Abstract
Japan’s winter and spring bell pepper agriculture has maintained stable production volumes in recent years. The 2022 harvest is the largest nationwide at 78.9kt, indicating sustained productivity. The cultivated area was 746 hectares in the same year, demonstrating that it is cultivated over a wide area. Miyazaki in particular recorded the largest shipment volume of 23.5kt, and production in that area is attracting attention. This trend indicates the importance of bell pepper cultivation throughout Japan. Due to the stability of demand and the production characteristics of each region, it appears that each region is actively producing while making use of its respective strengths. It is expected that production of winter-spring peppers will continue in a sustainable manner, subject to changes in demand and weather conditions in the future.
Winter-spring pepper harvest yields (main data).
Japan’s winter and spring bell pepper farming has maintained stable production volumes for a long period of time. In particular, the harvest volume of 84kt recorded nationwide in 2002 was the highest ever recorded and represents a peak. However, current yields are slightly lower than the peak, remaining at 93.9%. This trend is likely due to overall changes in agriculture and fluctuations in demand. Climate conditions and advances in agricultural technology may also affect production volumes. On the other hand, demand for winter-spring peppers remains stable, and farmers are balancing production with demand. Under these circumstances, producers are striving to improve efficiency and quality, while also working to maintain sustainable production. Going forward, production of winter and spring peppers is expected to continue at a stable level while responding to changing demand and environmental factors.


The maximum is 84kt[2002] of Japan, and the current value is about 93.9%
Winter/spring bell pepper harvest volume (by prefecture).
Japan’s fruit vegetable harvest volume was compiled by prefecture for the latest year, 2022, with Miyazaki recording the highest harvest overall. This indicates that Miyazaki holds a leading position in fruit and vegetable production. Fruit and vegetable production varies between regions depending on factors such as climatic conditions and land use. It is also possible that productivity has improved due to advances in agricultural technology and the introduction of greenhouse cultivation. It is speculated that these factors were behind Miyazaki achieving the largest harvest. In addition, fruit vegetables are produced in other regions as well, and a supply system is in place to meet demand. This allows consumers to receive fruit and vegetables of consistent quality. It is important that each region continues to maintain appropriate production volumes in accordance with its own characteristics and changes in demand.


The maximum is 24.9kt of Miyazaki, the average is 2.8kt, and the total is 78.4kt
Area planted with winter/spring bell peppers (main data).
The area planted with winter and spring bell peppers in Japan has fluctuated over a long period of time. The peak cultivated area recorded nationwide was 926 hectares in 1978, and has been declining since then. The current cultivated area has fallen to 80.6% of its peak. This trend is thought to be due to structural changes in agriculture and fluctuations in demand. Depending on advances in agricultural technology and market demands, there may be a shift to other crops or the introduction of greenhouse cultivation. Additionally, climatic conditions and the characteristics of the production area can also affect the area under cultivation. Despite this, the area planted to winter and spring peppers remains above a certain level, and supply is meeting demand. Farmers aim to produce efficiently by responding flexibly to changes in demand trends and the market. It is expected that the area planted with winter and spring peppers will continue to be adjusted in line with changes in the agricultural structure and demand.


The maximum is 926ha[1978] of Japan, and the current value is about 80.6%
Areas planted for winter and spring bell peppers (by prefecture).
Japan’s area planted with fruit vegetables was compiled by prefecture for the latest year, 2022, with Ibaraki recording the largest area overall. This indicates that Ibaraki occupies a leading position in fruit vegetable cultivation. The cultivation of fruit vegetables is influenced by the climatic conditions and land use status of each region. The reason why Ibaraki has the largest cultivated area may be that the region’s climate and soil are suitable for growing fruit vegetables. It is also believed that the skills and experience of farmers in Ibaraki Prefecture are also behind the high productivity. On the other hand, fruit vegetables are also grown in other regions, and a supply system is in place to meet demand. This allows consumers to receive fruit and vegetables of consistent quality. It is important for each region to maintain an appropriate amount of cultivated land in accordance with its own characteristics and changes in demand. It is expected that the company will be able to continue to respond flexibly to changes in the characteristics and demand of local agriculture, and ensure a stable supply of fruit and vegetables.


The maximum is 236ha of Ibaraki, the average is 26.4ha, and the total is 739ha
Winter and spring bell pepper shipment volumes.
Japan’s winter/spring pepper shipments reached 74.1kt overall in 2022, the latest available year. Of these, Miyazaki recorded the largest shipment at 23.5kt. The average shipment volume was 2.65kt, with some regional variations but generally stable supplies. The reasons why Miyazaki has the largest shipping volume are likely due to the region’s high productivity, climatic conditions, and the technical skills of its farmers. In addition, demand for winter and spring peppers has remained above a certain level, which is also an important factor in maintaining shipping volumes. The development of a supply system that meets demand and improved quality control are factors that support stable shipping volumes. Since each region has different characteristics and production capacity, each region is required to efficiently maintain shipping volumes while balancing with demand. Going forward, efforts will be made to ensure sustainable shipments of winter and spring bell peppers, taking into account fluctuations in demand and the effects of weather conditions.
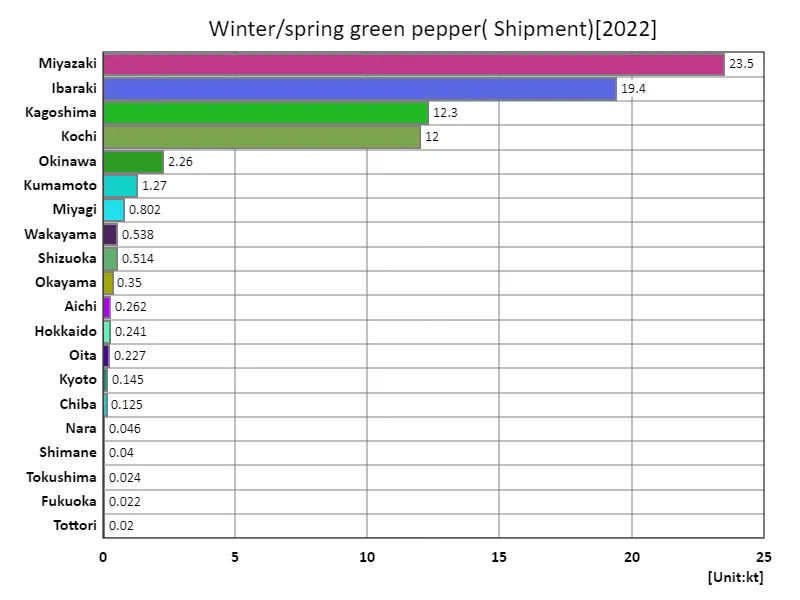

The maximum is 23.5kt of Miyazaki, the average is 2.65kt, and the total is 74.1kt



Comments