Abstract
France’s vegetable production consists of a wide variety of vegetables, with lettuce having the largest production volume, reaching 439 kt in 2022. This is thought to be due to the fact that cultivation methods are suited to France’s climate and soil conditions. Lettuce in particular is being cultivated thanks to the mild winter climate, and demand has been steady. Among other vegetables, tomatoes occupy a very important position, and many are produced for different purposes, with some for processing and others for the fresh market. Tomato production areas, particularly in the south, take advantage of the warm climate and large areas of land are allocated to tomatoes. In recent years, with the promotion of sustainable agriculture and the effects of climate change, there have been changes in crop cultivation techniques and production methods, for example the evolution of water management and soil management methods. Furthermore, due to consumers’ health consciousness and changes in food culture, the demand for certain vegetables (such as lettuce and tomatoes) continues to increase, and fluctuations in production volumes and land use are expected to continue in the future.
Production (by vegetables)
Looking back at French vegetable production data from 1961 to 2022, lettuce had the highest production volume in 2018, reaching a record 734 kt. However, production volume will subsequently decline, reaching 439 kt in 2022, about 60% of the peak. This decline can be attributed to a variety of factors. First, this could be due to changing consumer preferences and increased demand for a greater variety of vegetables. Furthermore, the impact of climate change cannot be ignored, and dryness and abnormal weather in particular are putting a strain on vegetable production, possibly resulting in reduced yields. Additionally, the diversification of crops aimed at improving agricultural efficiency and reducing costs may have also led to a reduction in the area of land used for lettuce cultivation. However, lettuce remains an important crop in France, with production tailored to regional cultivation techniques and market demand. In the future, it will be necessary to introduce sustainable agricultural techniques and adjust production systems to respond to market fluctuations.
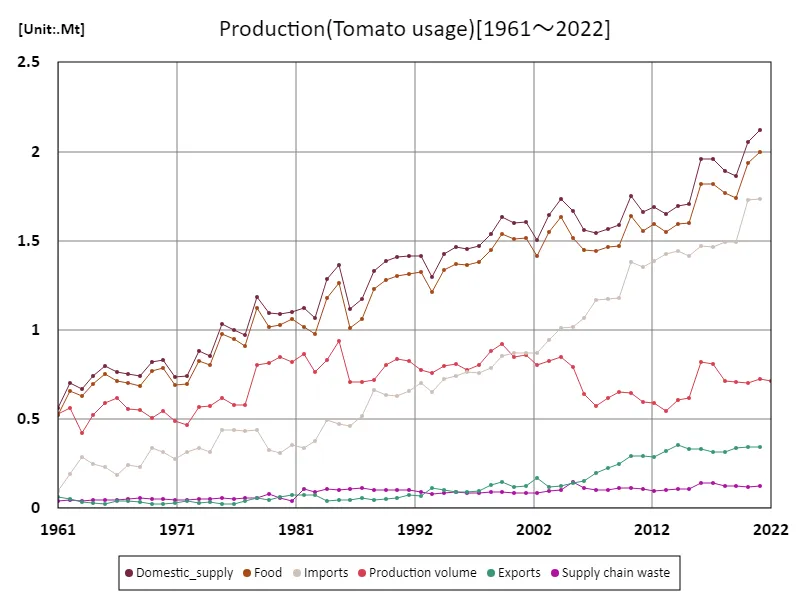

The maximum is the latest one, 2.12Mt of Domestic_supply
Yield(by vegetable)
Tomato is a particularly important crop in France’s vegetable production, reaching a peak yield of 189 t/ha in 2015. However, by 2022, the yield will be 63.9% of its peak. This decline can be attributed to several factors. First, there is the impact of climate change. Extreme weather and warming temperatures have made growing difficult, especially in the south, and may have reduced tomato yields. In addition, while advances in agricultural technology are creating a demand for more efficient production, the conversion of farmland and the reduction in cultivated area may also be having an impact. In addition, diversifying consumer tastes and market fluctuations may have led to increased interest in other crops and varieties, resulting in a partial decline in the area of tomato cultivation. However, tomatoes still play an important role in French agriculture and are in particular demand for processing and the fresh market. In the future, as there is an increased demand for sustainable agricultural techniques and measures to adapt to climate change, tomato cultivation methods are expected to be reconsidered.
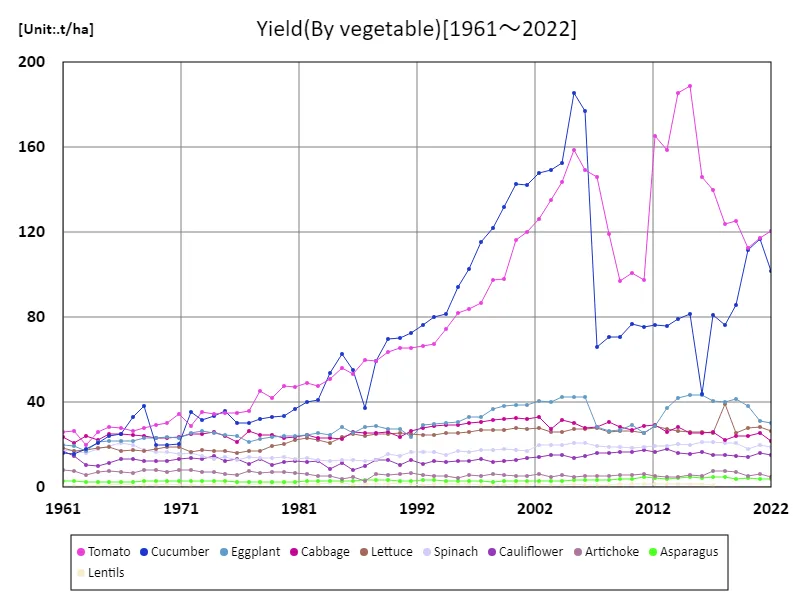

The maximum is 189t/ha[2015] of Tomato, and the current value is about 63.9%
Land use (by vegetables)
Looking at data on vegetable land use in France (2022), lettuce occupies the largest area, reaching 16.7 kha. This area is the largest of the total and shows that lettuce is the main vegetable crop in France. The average land use area is 7.14 kha, and the total is 64.3 kha. These data give an idea of the scale and concentration of vegetable production in France. The high proportion of lettuce suggests that French agriculture is dependent on a specific crop, with lettuce cultivation being the dominant agricultural activity, especially in areas where production is concentrated. In recent years, due to climate change and increasing efficiency in land use, France’s agriculture has seen fluctuations in the area devoted to each crop. Vegetables other than lettuce also occupy a certain amount of land area, especially tomatoes and cabbages, which are grown in different regions, but there are few crops that are grown on such a large scale as lettuce. In the future, efficient land use and the introduction of new cultivation techniques will be important in order to achieve sustainable agriculture. Changes in land use area need to be accommodated flexibly according to climatic conditions and market demand.

The maximum is 711kt of Production volume, the average is 711kt, and the total is 711kt
Tomato usage
Based on data from 1961, tomato production in France by use had a maximum domestic supply of 2.12 Mt, which represented the peak of tomato production. At this time, the demand for tomatoes for the domestic market was very high and tomatoes played an important role both in the fresh market and for processing. In particular, the warm climate of the south of France allowed for large-scale production, ensuring a stable supply for domestic consumption and processing. In recent years, changes in consumer preferences and the market have influenced the composition of tomato production by use, which has been changing. The production of processing tomatoes has increased, especially the varieties used in the production of tomato sauce and juice. On the other hand, although production for the fresh market remains stable, the proportion of domestic supply is gradually changing due to increased competition and an increase in imports. In addition, climate change and innovations in agricultural technology have led to the evolution of tomato cultivation methods, creating a demand for more efficient production. Taking these factors into account, tomato production will continue to fluctuate according to demand for each use, and the introduction of sustainable agricultural techniques will become an important issue.
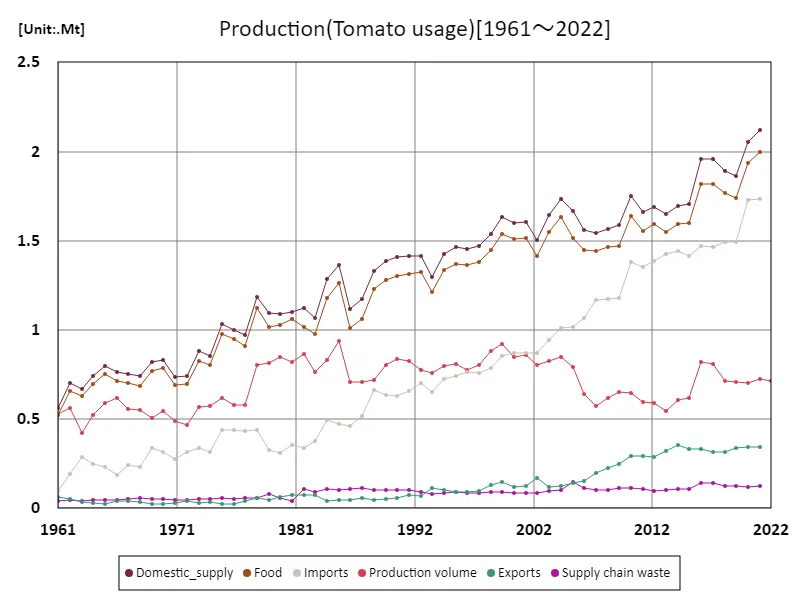

The maximum is the latest one, 2.12Mt of Domestic_supply



Comments