Abstract
Among the fruit vegetables in Japanese agriculture, immature corn (sweet corn) is attracting attention. According to 2022 data, the national harvest is 209kt and the cultivated area is 21.3kha. Hokkaido accounted for the largest shipment volume at 76.3kt. These figures indicate that immature corn production is stable nationwide, with Hokkaido being particularly central. Hokkaido is blessed with favorable climate and soil conditions, making it an ideal region for growing sweet corn. Although it is also produced in other regions, Hokkaido boasts an overwhelming amount of production. Due to increasing demand and technological advances, immature corn production is likely to continue to expand.
Green corn yield (main data).
Looking at data from 1973 to 2022, Japan’s immature corn (sweet corn) yields show fluctuations. The highest level was recorded nationwide in 1990 at 409 kt, but has been declining since then, reaching 209 kt in 2022, which is 51.1% of the peak level. The reasons behind this decline are thought to be changes in the structure of agriculture, changes in economic conditions, and changes in consumer preferences. In recent years, there has been growing awareness of food safety and health, and demand for pesticide-free and organic farming has increased, but this may also be contributing to a decrease in production. Other factors that could affect the results include climate change and natural disasters. Considering these factors, immature corn yields are likely to remain variable in the future. It is expected that agricultural policies and technological advances will contribute to stabilizing and increasing yields.
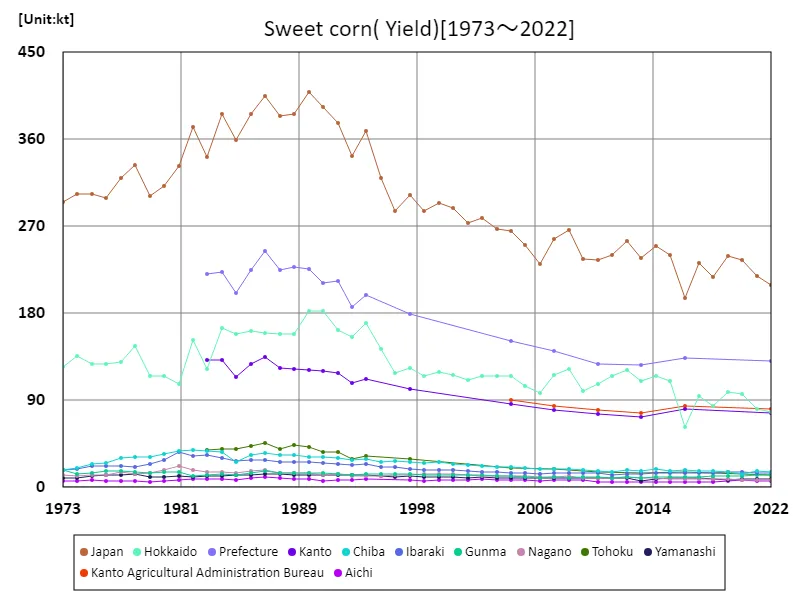

The maximum is 409kt[1990] of Japan, and the current value is about 51.1%
Green corn harvest volume (by prefecture).
According to data for 2022, Hokkaido recorded the highest fruit vegetable harvest in Japan at 78.1kt. This is the highest value ever recorded, indicating that Hokkaido is a center for fruit and vegetable production. Hokkaido has vast farmland, abundant water sources and diverse climatic conditions, making it an ideal environment for cultivating fruit and vegetables. Additionally, Hokkaido has the largest harvest of fruit and vegetables overall, which is an indication of its high productivity. On the other hand, fruit vegetables are also cultivated in other regions, and each region has its own characteristics. For example, apple cultivation is popular in areas such as Aomori and Yamagata prefectures, and the associated fruit vegetable yields also tend to be high. Additionally, in warmer regions, greenhouse cultivation of tomatoes, cucumbers, and other crops is popular, and the yields are unique to that region. Fruit vegetable yields vary depending on local climatic conditions, agricultural techniques, agricultural policies, etc. Changes in demand and international competition also play a role and are factors that lead to fluctuations in production volumes. It is expected that in the future, cultivation that makes use of the characteristics of each region and the promotion of sustainable agriculture will have an impact on fruit and vegetable harvests.
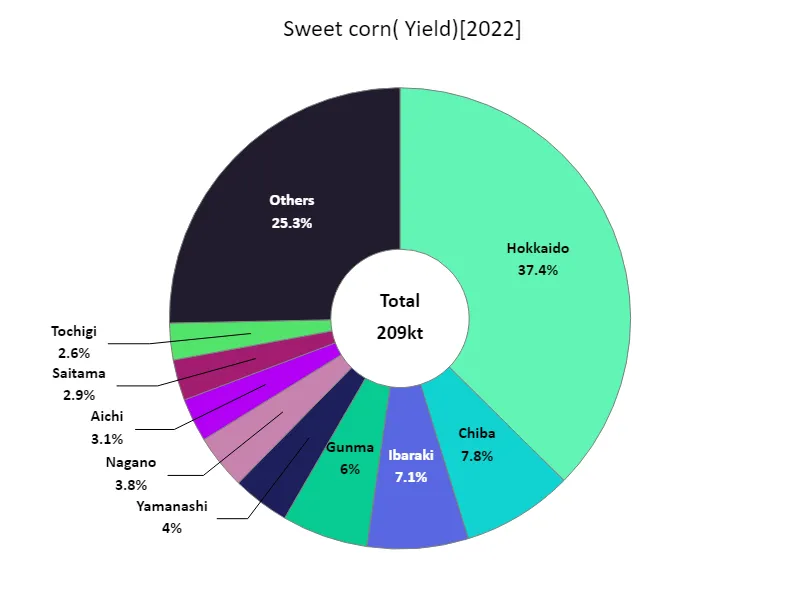

The maximum is 78.1kt of Hokkaido, the average is 4.44kt, and the total is 209kt
Area planted to green corn (main data).
Looking at data from 1973 to 2022, the area of land planted with immature corn (sweet corn) in Japan shows fluctuations. The maximum value recorded nationwide was 39.5kha in 1987, but it has been declining since then. As of 2022, the area under cultivation will be 53.9% of its peak. The reasons behind this decline are thought to be changes in the structure of agriculture, changes in economic conditions, and changes in consumer preferences. In recent years, there may be a shift to other crops due to food diversification and changes in demand. In addition, advances in agricultural technology and increased efficiency have made it possible to achieve greater yields from the same area, and this impact is also taken into consideration. On the other hand, sweet corn is in high demand during the summer months and is popular with consumers. Therefore, changes in demand and responding to demand can affect acreage. The impact of climate change and natural disasters are also factors to consider. Considering these factors, sweet corn acreage is likely to fluctuate in the future. Agricultural policies, demand trends and climatic conditions will be factors that will affect the area planted.
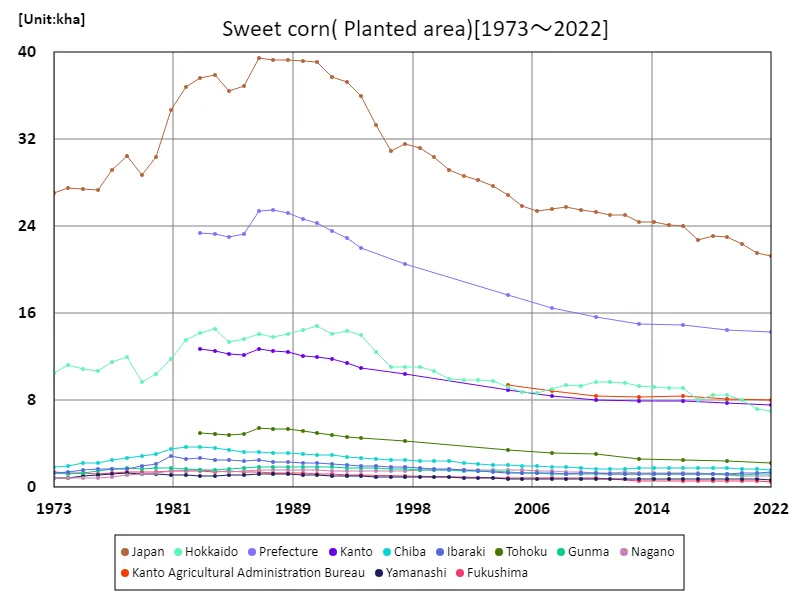

The maximum is 39.5kha[1987] of Japan, and the current value is about 53.9%
Area planted with green corn (by prefecture).
According to data from 2022, Hokkaido has the largest area of land cultivated with fruit vegetables in Japan, at 7.04kha. This is the highest value ever recorded and indicates that Hokkaido is a center for fruit and vegetable cultivation. Hokkaido has vast farmland, abundant water sources and diverse climatic conditions, making it an ideal environment for cultivating fruit and vegetables. Additionally, Hokkaido has the largest area of land cultivated with fruit vegetables in the world, which indicates its high productivity. On the other hand, fruit vegetables are also cultivated in other regions, and each region has its own characteristics. For example, apple cultivation is popular in areas such as Aomori and Yamagata prefectures, and the area of land planted to fruit vegetables also tends to be large. In addition, in warmer regions, greenhouse cultivation of tomatoes, cucumbers, and other crops is popular, and the area of land used for cultivation is specific to each region. The area of land cultivated with fruit vegetables fluctuates depending on local climatic conditions, agricultural techniques, agricultural policies, etc. Changes in demand and international competition also play a role, contributing to fluctuations in acreage. It is expected that in the future, cultivation methods that take advantage of the characteristics of each region and the promotion of sustainable agriculture will have an impact on the area of fruit and vegetable cultivation.
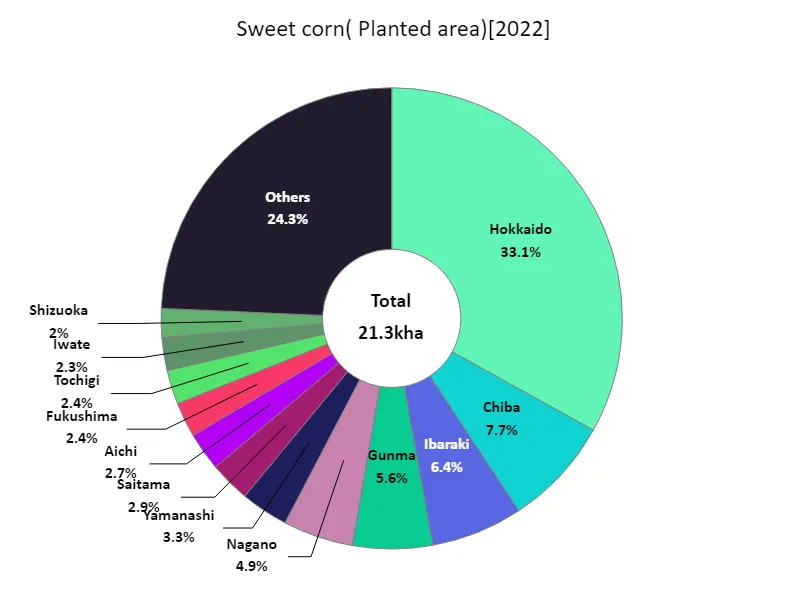

The maximum is 7.04kha of Hokkaido, the average is 453ha, and the total is 21.3kha
Shipment volume of green corn.
In 2022, the largest shipment volume of immature corn (sweet corn) in Japan was 76.3kt in Hokkaido, with an average of 3.67kt, and a total of 173kt. These figures clearly show that Hokkaido is a major shipping area for immature corn. Hokkaido has vast farmland and suitable climate conditions, making it an ideal environment for growing sweet corn. Sweet corn shipments are generally related to demand. Sweet corn is in high demand during the summer, and Hokkaido’s productivity helps meet that demand. Furthermore, Hokkaido’s sweet corn is of high quality and meets demand nationwide. The average shipping volume of 3.67kt suggests that a certain amount of production is taking place in areas other than Hokkaido, but Hokkaido’s production volume is particularly outstanding. In regions outside Hokkaido, production volumes are likely to vary depending on climatic conditions and regional characteristics. In the future, factors such as shifting demand and changing weather conditions will affect sweet corn shipments. Agricultural policies and technological advances are expected to be important factors in sweet corn production and shipping.
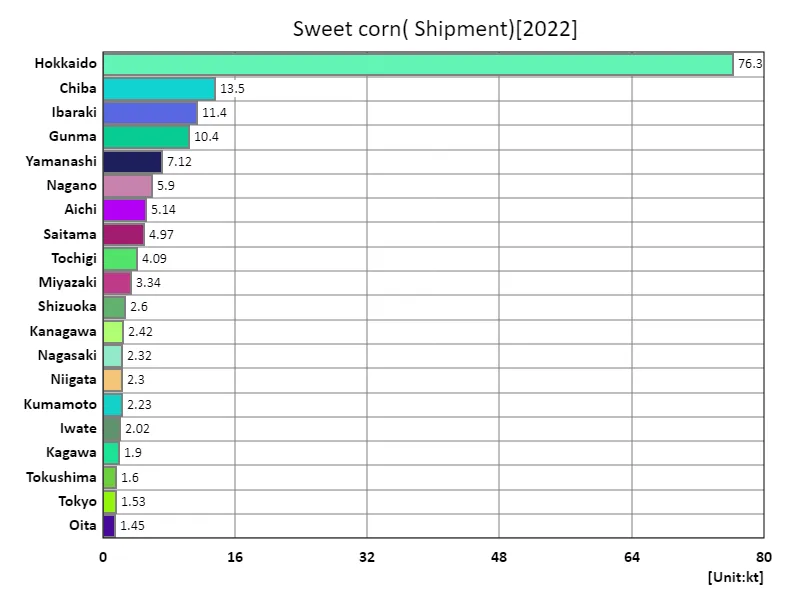

The maximum is 76.3kt of Hokkaido, the average is 3.67kt, and the total is 173kt



Comments