Abstract
Data on root crops in Japanese agriculture, particularly potatoes, shows that the 2022 harvest volume nationwide will be 2.28Mt, with the maximum cultivated area being 71.4kha, and the maximum shipping volume being 1.62Mt in Hokkaido. The trends and characteristics that can be inferred from these figures are that Hokkaido is a major potato producing area, and its shipping volume accounts for a large proportion of the national total. In addition, potato production volume and cultivated area are relatively large when viewed nationwide. For this reason, potatoes occupy an important position in Japan’s root vegetable market, and Hokkaido can be said to be the center of potato production.
Potato harvest yield (main data).
Looking at data on potato harvests in Japan from 1973 to 2022, the peak was recorded in 1986, with 4.07Mt recorded nationwide. However, current yields have fallen to just 56.1% of their peak. This trend suggests that potato production is declining compared to its peak. This is due to a variety of agricultural factors, including a decline in farmland, labor shortages, and climate change. Changes in demand for other agricultural and food products may also be affecting potato production. Given this background, potato production in Japan is declining from its peak and it is necessary to adapt to sustainable production methods and market demand.
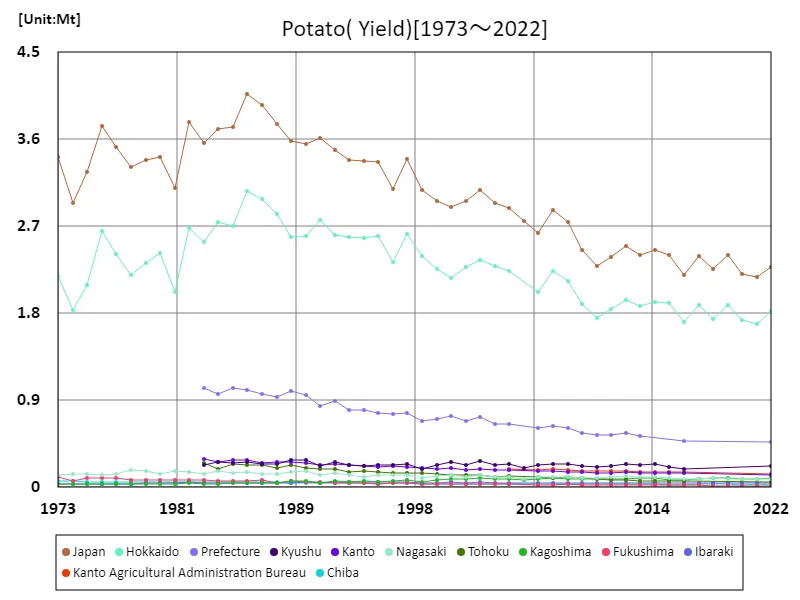

The maximum is 4.07Mt[1986] of Japan, and the current value is about 56.1%
Potato harvest volume (by prefecture).
The latest data for root crop yields in Japan for 2022 shows Hokkaido recorded the highest overall yield of 1.82Mt, which is currently the highest. This clearly shows that Hokkaido is the center of root vegetable production in Japan. Hokkaido has vast farmland and suitable climatic conditions, making it ideal for growing root vegetables. Hokkaido is also advanced in terms of technology and facilities, enabling efficient production. On the other hand, root vegetable yields in other regions tend to be lower than in Hokkaido. This is due to differences in regional climatic conditions, land constraints, and agricultural technology levels. For Japan as a whole, root vegetable harvests depend heavily on production in Hokkaido, with Hokkaido’s production volume determining the overall trend. In the future, it will be necessary to improve production methods that take advantage of the characteristics of each region and disseminate the technology.
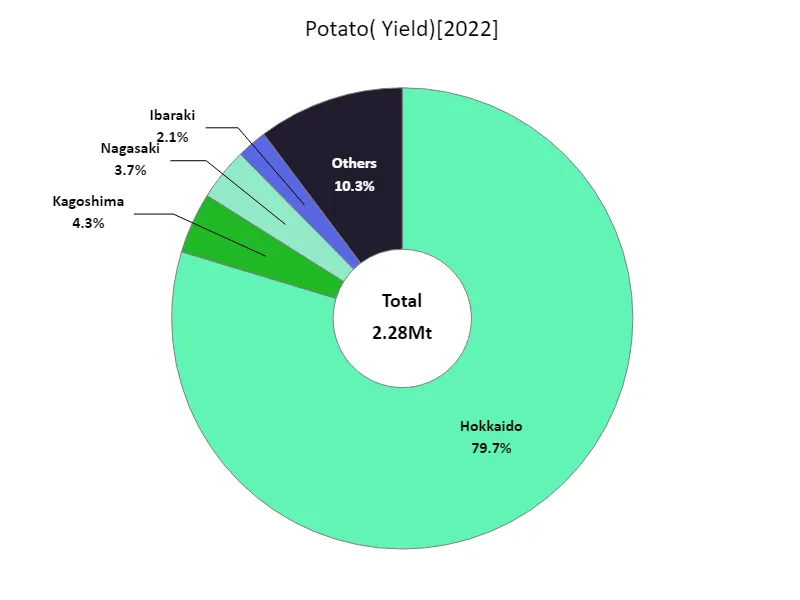

The maximum is 1.82Mt of Hokkaido, the average is 48.6kt, and the total is 2.28Mt
Potato cultivation area (main data).
Looking at data on potato cultivation area in Japan from 1973 to 2022, the peak was recorded in 1973 at 147kha nationwide. However, the current area under cultivation has fallen to just 48.5% of its peak. This trend suggests that the area under potato cultivation is decreasing compared to the past. This decline is believed to be due to a variety of agricultural factors. For example, there are reductions in farmland due to urbanization and industrialization, a decrease in the agricultural labor force, and changes in agricultural policies. Additionally, shifts to other crops and changes in demand may also be contributing to the decline in planted area. Under these circumstances, potato producers and stakeholders need to consider sustainable production methods and cultivation plans that meet demand. It is also important to establish a production system that suits the characteristics and demand of each region.
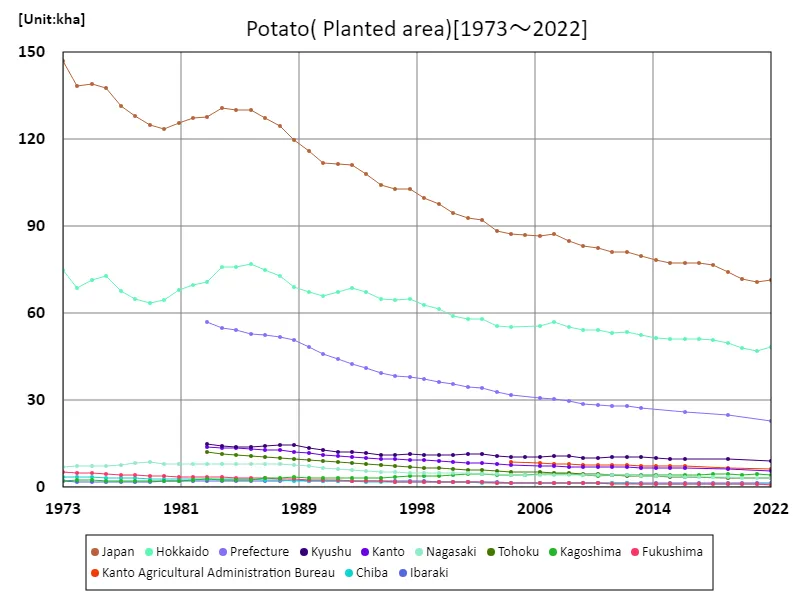

The maximum is 147kha[1973] of Japan, and the current value is about 48.5%
Potato cultivation area (by prefecture).
According to data from 2022, the largest area cultivated with root vegetables in Japan is Hokkaido, at 48.5kha. This is the highest value compared to past data, indicating that Hokkaido is a major producer of root vegetables. Hokkaido has vast farmland and a relatively cool climate, making it ideal for growing root vegetables. Additionally, Hokkaido’s agricultural techniques and facilities are advanced, enabling efficient production. On the other hand, the area cultivated with root vegetables in other prefectures tends to be lower than in Hokkaido. This is due to the climatic conditions, land constraints, and agricultural characteristics of each region. For example, growing root crops may be constrained in warmer regions. Additionally, the decline in cultivated area may also be due to the reduction in agricultural land caused by urbanization and industrialization. Generally speaking, root vegetables are produced mainly in Hokkaido, while other regions develop their own agricultural methods according to their respective characteristics. In the future, there will be a need to promote production methods that make use of the characteristics of each region and sustainable agriculture.
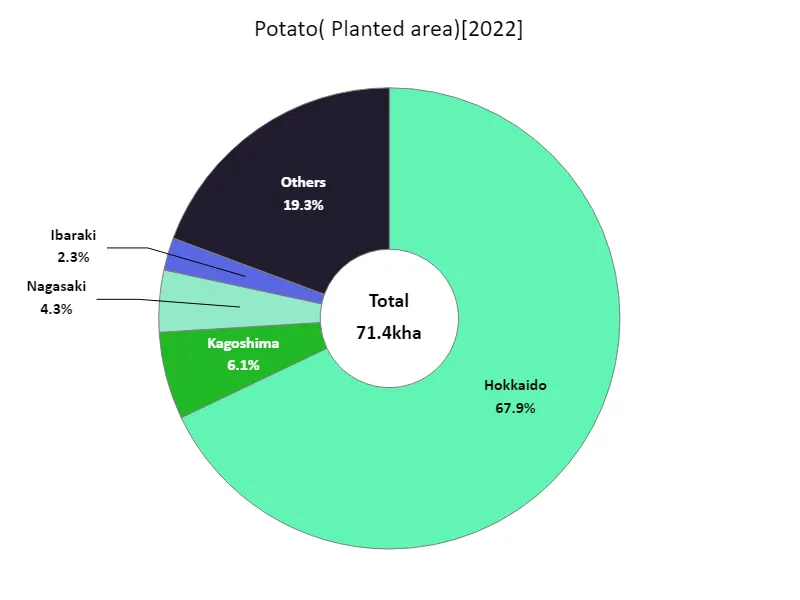

The maximum is 48.5kha of Hokkaido, the average is 1.52kha, and the total is 71.4kha
Potato shipment volume.
According to data for 2022, Japan’s total potato shipments were 1.93 Mt, of which Hokkaido accounted for 1.62 Mt. With the largest shipment volume, Hokkaido is clearly the major producer of potatoes. Hokkaido has vast farmland and suitable climatic conditions, making it ideal for potato production. Hokkaido also has advanced agricultural techniques and equipment, allowing for efficient production. On the other hand, Japan’s total shipping volume is 1.93 Mt, with Hokkaido’s production accounting for the majority of the total. While this indicates Hokkaido’s high productivity, it also shows that production in other regions is relatively low. Potato production varies by region due to the climatic conditions and agricultural characteristics of each region. In general, potatoes are produced mainly in Hokkaido, which accounts for the majority of the total shipment volume. In areas outside of Hokkaido, cultivation takes advantage of the characteristics of each region, but production volumes tend to be relatively low. In the future, there will be a need to promote sustainable agriculture that makes use of the characteristics of each region and improve productivity.
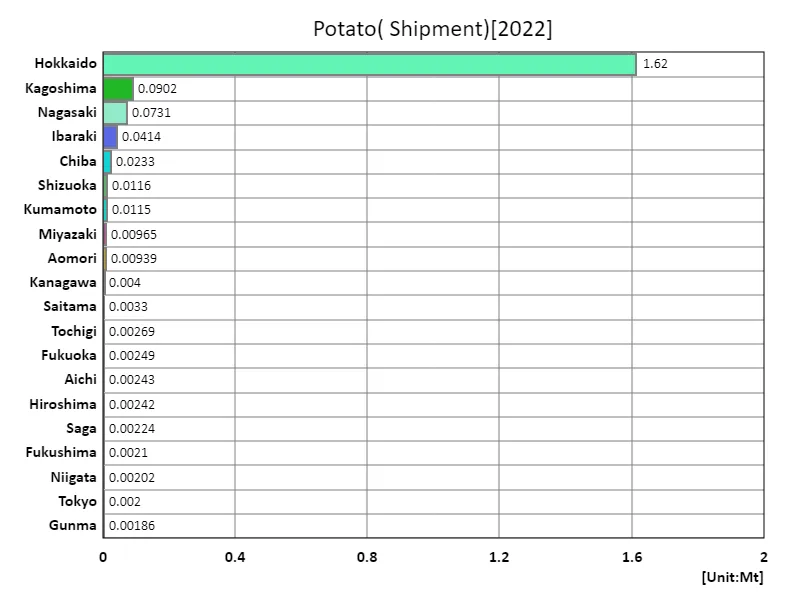

The maximum is 1.62Mt of Hokkaido, the average is 41.1kt, and the total is 1.93Mt



Comments