Abstract
Looking at data on leafy vegetables in Japanese agriculture, particularly spinach, the national harvest volume in 2022 will be 210kt, with the maximum cultivated area being 18.9kha. In terms of shipping volume, Gunma recorded the highest volume at 20.2kt. The trend inferred from these figures indicates that production of leafy vegetables is thriving in Japan. Spinach in particular is widely cultivated, and the yields and cultivated areas are large. Also, since Gunma has the largest shipping volume, it is suggested that production volumes vary by region and that each region has its own characteristics. From this data, it can be said that Japan’s leafy vegetable agriculture has a stable production base and supply is in line with demand.
Spinach yield (main data).
Looking at data from 1973 to 2022 on Japan’s spinach harvest, the national yield hit a record peak of 400kt in 1987. However, since then, harvest volumes have fallen to about half of their peak level, and as of 2022, the national harvest volume remains at about 52.4%. This may be due to changes in agricultural structure and market demand. For example, there are the reduction in farmland, efficiency improvements due to the modernization of agricultural production, and competition from imports. It is also possible that as consumers become more health conscious, demand for other vegetables and foods is increasing. Due to these factors, spinach harvest volumes are lower than their peak, but production volumes are being adjusted in response to demand and market trends.
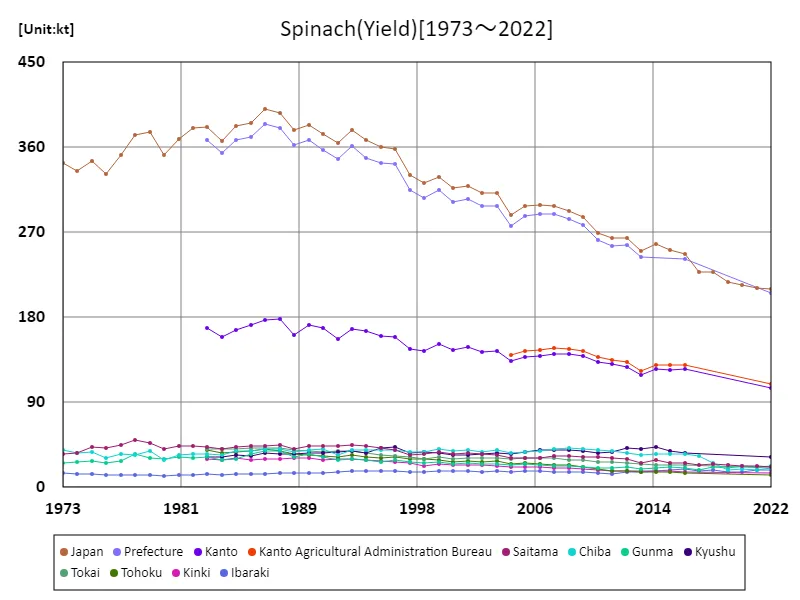

The maximum is 400kt[1987] of Japan, and the current value is about 52.4%
Spinach harvest volume (by prefecture).
Gunma recorded the largest overall leafy vegetable harvest in Japan in 2022. This data indicates that Gunma is a particularly outstanding region for the production of leafy vegetables. It also shows that Gunma’s harvest volume stands out when compared to other prefectures. This may be due to a combination of factors, including Gunma’s climate, soil conditions, and developments in agricultural technology. On the other hand, depending on the harvest yields in other prefectures, regional disparities and characteristics become apparent. The locations suitable for growing leafy vegetables vary depending on the climatic conditions and agricultural characteristics of each region, so it is believed that each region produces them by taking advantage of its respective strengths. These data suggest that leafy vegetable yields in Japan vary by region, with Gunma being a particularly prosperous production area.
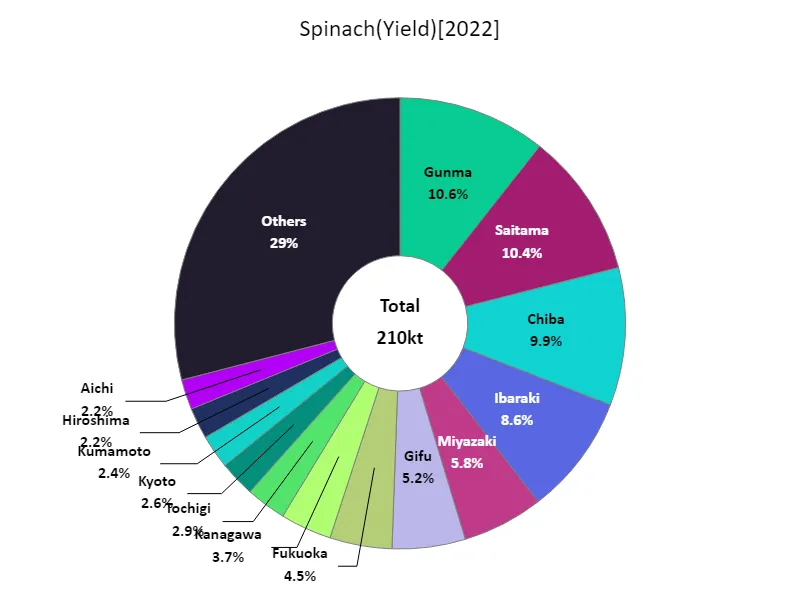

The maximum is 22.3kt of Gunma, the average is 4.46kt, and the total is 210kt
Area cultivated with spinach (main data).
Looking at data from 1973 to 2022 on the area of land planted with spinach in Japan, the national area peaked at 27.5 kha in 1988. However, since then, it has remained at about 68.7% of its peak level. This trend reflects changes in Japan’s agricultural structure and market demand. For example, one possibility would be to urbanize farmland and make more efficient use of farmland through modernizing agricultural production. It is also possible that changes in consumer eating habits and health consciousness are increasing demand for other vegetables and foods, resulting in a decrease in the area planted with spinach. Due to these factors, the area planted to spinach has decreased from its peak, but it is thought that agricultural production is being adjusted in response to changes in demand and the market.
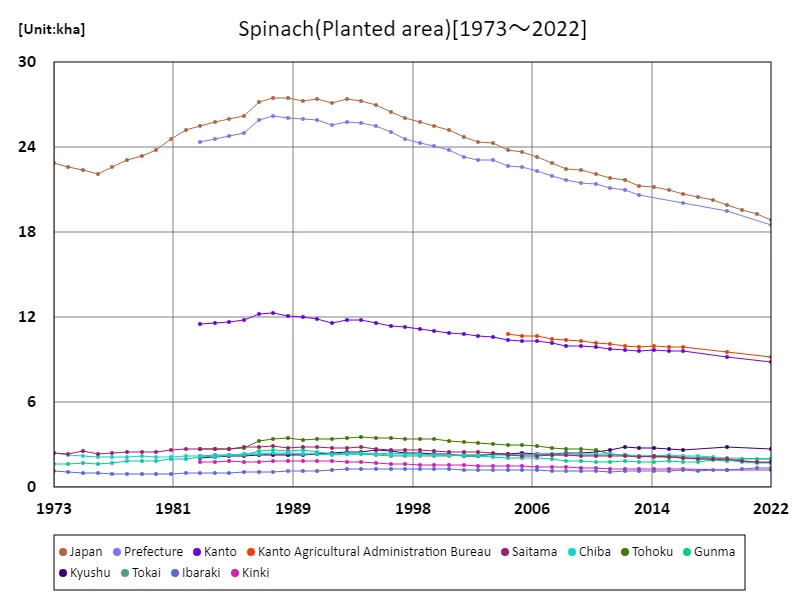

The maximum is 27.5kha[1988] of Japan, and the current value is about 68.7%
Spinach cultivation area (by prefecture).
Gunma recorded the largest area planted with leafy vegetables in Japan in 2022. This data shows that Gunma is a particularly excellent region for growing leafy vegetables. We can also see that Gunma’s cultivated area stands out compared to other prefectures. This may be due to Gunma’s climatic conditions, soil characteristics, and developments in agricultural technology. On the other hand, depending on the cultivated area of other prefectures, disparities and characteristics between regions become apparent. The area planted with leafy vegetables may vary depending on the agricultural characteristics and demand of each region. It is also possible that Gunma, which has the largest cultivated area, employs a greater variety of varieties and cultivation methods than other regions. These data suggest that the area cultivated with leafy vegetables in Japan varies by region, with Gunma being a particularly active production area.
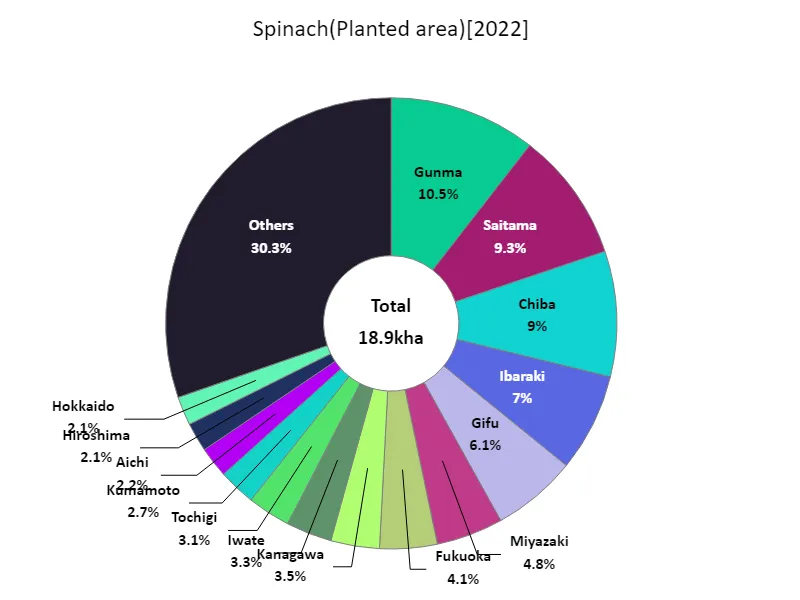

The maximum is 1.99kha of Gunma, the average is 402ha, and the total is 18.9kha
Spinach shipping volume.
Gunma recorded the highest overall spinach shipment volume in Japan in 2022. The overall average was 3.81kt, bringing total shipping volume to 179kt. This data shows that Gunma plays a particularly important role in spinach shipments. Since Gunma is far ahead of other regions, it can be inferred that spinach production is thriving in the area. Additionally, the overall average was 3.81kt, suggesting some variation in shipping volumes across regions. This may be due to differences in the agricultural environment from region to region, such as climatic conditions, soil characteristics, and development of agricultural technology. Furthermore, with the total shipment volume being 179kt, it can be seen that spinach production is thriving throughout Japan and that supply is being met in response to demand. These data suggest that Japan’s spinach shipping volumes vary by region, with Gunma being a particularly active producing area, but that overall there is a stable supply.
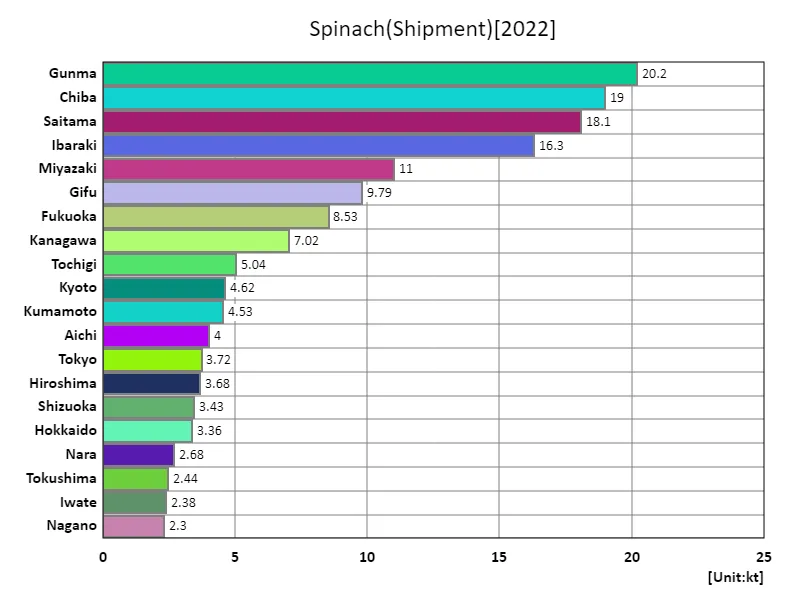

The maximum is 20.2kt of Gunma, the average is 3.81kt, and the total is 179kt



Comments