Abstract
Looking at carrots, the main root vegetable in Japanese agriculture, data from 2022 shows that the national harvest volume was the largest at 582kt. The cultivated area is also the largest in the country at 16.5kha, indicating that production is being carried out in response to demand. On the other hand, Hokkaido had the highest shipping volume at 157kt, showing that production volumes vary by region. This is thought to be due to Hokkaido’s cool climate and abundant soil, which makes it ideal for growing carrots. Production is carried out nationwide according to demand, with Hokkaido in particular functioning as a large-scale production base.
Carrot yield (main data).
Data on carrot harvest in Japan from 1973 to 2022 shows that the highest harvest was recorded in 1996 at 736kt. Since then, current yields have fallen to 79.1% of their peak levels. This trend is likely due to structural changes in agriculture and changes in market demand. In recent years, carrot production may be declining due to factors such as urbanization, increased productivity due to more advanced agriculture, and competition from imports. Additionally, we may also see changes in demand due to diversification of food and growing health consciousness. Against this background, although carrot production in Japan is lower than at its peak in the past, there is a need to produce efficiently while maintaining a balance with demand.
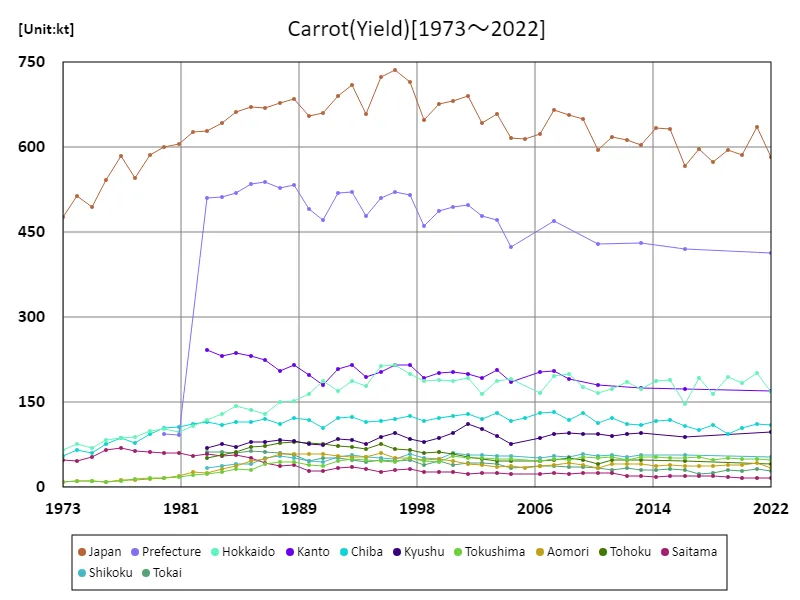

The maximum is 736kt[1996] of Japan, and the current value is about 79.1%
Carrot harvest volume (by prefecture).
Looking at data for 2022 on root vegetable harvests in Japan, Hokkaido recorded the highest yield overall at 168kt, which is currently the highest. This is due to the fact that Hokkaido has a cool climate and vast farmland, providing ideal conditions for growing root vegetables. Meanwhile, other prefectures are also focusing on root vegetable production, and a variety of crops are being cultivated to meet demand. Technological innovations in Japanese agriculture and changes in agricultural policies are also affecting root vegetable yields. It is characterized by efficient production in each region while responding to changes in demand and fluctuating weather conditions. While there are production bases for root vegetables, centered in Hokkaido, a wide variety of production is also carried out in other regions, ensuring a stable supply throughout Japan.
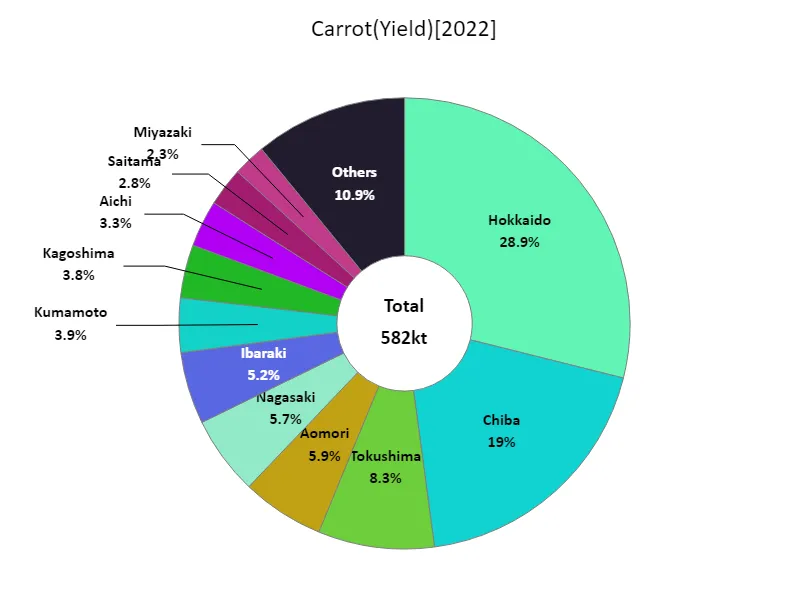

The maximum is 168kt of Hokkaido, the average is 12.4kt, and the total is 582kt
Carrot cultivation area (main data).
Looking at data from 1973 to 2022, the area of land cultivated with carrots in Japanese agriculture reached a peak of 25 kha nationwide in 1985. Since then, the current area under cultivation has fallen to 66% of its peak. This trend is thought to be due to structural changes in agriculture and changing consumer preferences. In recent years, amid diversifying demand and intensifying competition from imports, it has become increasingly important for farmers to select crops that are economically viable and responsive to market demand. Additionally, factors such as urbanization and the decline in agricultural land may also be contributing to the decline in acreage. Against this background, the area of land planted to carrots has decreased from its peak, but there is a need for efficient production while maintaining a balance with demand.
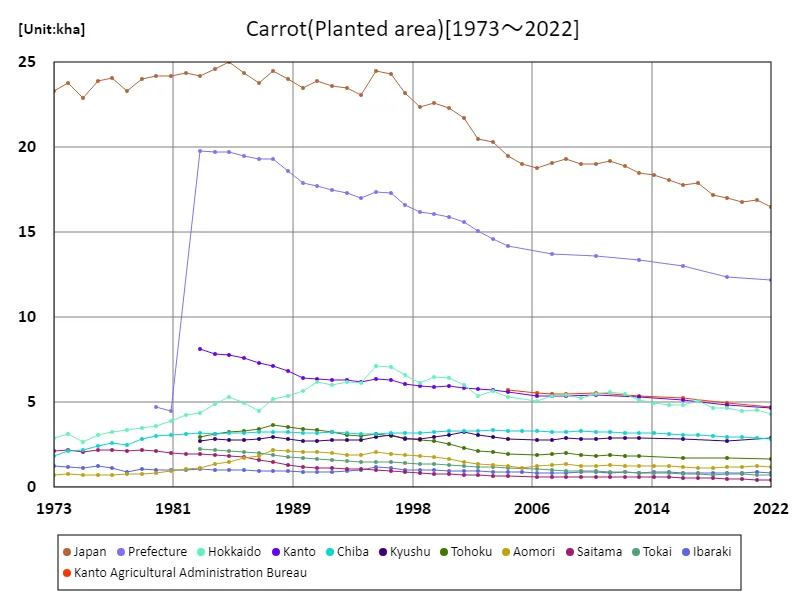

The maximum is 25kha[1985] of Japan, and the current value is about 66%
Carrot cultivation area (by prefecture).
Looking at data for 2022 regarding the area planted with root vegetables in Japan, Hokkaido recorded the largest area overall at 4.31kha, currently the largest. This is due to the fact that Hokkaido has vast farmland and abundant water sources, providing an ideal environment for cultivating root vegetables. Meanwhile, other prefectures are also actively working on root vegetable production and are producing to meet demand. Because each region has different climatic conditions and soil conditions, cultivation methods and selection of varieties tend to differ. Furthermore, in recent years, advances in agricultural technology and an emphasis on sustainability have led to more efficient and environmentally friendly cultivation methods. While there are production bases for root vegetables, centered in Hokkaido, a variety of crops are also cultivated in other regions, ensuring a stable supply throughout Japan.
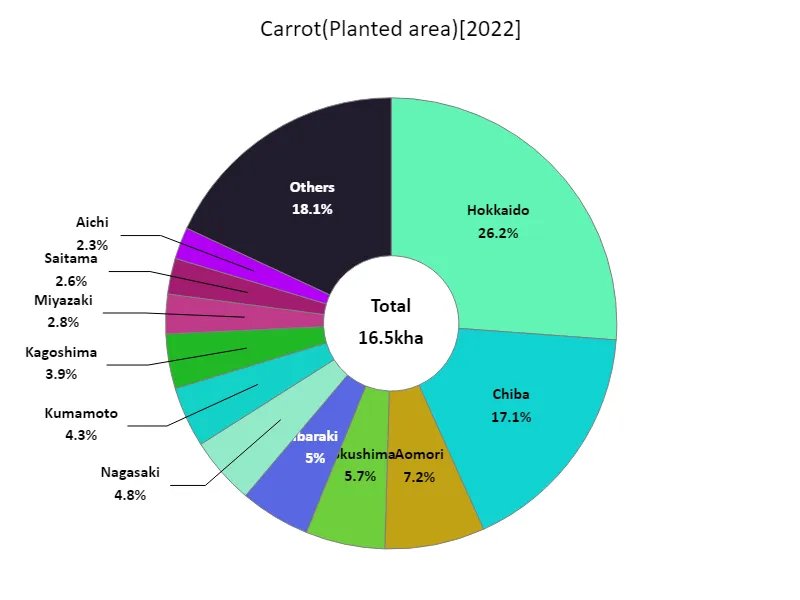

The maximum is 4.31kha of Hokkaido, the average is 350ha, and the total is 16.5kha
Carrot shipment volume.
Looking at data for 2022 on carrot shipments in Japanese agriculture, Hokkaido had the highest overall volume at 157kt, and the average was 11.2kt. The overall total shipping volume is 525kt. A notable feature of these figures is that Hokkaido boasts the largest shipping volume in the country. Hokkaido has vast farmland and suitable climatic conditions, making it ideal for growing carrots. However, the overall average shipment volume of 11.2kt suggests that shipment volumes vary by region. This is due to differences in climatic conditions, soil, and the technical capabilities of farmers. Additionally, in Japanese agriculture, production volumes tend to be adjusted in response to fluctuations in demand. A stable market is maintained through efficient production and supply in line with demand. Overall, carrot production, centered in Hokkaido, plays a major role nationwide, and a production system is in place that makes use of the characteristics of each region.
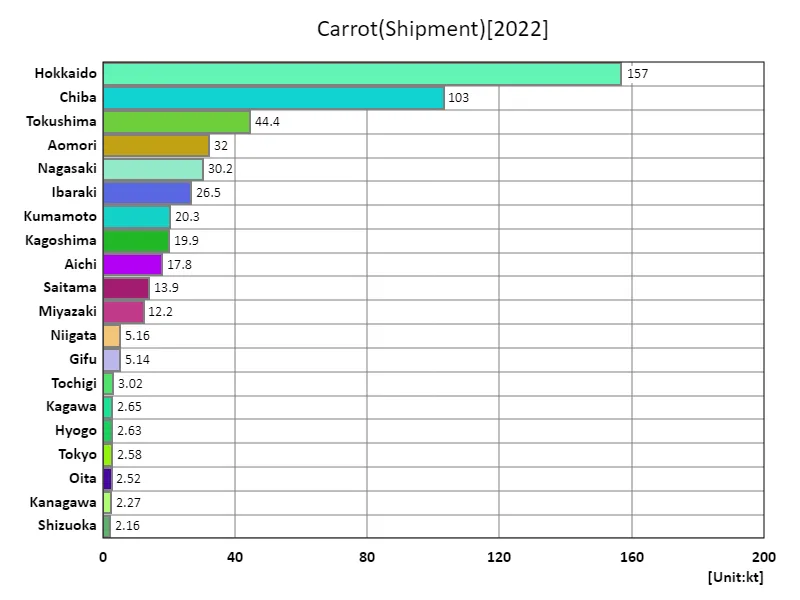

The maximum is 157kt of Hokkaido, the average is 11.2kt, and the total is 525kt



Comments