Abstract
In recent years, komatsuna production in Japan has shown stability with a peak harvest volume of 120kt in 2022 and a cultivated area of 7.39kha. Ibaraki leads in shipping, contributing 23.3kt of the total. Historically, komatsuna has been valued for its adaptability and nutritional benefits, maintaining consistent yields and cultivation despite fluctuating conditions. The data reflects a well-established cultivation area with Ibaraki emerging as a key player in national shipping volumes.
Komatsuna harvest volume (main data).
Komatsuna harvest yields in Japan have shown resilience and stability, peaking at 122kt in 2020. As of 2022, yields are at 98.5% of this peak level, indicating a slight decrease but overall steady production. The consistent performance over two decades highlights komatsuna’s robustness and enduring popularity in Japanese agriculture. Trends suggest that while yields may fluctuate, komatsuna remains a key leafy vegetable, reflecting its reliable cultivation and steady market presence.
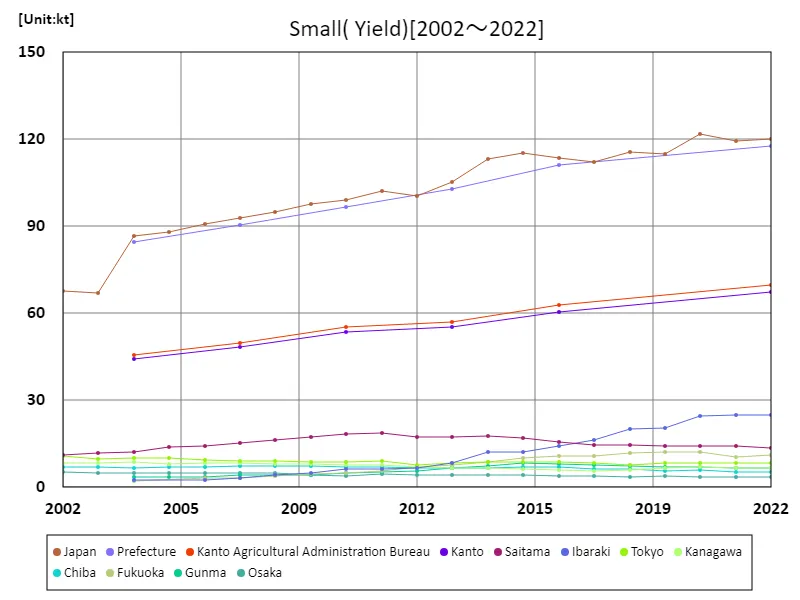

The maximum is 122kt[2020] of Japan, and the current value is about 98.5%
Komatsuna harvest volume (by prefecture).
In 2022, Ibaraki leads Japanese leafy vegetable yields with a notable 25.1kt, reflecting its prominence in production. This figure highlights Ibaraki’s strong agricultural capacity and specialization in leafy vegetables. Over time, prefectures like Ibaraki have consistently demonstrated high yields, underscoring regional expertise and favorable growing conditions. The data suggests that while specific yields may vary, Ibaraki remains a key player, maintaining its position at the forefront of leafy vegetable production in Japan.
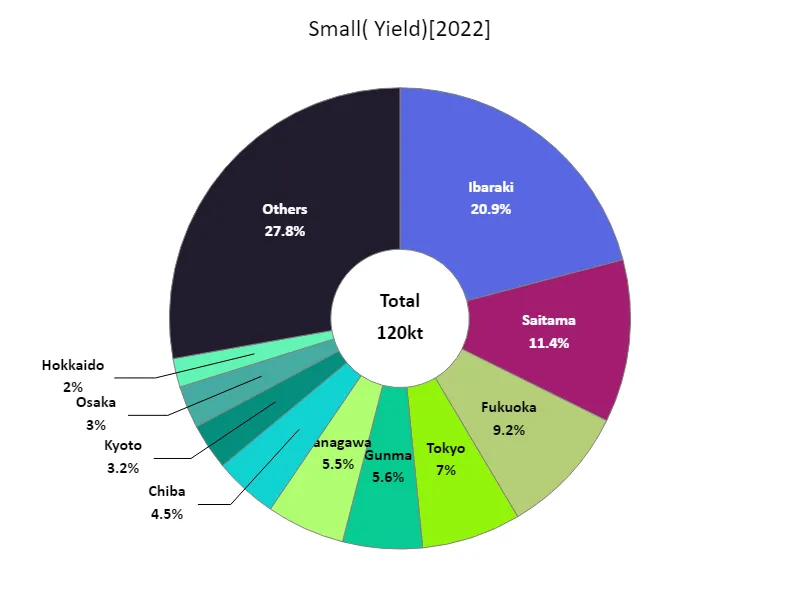

The maximum is 25.1kt of Ibaraki, the average is 2.56kt, and the total is 120kt
Area of Komatsuna cultivation (main data).
Japan’s komatsuna cultivation peaked at 7.55kha in 2020, with current planting areas at 97.9% of this maximum level as of 2022. This data reveals a slight decline but overall stability in komatsuna farming. The trend indicates a consistent commitment to growing this leafy vegetable, reflecting its steady demand and adaptability. Despite minor fluctuations, the national planting area for komatsuna has maintained a robust presence, showcasing its ongoing importance in Japanese agriculture.
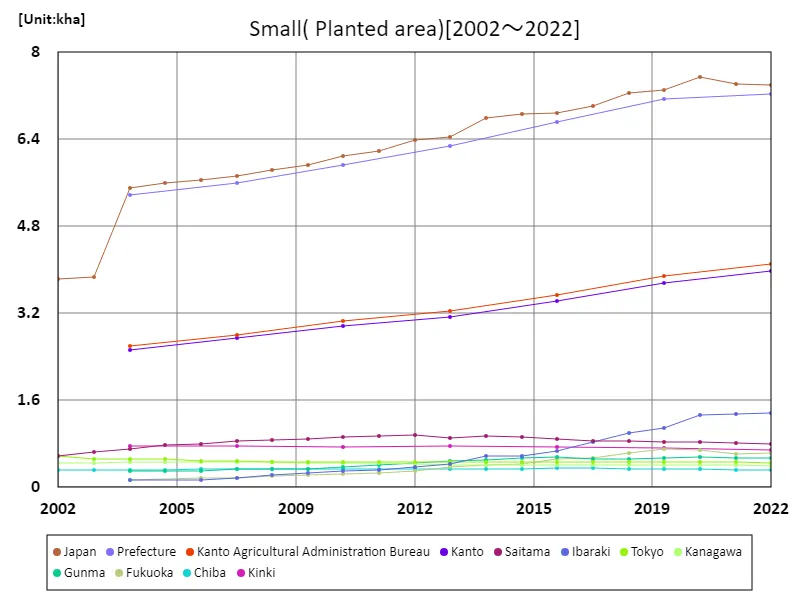

The maximum is 7.55kha[2020] of Japan, and the current value is about 97.9%
Area cultivated with Komatsuna (by prefecture).
Looking at the data on the planted area of leafy vegetables in Japan in 2022, Ibaraki Prefecture recorded the largest area overall at 1.37kha, which is currently the largest value. Ibaraki Prefecture is an important agricultural region in Japan and plays a major role in the cultivation of leafy vegetables. In general, Ibaraki Prefecture has climatic and soil conditions suitable for growing leafy vegetables, providing an ideal environment for agricultural production. Therefore, it is only natural that the area planted to leafy vegetables is the largest nationwide. Leafy vegetable cultivation is also carried out in other prefectures, but not on the same scale as Ibaraki Prefecture. This reflects differences in agricultural characteristics and demand from region to region. For example, cultivation of leafy vegetables is popular in Hokkaido and Tochigi Prefecture, but on a smaller scale than in Ibaraki Prefecture. Generally speaking, the area of land cultivated with leafy vegetables in Japan varies by region, but they are mainly cultivated in Ibaraki Prefecture. It can be said that Ibaraki Prefecture’s leadership and technical capabilities in agricultural production play a major role in the cultivation of leafy vegetable crops in this region.
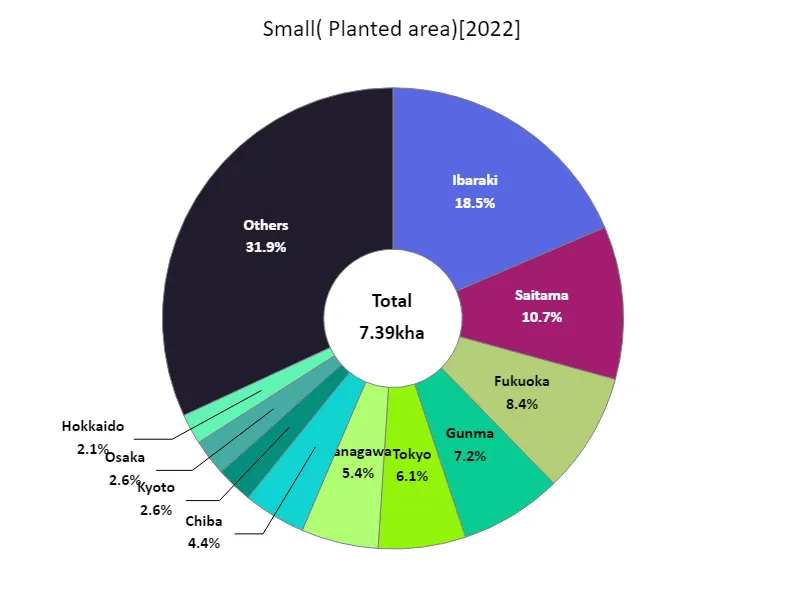

The maximum is 1.37kha of Ibaraki, the average is 157ha, and the total is 7.39kha
Shipping volume of komatsuna.
In 2022, Ibaraki leads Japan in komatsuna shipping with a substantial 23.3kt, highlighting its pivotal role in the national supply. The total shipping volume for komatsuna was 108kt, with an average of 2.3kt per prefecture, indicating a high concentration in Ibaraki. This trend underscores Ibaraki’s dominance and expertise in komatsuna production and distribution. Despite a few key players, the data shows Ibaraki’s continued prominence in meeting national demand for this leafy vegetable.
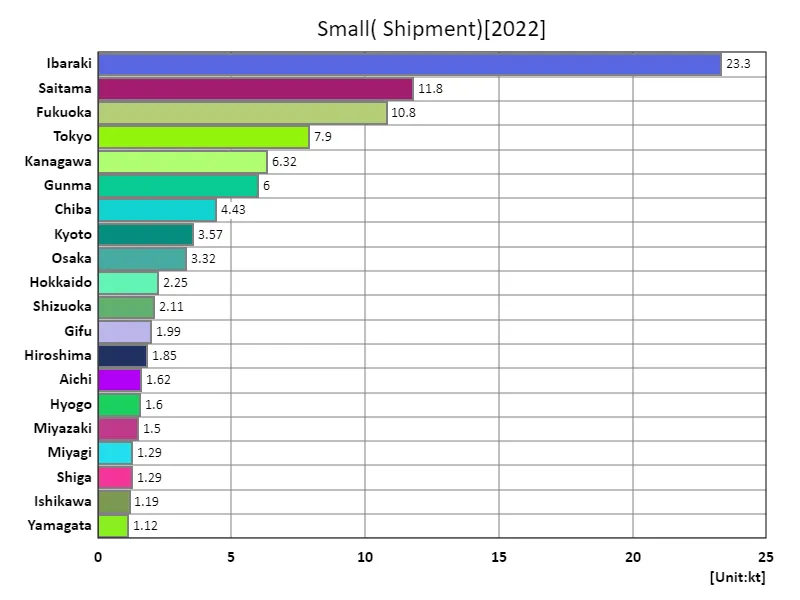

The maximum is 23.3kt of Ibaraki, the average is 2.3kt, and the total is 108kt



Comments