Abstract
Looking at data on leafy vegetables in Japanese agriculture, the nationwide harvest volume in 2022 was 1.22 Mt, and the cultivated area was 25.2 kha. Hokkaido had the highest shipping volume at 773kt. These figures suggest that the cultivation of leafy vegetables is thriving throughout Japan, with Hokkaido being one of its centers. Since Hokkaido far surpasses other regions in terms of shipping volume, it is possible that the region has advanced cultivation and harvesting techniques, and that its climate and land conditions are suitable. However, it is also cultivated in other regions, and it is assumed that each region has its own varieties and production styles suited to its characteristics and demand. Overall, the results suggest that leafy vegetable cultivation is an important agricultural activity throughout Japan, with regional characteristics and competitiveness existing.
Onion harvest yield (main data).
Onion yields in Japanese agriculture have changed between 1973 and 2022. At its peak in 1992, the national harvest reached 1.4Mt, but currently it is only 87.3% of that peak. This suggests that onion production is below peak levels. Possible factors behind this trend include technological innovations in agriculture, changes in production systems, and the influence of climatic conditions. Changes in demand and domestic and international competitive conditions may also be contributing factors. On the other hand, onion farming in Japan has had a stable foundation for many years and appears to be important to producers and related industries. In the future, there will be a demand for sustainable production methods and the development of varieties that meet demand.
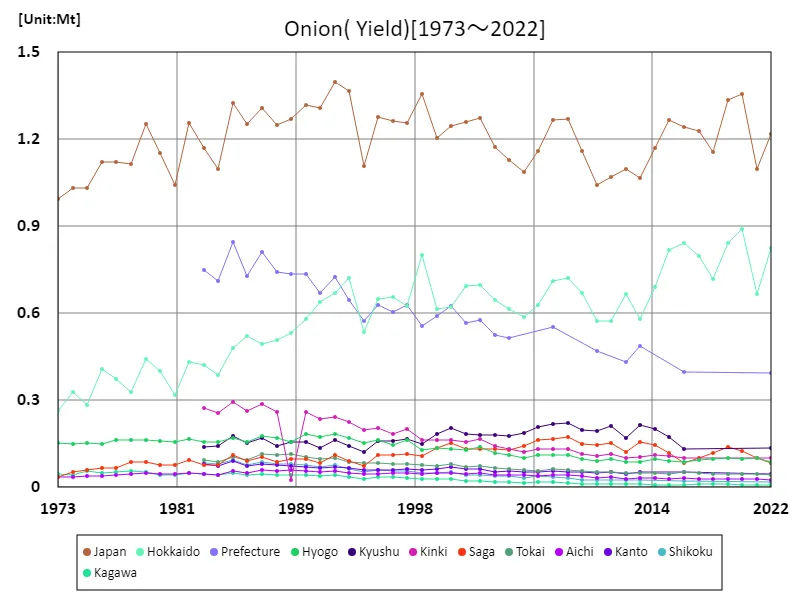

The maximum is 1.4Mt[1992] of Japan, and the current value is about 87.3%
Onion harvest volume (by prefecture).
According to data for 2022, Hokkaido recorded the highest yield of leafy vegetables in Japanese agriculture at 826kt, the highest overall. This suggests that Hokkaido is the leading region in Japan for leafy vegetable production. Hokkaido has vast farmland and abundant water sources, and its climatic conditions are suitable for cultivation, so it tends to produce high yields. On the other hand, leafy vegetables are also produced in other regions, but the scale and yields are likely to be smaller than in Hokkaido. Additionally, there are differences in the varieties and production techniques cultivated in each region, which may affect yields. In general, Hokkaido is the main region for leafy vegetable production, and there are differences with other regions.
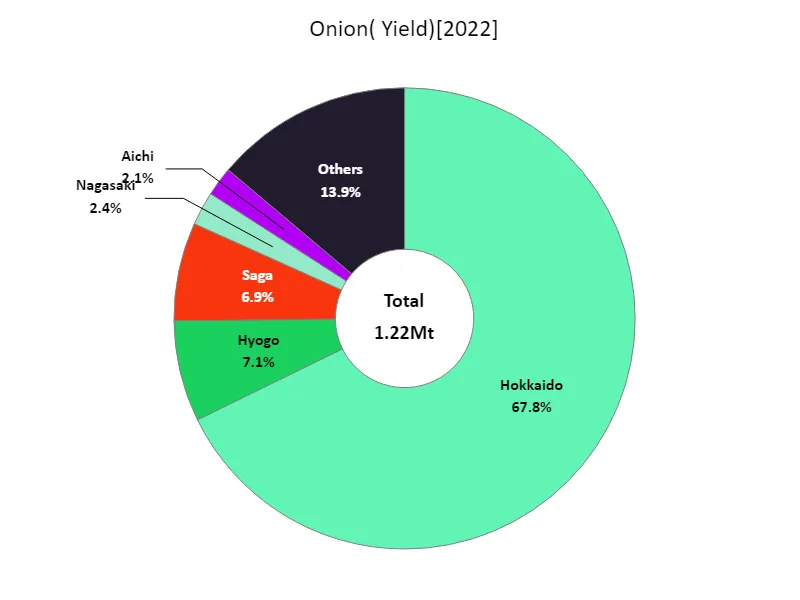

The maximum is 826kt of Hokkaido, the average is 25.9kt, and the total is 1.22Mt
Area cultivated with onions (main data).
The area of land area cultivated with onions in Japanese agriculture has fluctuated between 1973 and 2022. At its peak in 1985, the entire country recorded 30.8kha, but the current area is equivalent to 81.8% of the peak. This trend suggests that onion production is below peak levels. Possible factors behind this include structural changes in agriculture, changes in demand, and the effects of climatic conditions. Competition from other crops and the impact of imports may also be contributing factors. On the other hand, onions are an essential ingredient in the Japanese diet and there is stable demand, so they remain an important crop for producers. In the future, it will be necessary to review production systems in response to changes in demand and the competitive situation both domestically and internationally.
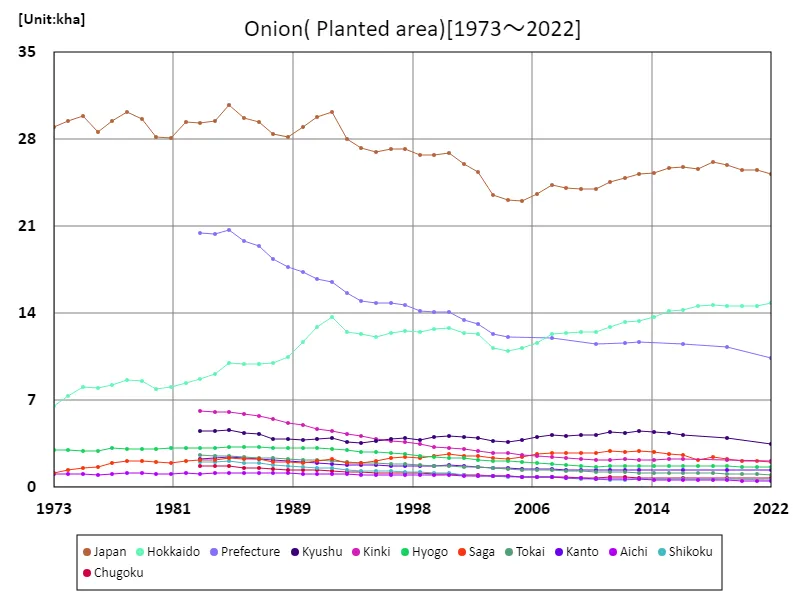

The maximum is 30.8kha[1985] of Japan, and the current value is about 81.8%
Onion cultivation area (by prefecture).
According to data from 2022, Hokkaido had the largest area of land planted to leafy vegetables in Japanese agriculture, at 14.8 kha, the largest overall. This suggests that Hokkaido is the leading region in Japan for the cultivation of leafy vegetables. Hokkaido has vast farmland and abundant water sources, and its climatic conditions are suitable for cultivation, so the area under cultivation tends to be large. On the other hand, leafy vegetables are also cultivated in other regions, but the scale and area of cultivation may be smaller than in Hokkaido. Differences in varieties and production techniques cultivated in each region may also affect the area planted. In general, it can be said that Hokkaido is the main region for the cultivation of leafy vegetables, and there are differences with other regions.
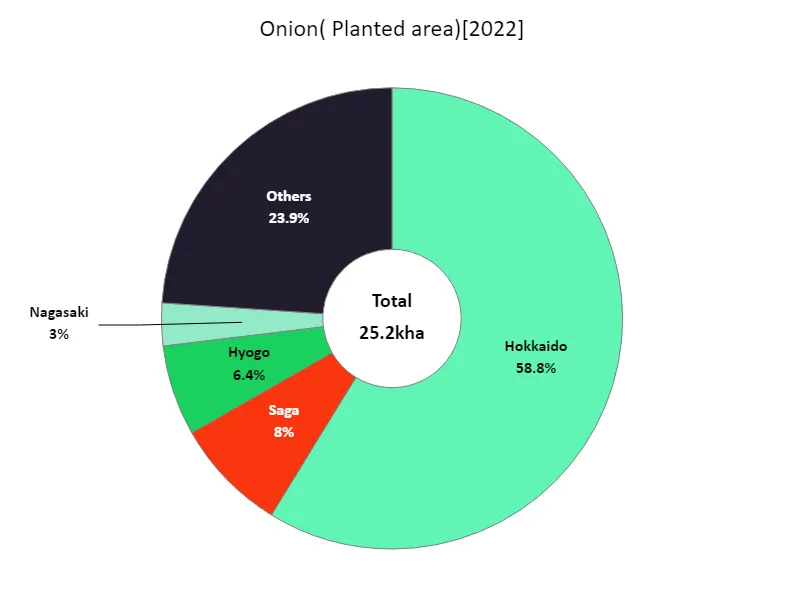

The maximum is 14.8kha of Hokkaido, the average is 536ha, and the total is 25.2kha
Onion shipment volume.
According to data for 2022, the total volume of onion shipments in Japanese agriculture is 1.1 Mt, of which Hokkaido accounts for 773 Mt. Hokkaido has the largest overall shipping volume, which shows that this region is the main onion producing area in Japan. Additionally, the overall average shipping volume is 23.5kt, which shows that Hokkaido’s shipping volume is extremely large. Hokkaido’s rich soil and suitable climatic conditions are thought to be ideal for onion production. On the other hand, onions are also produced in other regions, but the scale and shipping volumes are likely to be smaller than in Hokkaido. Additionally, changes in demand and domestic and international competitive conditions are also factors that affect shipping volumes. Overall, this suggests that Hokkaido is the main onion producing region in Japan and that there are differences with other regions.
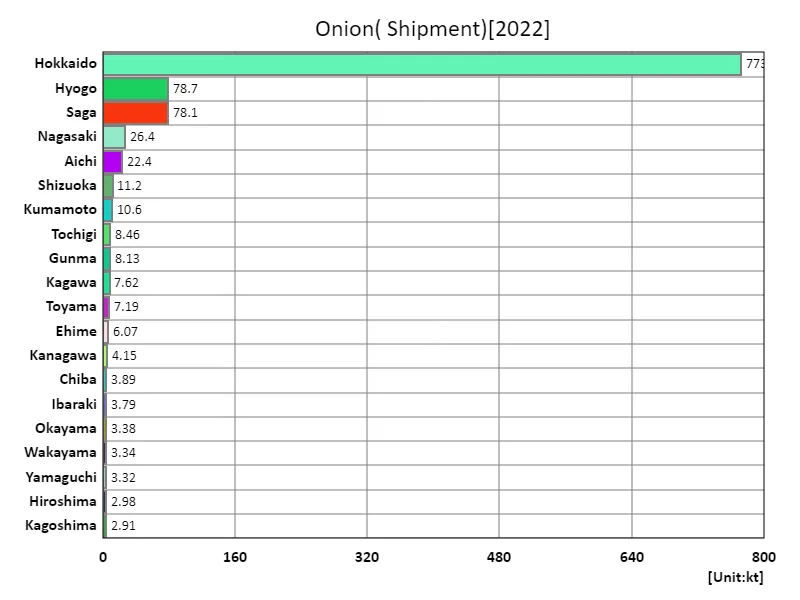

The maximum is 773kt of Hokkaido, the average is 23.5kt, and the total is 1.1Mt



Comments