Abstract
A recent trend in Austria’s vegetable production is that cabbage is by far the most highly produced. According to data for 2022, cabbage production volume was 66.5kt, making it the most produced vegetable. Cabbage has suitable climatic conditions and soil and is cultivated over a wide area, allowing for stable production. The next most common vegetables are potatoes and tomatoes, which are also important and essential items in Austrian food culture. In terms of land use, there are particular trends towards ”by vegetable.” For example, tomatoes prefer warm climates, so they are often grown in greenhouses or greenhouses. Tomatoes in particular are characterized by the fact that they are produced for different purposes, and are generally divided into those for processing and those for eating raw. Processing tomatoes are made into products such as juices, sauces and ketchup and are in high demand both in Austria and abroad. These production volumes and land use trends are strongly influenced by Austria’s climatic conditions, advances in agricultural technology, and consumer eating habits, and it is expected that efficient cultivation methods and production diversification will continue to progress in the future.
Production (by vegetables)
Vegetable production in Austria showed large fluctuations between 1961 and 2022. Cabbage in particular recorded a peak production volume of 195kt in 1980, but current production volume is 66.5kt, or 34% of that figure. This decline is thought to be due to changes in consumer eating habits and increased efficiency in agricultural production. In the 1980s, cabbage was an important staple vegetable, but in recent years, a variety of vegetables have appeared on the dinner table, and the demand for cabbage has decreased relatively. Meanwhile, in Austria, production of other vegetables is increasing, with cultivation of potatoes, tomatoes and lettuce in particular remaining stable. Demand for these vegetables has increased in response to consumers’ growing health consciousness and diversification of diets. Tomatoes are in particular in high demand for processing, and are widely used to make sauces and juices. Additionally, advances in land use and cultivation techniques also affect production volume. Due to the effects of global warming and the introduction of new agricultural techniques, some vegetables can now be produced more efficiently. In the future, Austrian agriculture is expected to evolve in a more sustainable way, responding to environmental concerns and market changes.
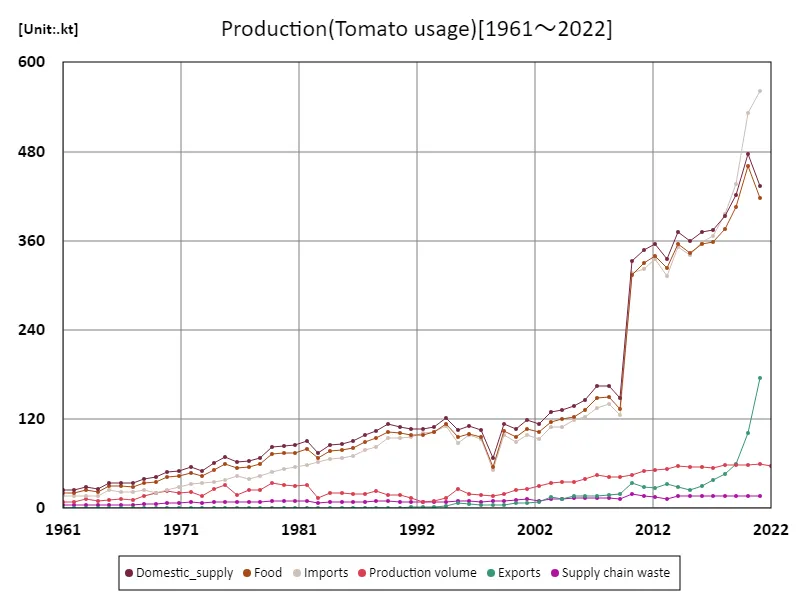

The maximum is the latest one, 562kt of Imports
Yield(by vegetable)
Vegetable production yields in Austria have shown significant changes between 1961 and 2022. In particular, tomato yield peaked at 310t/ha in 2016, and although it has maintained high productivity since then, it is currently at a level equivalent to 91.9% of that. This decrease in tomato yield is not simply a decline in production efficiency, but is thought to be influenced by climate change, advances in cultivation techniques, and fluctuations in market demand. Greenhouse cultivation of tomatoes is widespread, and in Austria much of the production takes place in greenhouses or greenhouses. This has made it possible to supply high-quality tomatoes throughout the year, realizing a stable supply that meets market demand. In addition, since tomato production in Austria is mainly for processing into sauces, ketchup, juice, etc., fluctuations in demand also affect yields. As such, although tomato yields have declined slightly compared to their peak, they still boast high productivity and are able to flexibly respond to market demand. As agricultural technology and environmental considerations continue to advance, there will be a demand for efficient and sustainable cultivation.
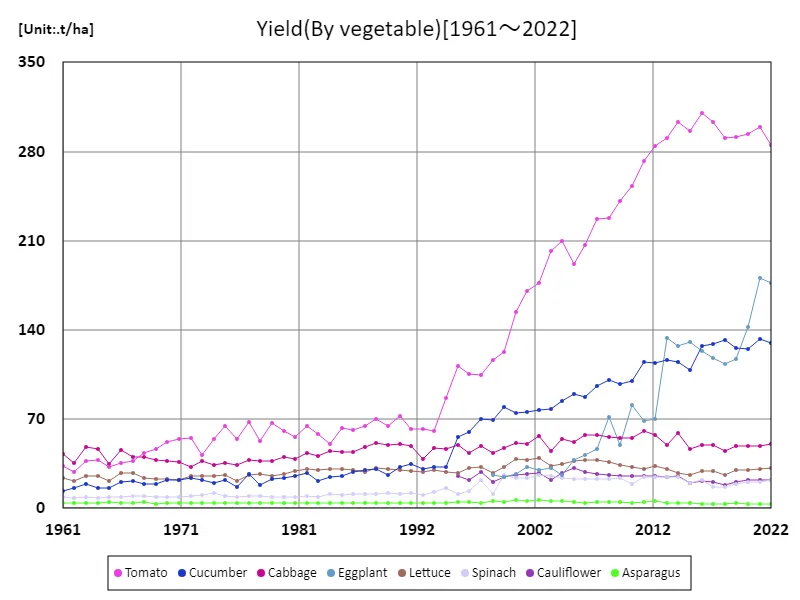

The maximum is 310t/ha[2016] of Tomato, and the current value is about 91.9%
Land use (by vegetables)
A characteristic of land use in vegetable production in Austria in 2022 is that lettuce will have the largest cultivation area of 1.38 kha. This area is relatively large compared to other vegetables, indicating that lettuce has a high demand in the market and is widely cultivated. Lettuce is a popular fresh vegetable in Austria, particularly used in salads and cooking, so the stability of demand is reflected in the land use. On the other hand, the average vegetable cultivation area is 593 ha, with the total area reaching 4.74 kha. As these figures show, a wide variety of vegetables are grown in Austria on a relatively small area. This reflects the tendency of Austrian agriculture to produce a highly efficient and diverse range of products, with the cultivation of various vegetable varieties being evenly spread. Furthermore, with recent improvements in agricultural technology and changes in market demand, more efficient land use is being promoted, and higher-yielding, economically sustainable cultivation methods are being chosen. Leafy vegetables such as lettuce in particular have a short harvest cycle and a high planting turnover rate, allowing for effective use of land. In the future, flexible land use that takes environmental considerations into account and responds to market fluctuations will become increasingly important.

The maximum is 57kt of Production volume, the average is 57kt, and the total is 57kt
Tomato usage
The amount of tomatoes produced in Austria by different uses has changed significantly between 1961 and the present day. In particular, imports of tomatoes reached a peak of 562kt and have remained at a stable high level ever since. Austria’s tomato production mainly meets domestic demand, but is partly supplemented by imports, especially for processing tomatoes. Domestic tomato production in Austria is mainly carried out through greenhouse cultivation, which provides a year-round supply of fresh tomatoes, increasing the need for imports. Tomatoes are mainly divided into those for eating raw and those for processing, with the processed tomatoes being made into ketchup, tomato sauce, juice, etc. Demand for processing tomatoes is stable and consumption is high both within Austria and abroad, so domestic production is insufficient and the country is partly dependent on imports. In addition, because Austria produces high-quality tomatoes, many of the imported products are also of high quality. As such, while tomato production in Austria is stable, the country remains dependent on imports for any amount that exceeds domestic demand, and this trend is expected to continue in the future. Additionally, there is a need to flexibly respond to demand for tomato production and imports in response to changes in consumer health consciousness and demand for processed foods.
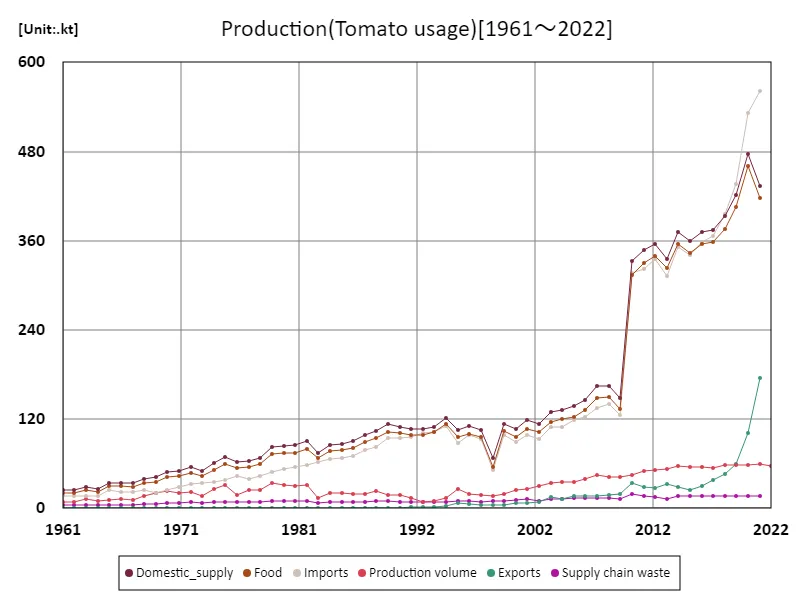

The maximum is the latest one, 562kt of Imports



Comments