Abstract
Japan’s agricultural vegetable market consists of both domestically produced and imported produce. According to data for 2022, the price of domestic vegetables is up to 233 yen/kg, while the price of imported vegetables is up to 300 yen/kg. Based on past trends, domestically grown vegetables are relatively inexpensive and are produced to meet local demand. On the other hand, imported vegetables are expensive and are mainly introduced to complement seasons or varieties that are in high demand. Japanese agriculture cultivates a wide variety of vegetables according to the local climate and seasonality, while also importing them to meet domestic demand. The price difference between the two is thought to be due to factors such as domestic production costs, transportation costs, and tariffs. Domestic vegetables meet the demand for quality and stability, while imported vegetables provide diversity and meet fluctuations in demand.
Domestic price of vegetable scale
The prices of domestically produced vegetables in Japanese agriculture have fluctuated from 2005 to 2022. In 2016, the vegetable price peaked at 238 yen/kg, but has since been on a downward trend, currently falling to 97.9% of its peak. This trend is influenced by technological innovation and efficiency improvements in agriculture, increased production, and changes in consumer values. Additionally, domestic and international economic and weather conditions also affect prices. In general, prices of domestically produced vegetables have remained stable compared to peak periods, with supply and demand maintaining a balance. Due to consumers’ health consciousness and the promotion of local production and consumption, local cultivation and the use of direct sales outlets are increasing, and interest in locally grown vegetables is also growing. These factors enable domestically produced vegetables to be provided to consumers at stable prices, while also contributing to improving farmers’ incomes and production environments.
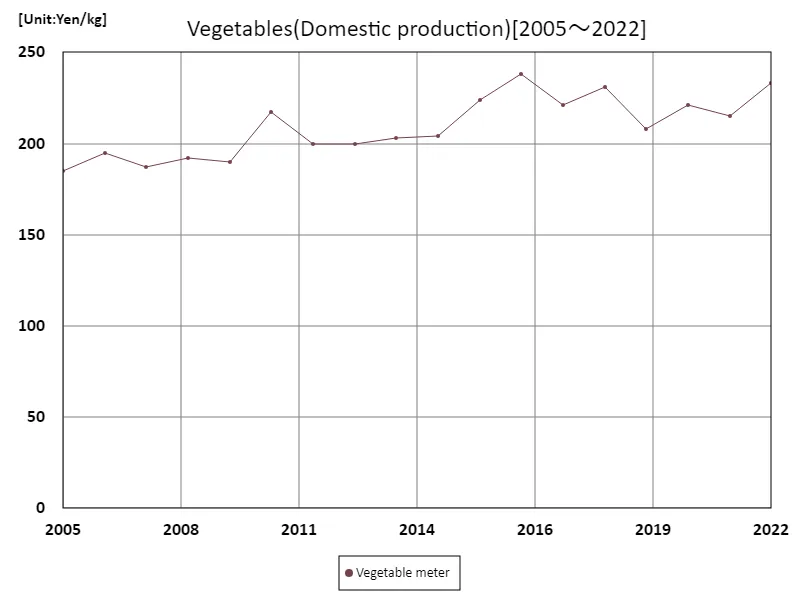

The maximum is 238Yen/kg[2016] of Vegetable meter, and the current value is about 97.9%
Import price of vegetable scale
Japan’s vegetable import market hit an overall high of 300 yen/kg in 2022. This figure is the highest compared to past data, indicating an increasing demand for imported vegetables. The increasing demand for imported vegetables may be due to a demand for diverse varieties or out-of-season vegetables, or a demand to supplement domestic production shortages with foreign vegetables. Japan’s imported vegetable market is dominated by imports from Asian countries and Europe, providing high-quality vegetables to consumers. With the prices of imported vegetables now at their highest, domestic consumers are demonstrating demand for higher priced imported vegetables, which could lead to changes in the structure of Japan’s agricultural market. On the one hand, while an increase in imported vegetables brings about tougher competition for domestic agricultural producers, it also has the advantage of expanding consumer choices and improving food diversity through the supply of a wider variety of vegetables.
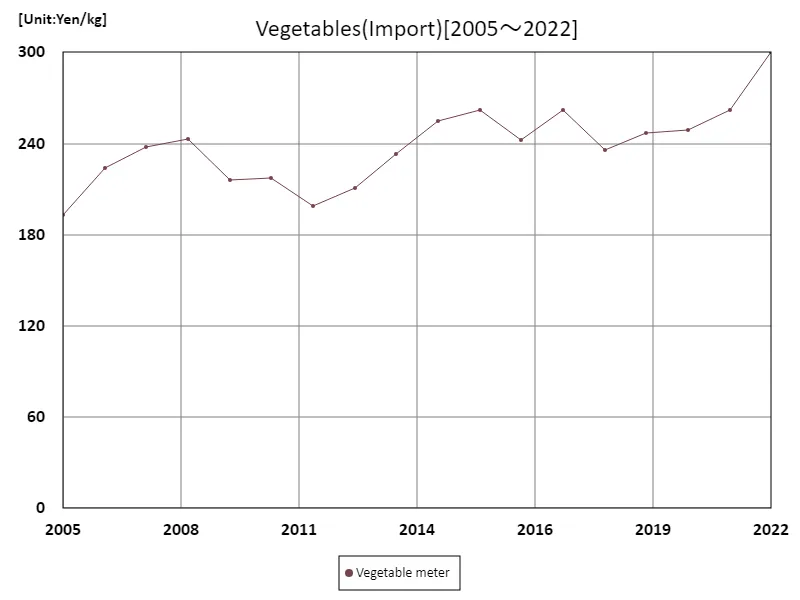

The maximum is the latest one, 300Yen/kg of Vegetable meter



Comments