Abstract
Root vegetables are one of the important crops in Japanese agriculture, and autumn-planted potatoes in particular are attracting attention. According to data for 2022, the maximum yield was 38.3kt in the prefectures, and the maximum cultivated area was 2.26kha. As these figures show, root vegetable cultivation is widespread, with prefectures playing a particularly important role. On the other hand, the largest shipping volume was in Nagasaki at 15kt, suggesting that shipments are made according to regional productivity and demand. Root vegetable production also contributes to the local economy, and these figures show the importance of root vegetables in Japanese agriculture and sustainable production practices.
Autumn-planted potato yield (main data).
The yield of autumn-planted potatoes in Japanese agriculture has fluctuated between 1983 and 2022. Particularly noteworthy is the peak in 1986, when the prefecture’s harvest reached 93.1kt. However, trends have fluctuated since then, with current harvest volumes remaining at just 41.1% of the peak. This suggests that there are a range of factors influencing root crop production, which may include changes in agronomy and fluctuating climatic conditions. Additionally, the decline in yields is likely due to factors such as changes in agricultural policies and technology across prefectures, which may affect future root crop production.
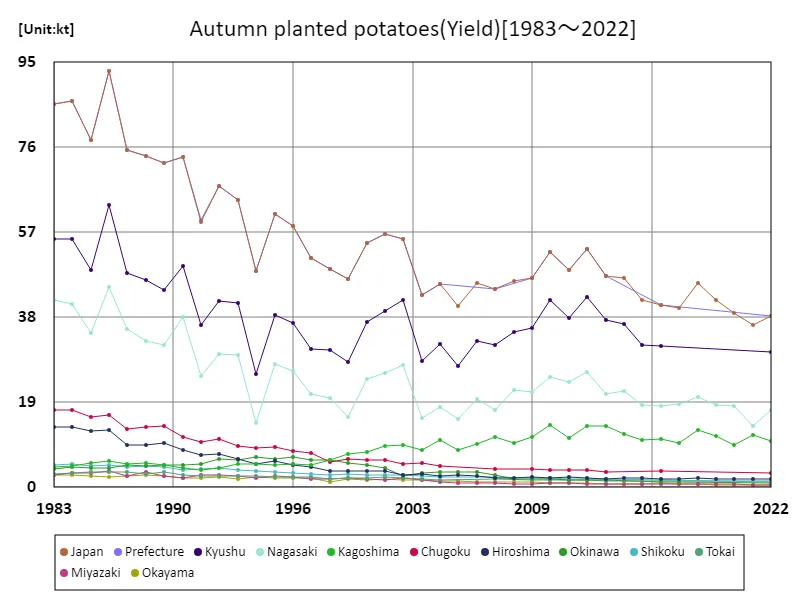

The maximum is 93.1kt[1986] of Japan, and the current value is about 41.1%
Autumn-planted potato harvest volume (by prefecture).
Root vegetable harvests in Japan are compiled by prefecture, according to the latest data for 2022. What is noteworthy here is that Nagasaki recorded the highest number overall. Nagasaki’s harvest of 17.3kt surpasses all other regions and is currently the largest. This indicates that Nagasaki plays an important role in the production of root vegetables. This data also shows that Nagasaki has high agricultural technology and productivity. On the other hand, it is not clear how much the harvest yields in other regions differ compared to Nagasaki, but it is possible that differences in regional climatic conditions and agricultural policies are influencing this. Overall, Nagasaki is the top producer of root vegetables, so regional production disparities and efforts to improve productivity will continue to be important issues.
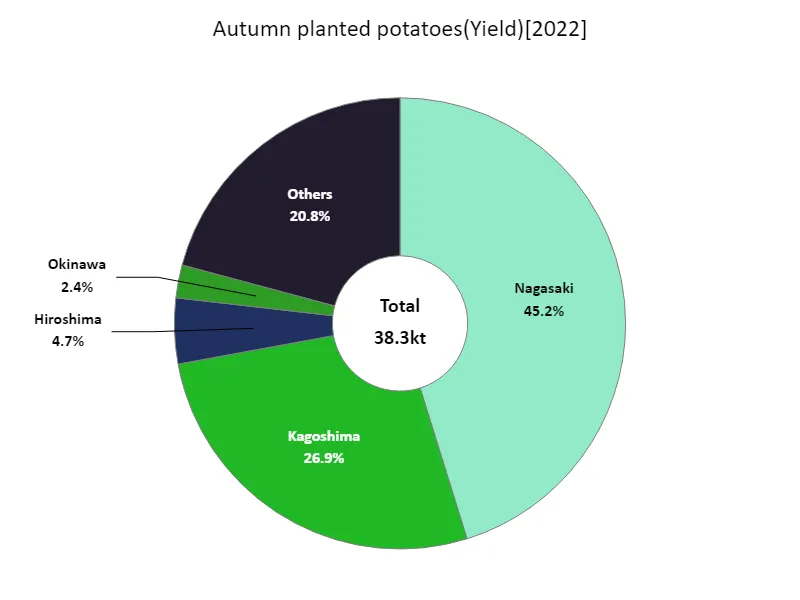

The maximum is 17.3kt of Nagasaki, the average is 1.03kt, and the total is 38.3kt
Area of potato cultivation planted in autumn (main data).
The area of land planted with autumn-planted potatoes in Japanese agriculture has fluctuated between 1983 and 2022. Particularly noteworthy is the peak in 1983, when the cultivated area in the prefecture reached 5.52 kha. However, trends have fluctuated since then, with the current cultivated area remaining at only 40.9% of the peak. This suggests that changes in agricultural structure and demand, as well as fluctuating climatic conditions, may be affecting the area planted. Additionally, the decline from the peak is likely due to factors such as changes in agricultural policies and technology across prefectures, and these factors may also affect the cultivation area of root vegetables in the future. In general, changes in cultivated area are influenced by agricultural conditions and socio-economic factors, and it is expected that regional agricultural policies and the direction of technological innovation will affect the cultivated area of root crops in the future.
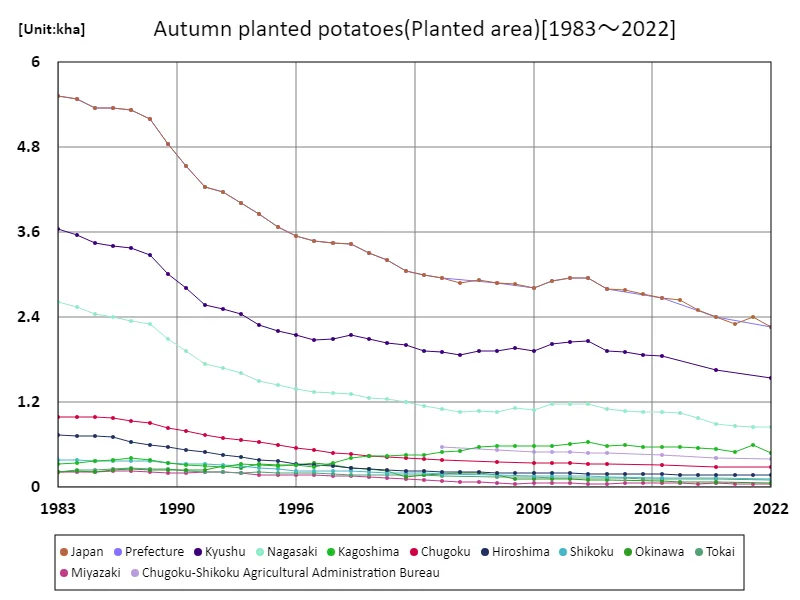

The maximum is 5.52kha[1983] of Japan, and the current value is about 40.9%
Area planted with autumn-planted potatoes (by prefecture).
The area cultivated with root vegetables in Japan is calculated by prefecture, according to the latest data for 2022. What is noteworthy here is that Nagasaki recorded the highest number overall. Nagasaki’s cultivated area of 847 hectares is the largest at present, surpassing any other region. This indicates that Nagasaki plays an important role in the cultivation of root vegetables. This data also reveals Nagasaki’s fertile soil and climatic conditions as an agricultural region, as well as the development of agricultural technology. On the other hand, it is not clear to what extent the cultivated area in other regions differs compared to Nagasaki, but it is possible that this is due to factors such as differences in land use characteristics and agricultural policies in each region. Overall, Nagasaki ranks first in terms of the area planted with root vegetables, so disparities in cultivated areas between regions and efforts to improve productivity will likely continue to be important issues in the future.
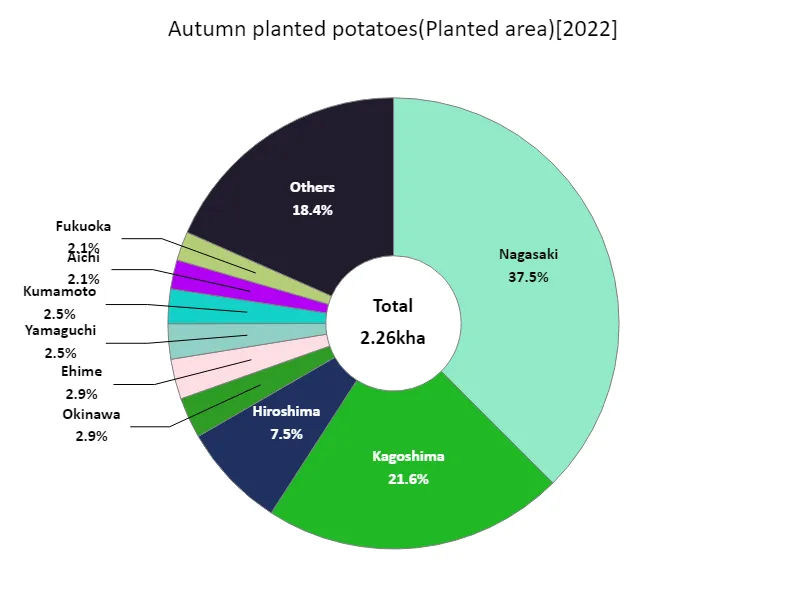

The maximum is 847ha of Nagasaki, the average is 61ha, and the total is 2.26kha
Shipping volume of autumn-planted potatoes.
According to the latest data for 2022, the overall shipment volume of autumn-planted potatoes in Japanese agriculture was highest in Nagasaki at 15kt, with an average of 802t and a total of 29.7kt. These figures show that root vegetable shipping volumes are widely dispersed among prefectures. Nagasaki, in particular, recorded the largest shipment volume, indicating the high agricultural productivity of the region. On the other hand, the average shipping volume of 802t suggests that there is variation in shipping volumes by region. This may be due to factors such as weather conditions and local agricultural policies that affect shipping volumes. Additionally, the total shipping volume of 29.7kt shows that autumn-planted potatoes are an important crop in Japanese agriculture. Data on root vegetable shipping volumes indicates that regional differences in productivity and changes in demand are affecting agricultural production. In the future, there will be a need to continue promoting agriculture in each region and improving sustainable productivity.
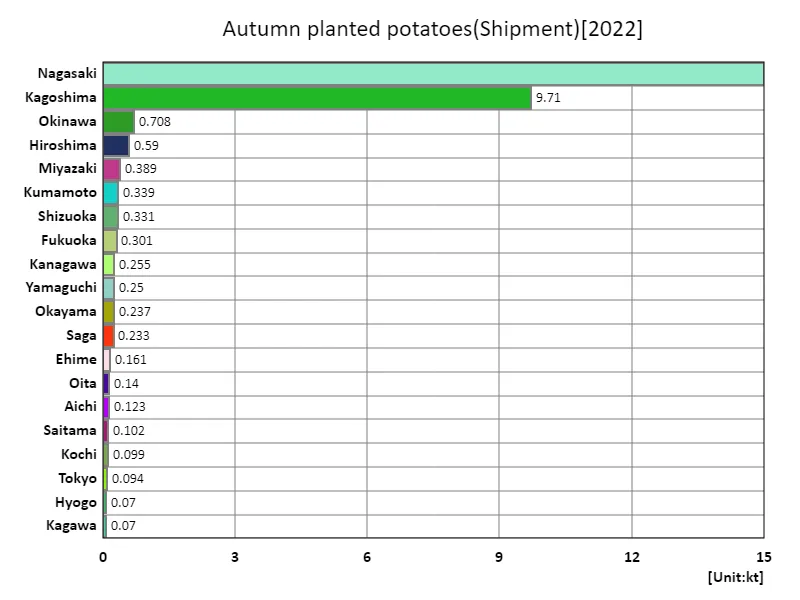

The maximum is 15kt of Nagasaki, the average is 802t, and the total is 29.7kt



Comments