Abstract
In recent years, Japan’s yam production has seen relatively stable trends. As of 2022, the nationwide cultivated area reached a peak of 139,000 tons (kt), with a corresponding harvest yield of 139kt. However, the shipment volume slightly lags behind, peaking at 120kt in 2022, reflecting both domestic consumption patterns and export dynamics. The gap between harvest yield and shipping volume suggests a significant amount is retained for domestic use, including fresh consumption and processed products. Over time, regional variations in yield and climate impacts have also influenced production efficiency.
Yam planting area and yield (main data).
Japan’s yam production has experienced a decline since its peak of 159,000 tons (kt) in 2007, with the national planting area and yield in 2022 at 87.8% of that level. This trend reflects a gradual reduction in cultivation, influenced by changing dietary preferences, labor shortages in agriculture, and competition from other crops. Despite this decline, yam remains a staple in Japanese cuisine, with regional variations in yield. The overall decrease in planting area and yield highlights challenges in maintaining production levels while adapting to evolving agricultural and consumer patterns.
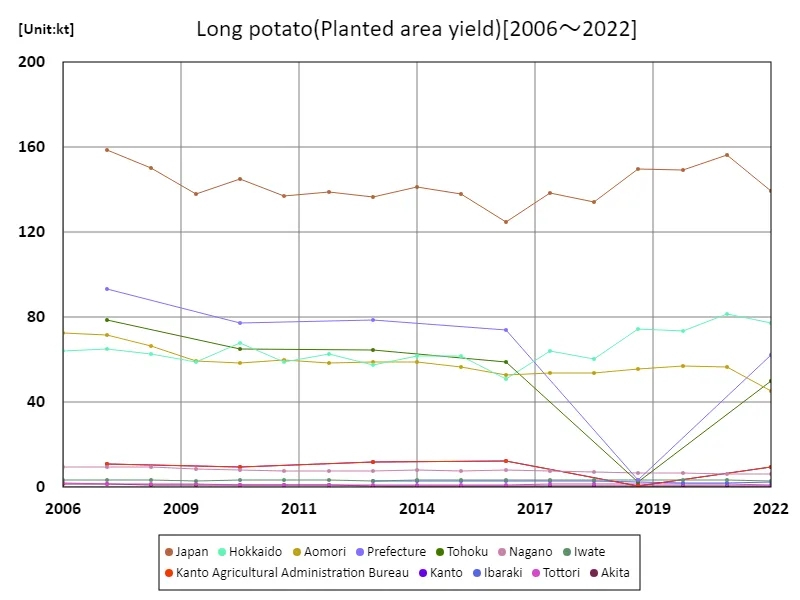

The maximum is 159kt[2007] of Japan, and the current value is about 87.8%
Nagaimo cultivation area and harvest volume (by prefecture).
In 2022, Hokkaido led Japan’s root vegetable production with the highest cultivation area and harvest volume, reaching 77.2kt. This figure reflects the region’s significant role in national agriculture, benefiting from favorable climate conditions and large-scale production capabilities. Overall, Japan’s root vegetable cultivation trends show regional concentration, with Hokkaido remaining dominant due to its extensive farmland. While other regions contribute to the national output, the reliance on Hokkaido highlights both its agricultural strength and the challenges faced by other areas in competing with its scale.
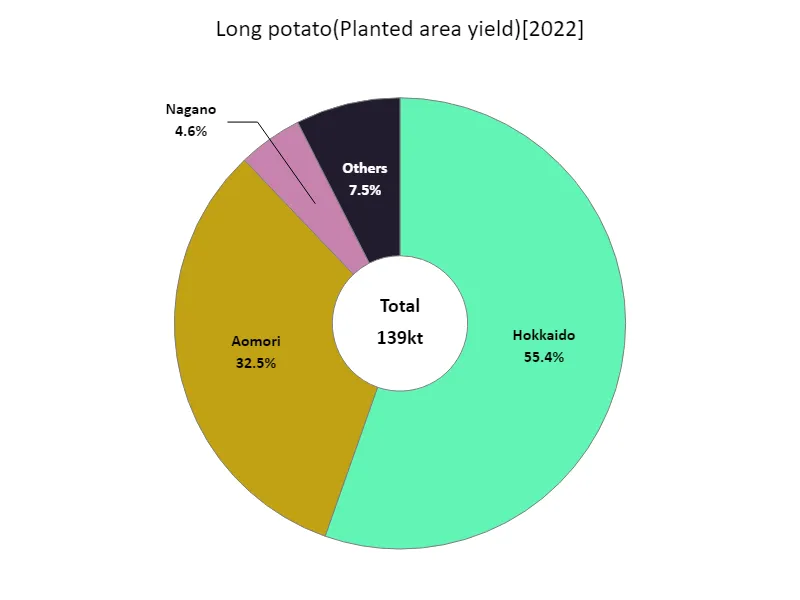

The maximum is 77.2kt of Hokkaido, the average is 4.65kt, and the total is 139kt
Nagaimo shipping volume (main data).
Japan’s yam shipping volume reached a peak of 136,000 tons (kt) in 2021, reflecting strong domestic demand and steady production. As of 2022, the shipping volume is at 88.6% of its peak, indicating a slight decline in distribution. This trend suggests a shift in consumption patterns, possibly due to changing dietary habits or increased competition from other vegetables. Despite this, yam remains an important crop, with stable regional production and a continued presence in both fresh and processed markets. The decline also highlights challenges in maintaining growth amid evolving consumer preferences.
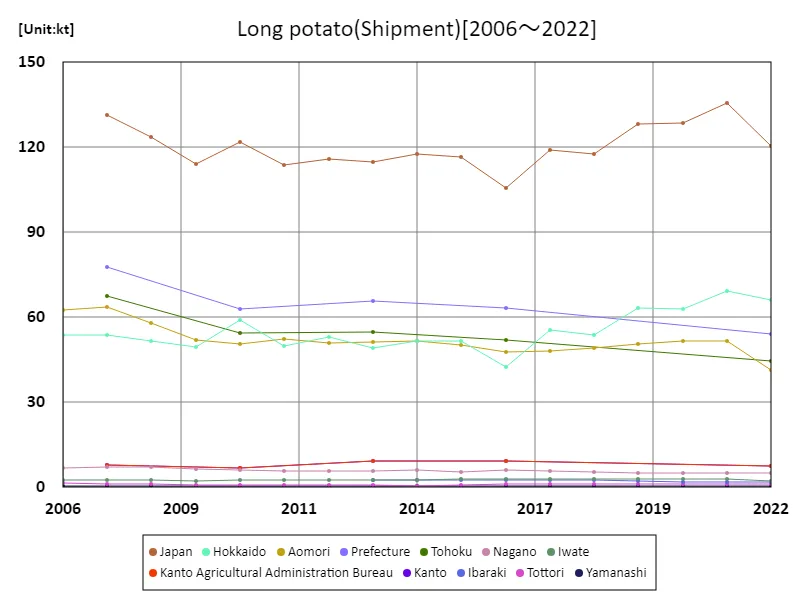

The maximum is 136kt[2021] of Japan, and the current value is about 88.6%
Nagaimo shipping volume (by prefecture).
In 2022, Hokkaido led Japan’s root vegetable shipments with the highest volume of 66.1kt, reflecting its dominance in the sector. The region benefits from favorable climate conditions, large-scale production, and efficient shipping networks. As the primary source of root vegetables, Hokkaido significantly influences national distribution. Other prefectures also contribute, but Hokkaido’s figures remain the highest, underscoring its key role in meeting both domestic demand and export needs. The trend highlights regional concentration in root vegetable production and the ongoing importance of Hokkaido in Japan’s agricultural landscape.
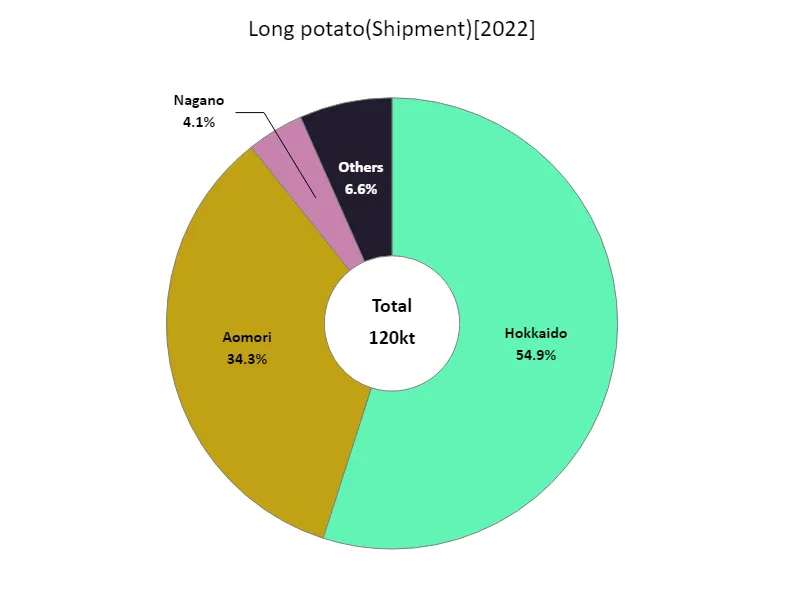

The maximum is 66.1kt of Hokkaido, the average is 4.01kt, and the total is 120kt



Comments