prefecture has an overwhelming shipping volume compared to other prefectures is due to its rich agricultural areas and appropriate agricultural policies. It is believed that Ibaraki Prefecture’s regional characteristics and proactive agricultural promotion policies are contributing to the production of tomatoes for processing. On the other hand, the relatively low overall average shipping volume also suggests that there are disparities in production between regions and issues with the balance between supply and demand for tomatoes for processing. Fluctuations in demand and intensifying market competition are factors that are pushing down average shipment volumes. The volume of tomatoes shipped for processing is an important indicator that has a significant impact on the health of agricultural production and local economies. It is necessary to build sustainable production systems and review market strategies in response to changes in regional characteristics and demand.
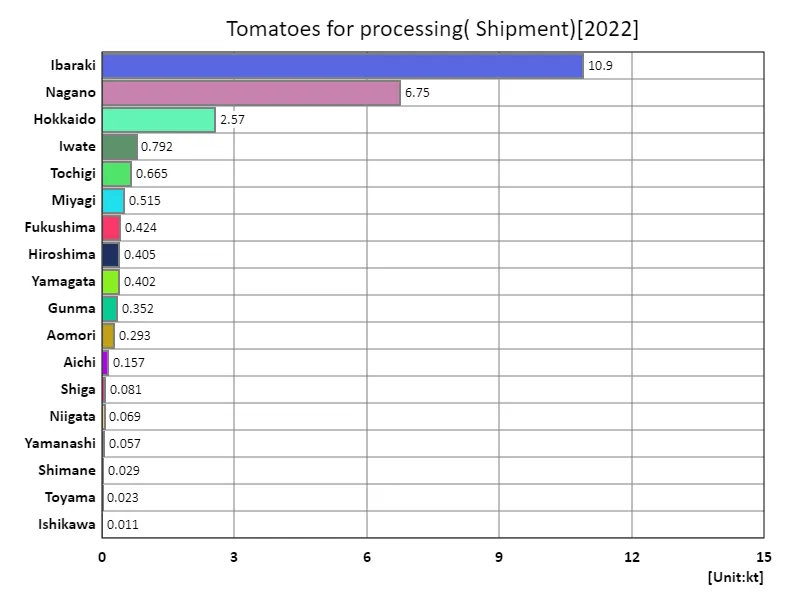

The maximum is 10.9kt of Ibaraki, the average is 1.36kt, and the total is 24.5kt



Comments