Abstract
Vegetable production and imports are important topics in Japanese agriculture. According to 2022 data, the price of domestic snow peas was 1,160 yen per kg, while imported whole peas were 971 yen. Based on this difference, it is possible that the supply of domestically produced snow peas is insufficient compared to demand, which is leading to higher prices. On the other hand, the supply and demand of imported peas is well balanced and prices are thought to be relatively stable. For Japanese agriculture, it is important to strike a balance between improving domestic productivity and relying on imports. This data can suggest the balance between supply and demand in the market and influence agricultural policies and production planning.
Domestic prices of pulses
Vegetable production and prices in Japanese agriculture show certain trends and fluctuations. Looking at data from 2004 to 2022, the prices of domestically produced vegetables have fluctuated but generally show an upward trend. In particular, in 2016, the price of snow peas peaked at 1,420 yen/kg, but subsequent data shows that it has fallen to 81.9% of the peak price. This decline is likely due to an increase in supply and changes in demand. As a general trend, advances in agricultural technology and improvements in production efficiency have led to increased production of some vegetables, which is acting as a suppression factor for prices. Changes in demand also affect prices, and changes in consumer tastes and lifestyles can be reflected in fluctuations in vegetable prices. These characteristics and trends are an important source of information for understanding Japan’s agricultural policies and market trends.
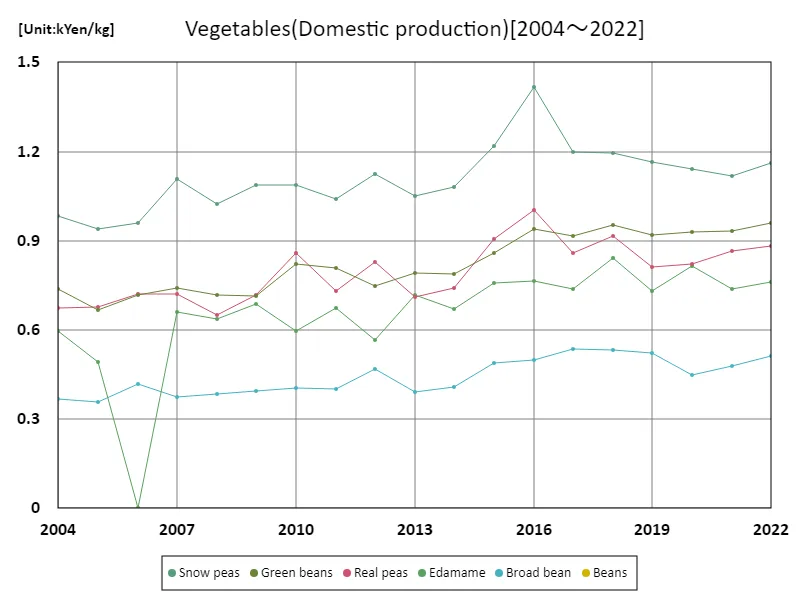

The maximum is 1.42kYen/kg[2016] of Snow peas, and the current value is about 81.9%
Import prices of pulses
Looking at data by prefecture for Japan’s vegetable import market in 2022, the highest overall was for peas at 971 yen/kg, which is recorded as the current value. Based on this data, it is possible that the prices of imported vegetables are relatively high. This is thought to be due to factors affecting the supply and demand balance, such as increased demand for vegetables from overseas or restrictions on supply. Japan’s vegetable import market is closely related to domestic production volumes, which are affected by the seasons and weather, so the balance between supply and demand is important. Fluctuations in currency exchange rates and international trade relations may also affect prices. Taking these factors into consideration, it is important to understand the characteristics and trends of the imported vegetable market in order to formulate agricultural policies and make market forecasts.
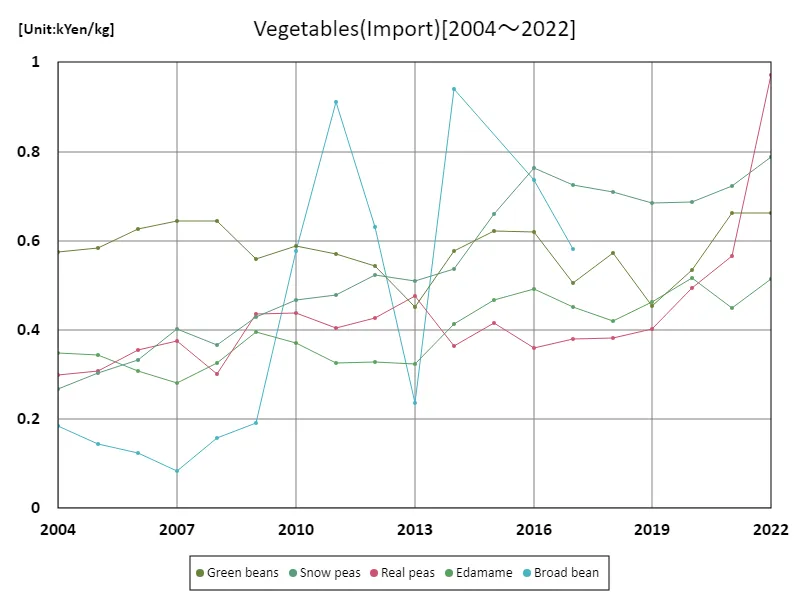

The maximum is the latest one, 971Yen/kg of Real peas



Comments