Abstract
In Lebanon’s 2022 crop vegetable production, cucumber was the most productive, recording a production volume of 124kt. This suggests that vegetable cultivation is well suited to Lebanon’s warm climate and topography. Tomatoes and potatoes are also produced as important crops, but what is notable is that cucumbers are produced in particularly large quantities. In terms of land use, most of the farmland is used for growing vegetables, with high-demand crops such as tomatoes and cucumbers being particularly widely grown. In terms of tomato production volume by use, eating raw is the majority, but demand for processing also accounts for a certain percentage, showing that the development of the processing industry is affecting agricultural production. Lebanese agriculture places emphasis on export production in addition to domestic consumption, and the warm Mediterranean climate is particularly well suited to vegetable cultivation, so stable production is expected to continue in the future.
Production (by vegetables)
Looking back at data on vegetable production in Lebanon from 1961 to 2022, the highest production volume for cucumbers was recorded in 1996, reaching 219 kt. However, production is expected to fall by around 56.5% to 124kt in 2022, reflecting changes in Lebanese agriculture. Cucumber remains a major crop, and the warm climate and adequate water resources are favourable for its cultivation, but production has declined in recent years, likely due to market demand and technological changes in agricultural production. Agricultural production peaked in the 1990s and has since shown a downward trend due to factors such as fluctuations in political stability, economic factors, a decrease in irrigation water sources, and stagnation of agricultural technology. This has led to changes in the production of not only cucumbers but also other vegetables, and may have led to agricultural diversification and a shift to other crops. Other vegetables such as tomatoes and potatoes also remain important production items, and Lebanon continues to produce for local consumption as well as for export markets. In the future, it is expected that technological innovation and efficient agricultural management will contribute to improving productivity.
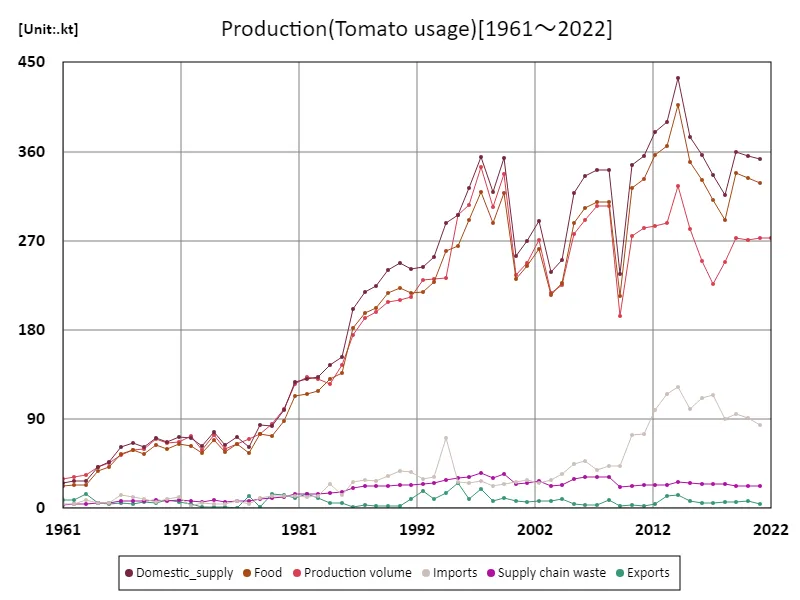

The maximum is 434kt[2014] of Domestic_supply, and the current value is about 81.1%
Yield(by vegetable)
Cucumber yield in Lebanon’s vegetable production peaked at 79.2 t/ha in 1997, but by 2022, the yield had decreased by 41.8% to around 33.1 t/ha. This decline suggests the influence of multiple factors, although there have been advances in agricultural technology. Lebanon’s agriculture reached its peak in the 1990s and maintained high yields, but since then, aging irrigation facilities, climate change, and changes in agricultural management are thought to have affected yields. Cucumber cultivation remains important, although land use efficiency and water resource constraints may now be affecting production. In addition, from an economic perspective, the aging of agricultural workers and the reduction in farmland are also thought to be contributing to the decline in yields. In addition, agricultural diversification is progressing in Lebanon, with a shift to other crops and changes in production methods. In the future, it is expected that the introduction of agricultural techniques adapted to climate change and efficient irrigation methods will contribute to restoring the productivity of cucumbers and other vegetables. In addition, selecting crops that meet market needs and improving productivity will be key to supporting a stable supply.
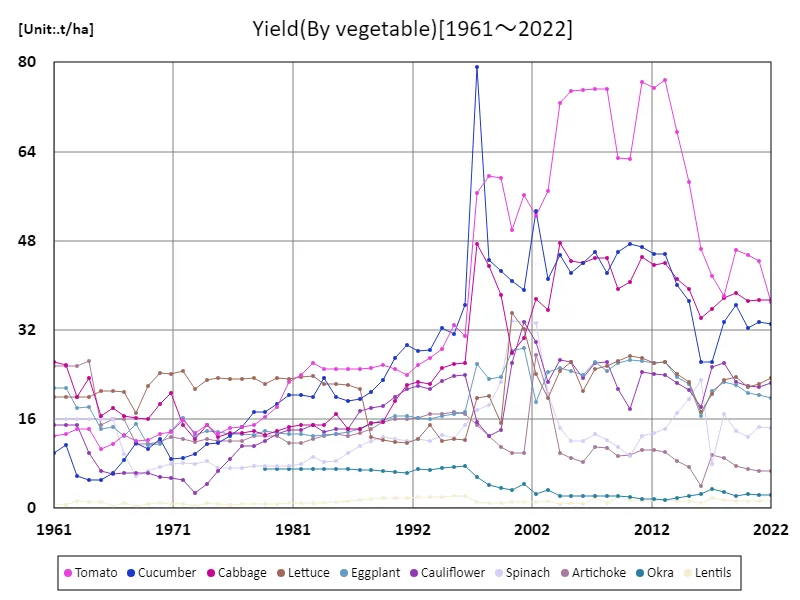

The maximum is 79.2t/ha[1997] of Cucumber, and the current value is about 41.8%
Land use (by vegetables)
Looking at the land use situation for vegetables in Lebanon in 2022, tomatoes occupy the largest area, being cultivated on 7.37 kha of land. This shows the importance of tomatoes in Lebanese agriculture, as they are produced not only for domestic consumption but also for export. The average land use area is 1.69kha, with the total land use area reaching 16.9kha. It is expected that the trend of tomatoes being cultivated as a staple crop will continue in the future. Looking at past trends, Lebanon has placed emphasis on efficient land use in vegetable production. In particular, the warm climate and the development of irrigation facilities contribute to the production of crops such as tomatoes and cucumbers, which is why these crops are cultivated over a wide area. On the other hand, while the area of land use is increasing, securing land for agriculture is becoming a challenge due to a decrease in farmland and the progress of urbanization. Agricultural diversification is progressing in Lebanon, and other vegetables and fruits are grown as important crops, but tomato production remains central. In the future, improving water resource and land use efficiency will be the key to increasing productivity. Additionally, irrigation technology and improved varieties are expected to play an important role in responding to climate change.

The maximum is 272kt of Production volume, the average is 272kt, and the total is 272kt
Tomato usage
Looking at the tomato production situation in Lebanon by use based on data from 1961, the largest use for tomatoes was for domestic supply, with production volume at the time reaching 434kt. At this time in Lebanon, agriculture played an important role in the economy, and a lot of tomatoes were produced to meet domestic consumption. The reason why Japan had the largest domestic supply was due to the development of agricultural technology at the time and the suitability of tomatoes for cultivation using stable water sources. Since then, Lebanese agriculture has changed, with more production for export and greater reliance on foreign markets rather than just domestic supplies. The warm climate, especially in the Mediterranean region, is ideal for growing tomatoes, and tomatoes for export also play an important role. Additionally, the demand for tomatoes for processing has increased in Lebanon, leading to a boom in the production of tomato products (tomato paste and juice). The current largest use is domestic supply, indicating that demand in the domestic market remains large, and although production for export and processing remains important, there is an increasing reliance on tomatoes for the local market. In the future, climate change and advances in irrigation technology are expected to affect the domestic and international supply balance.
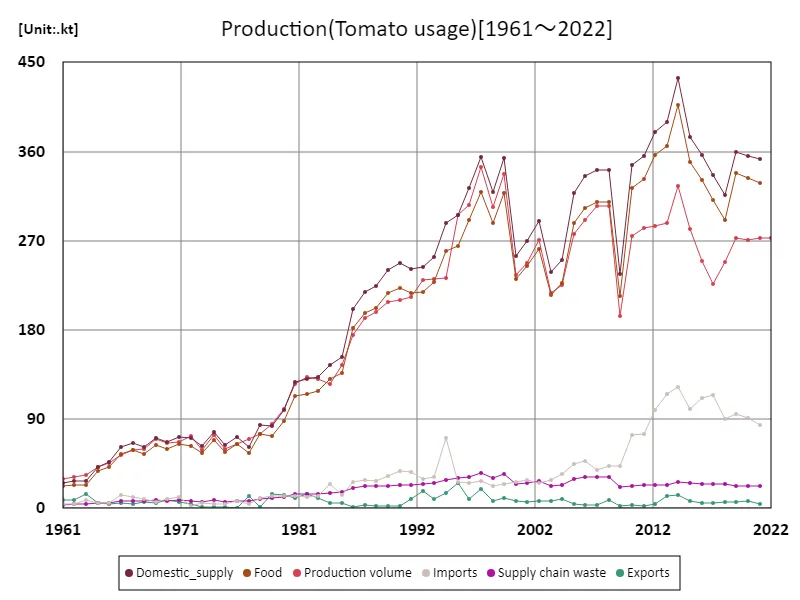

The maximum is 434kt[2014] of Domestic_supply, and the current value is about 81.1%



Comments