Abstract
Looking at data on domestic and import vegetable production in Japan’s agriculture, focusing on root vegetables, daikon radish had the highest domestic production volume in 2022, recording 420kt. On the other hand, carrots are the main imported vegetable, with 4.14kt imported in 2022. Furthermore, bamboo shoots are attracting attention among imported vegetables, accounting for 2.8% of imports in 2022. These data show that while domestic daikon cultivation is a major part of root vegetable production in Japanese agriculture, there is also demand for imported carrots and bamboo shoots, and imports account for a certain proportion of the total.
Domestic production of root vegetables
Looking at the data on domestically produced root vegetables in Japanese agriculture, the production volume of daikon radish is particularly noteworthy from 2004 to 2022. In 2005, production hit a record high of 867kt, but has since declined gradually and is currently at 48.5% of its peak. This trend clearly indicates that radish production is declining. Possible reasons for this decrease include changes in demand and improved production efficiency. It will also be important to continue collecting and analyzing data to see if similar trends are observed for other root crops.
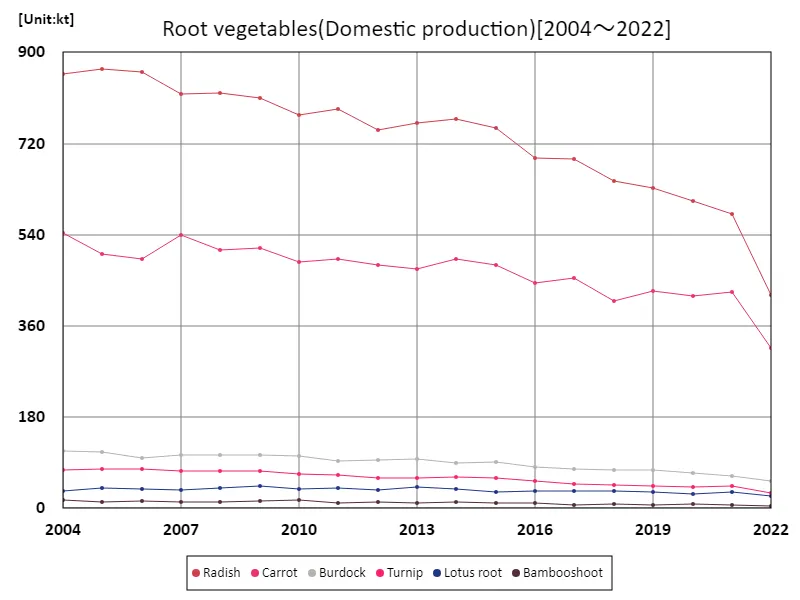

The maximum is 867kt[2005] of Radish, and the current value is about 48.5%
Import volume of root vegetables
Looking at the data on vegetable imports in Japanese agriculture, the latest for 2022, we can look at the total market price of imported vegetables by prefecture. According to this data, the largest overall imported vegetable was carrots, with import volume of 30.7kt. Moreover, this figure breaks previous records, suggesting that current imports are at an all-time high. This trend may be contributing to an increase in vegetable imports into Japan’s agriculture industry. This is due to factors including an increase in domestic demand and a shortage of domestic production of certain vegetables. It is also possible that foreign vegetables are becoming popular in the Japanese market. Such an increase in imported vegetables could have an impact on domestic agricultural producers and markets. It will be necessary to strengthen the competitiveness of domestic producers, improve production efficiency, and respond to changes in international trade relations.
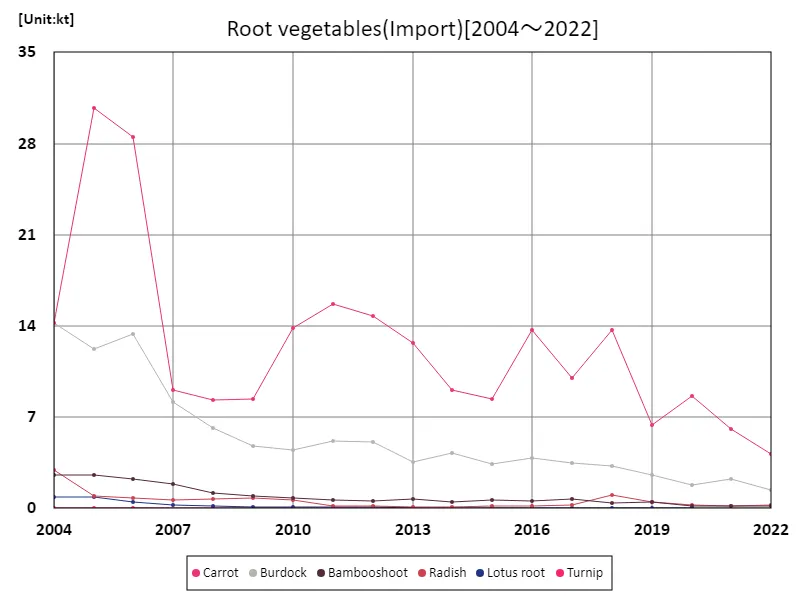

The maximum is 30.7kt[2005] of Carrot, and the current value is about 13.5%
Import (proportion) quantity of root vegetables
Looking at the data on the import proportion of root vegetables in Japan’s agriculture, the proportion of bamboo shoots is particularly noteworthy. From 2004 to 2022, the import share recorded a high of 16.4% in 2005, but has since declined somewhat and is currently slightly lower than its peak of 17.1%. This trend indicates that the import share of root vegetables has remained relatively stable. Bamboo shoots are a particularly notable imported product, and demand for them appears to be high. However, there has been a slight decline since the peak, which may indicate an increase in domestic production or a shift in demand to other imports. These trends may be influenced by changes in Japan’s agricultural policies and international trade. Whether the import ratio of root vegetables, including bamboo shoots, will remain stable or fluctuate in the future will depend on the balance of market demand and supply.
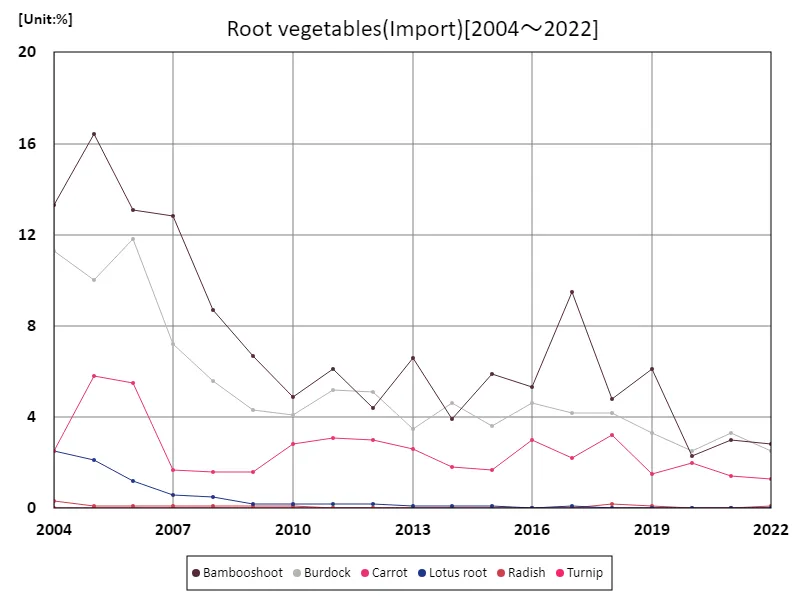

The maximum is 16.4%[2005] of Bambooshoot, and the current value is about 17.1%



Comments