Abstract
In Germany’s vegetable production in 2022, cabbage recorded the largest yield at 650kt. Cabbage is deeply rooted in German culinary tradition and plays an important role in agricultural production. Other major vegetables include potatoes and carrots, which also maintained stable production volumes. Potatoes in particular are widely used in food culture and the processing industry, and consumption is high throughout Germany. In terms of land use, cabbage and potatoes occupy a relatively large area, and these vegetables are in high demand and have been produced for many years. When it comes to tomatoes, they can be classified according to their uses; they are mainly consumed as fresh vegetables and used for processing (tomato sauce and ketchup), with the production of processed tomatoes showing an upward trend. Tomato production is concentrated in warm regions, and greenhouses and vinyl houses are often used for cultivation. Overall, German vegetable production remains stable, dominated by certain vegetables (especially cabbage and potatoes). Production volumes and land use trends continue to be influenced by consumer trends and developments in the processing industry.
Production (by vegetables)
Looking at the history of vegetable production in Germany, cabbage production in particular shows some notable features. The highest cabbage production volume was recorded in 1985 at 1.08 Mt. However, production has declined since then, and is currently at 60.5% of its peak level. This decrease is thought to be due to factors such as changes in consumer eating habits, increased agricultural efficiency, and crop diversification. Although cabbage production has remained stable, fluctuations in demand have led to increased production of other vegetables. From the 1960s to the 1980s, the production volume of cabbage and other vegetables reached its peak, and cabbage in particular occupied an important position as a representative vegetable of Germany. However, production volume subsequently decreased due to changes in consumer tastes and an increase in imported vegetables. Recently, the production of traditional vegetables, including cabbage, has decreased, and instead other vegetables, such as tomatoes and peppers, have increased. Overall, it is clear that German vegetable production has adapted flexibly to advances in agricultural technology and market demand. The decline in cabbage production reflects past changes, and production adjustments based on consumer needs will likely continue in the future.
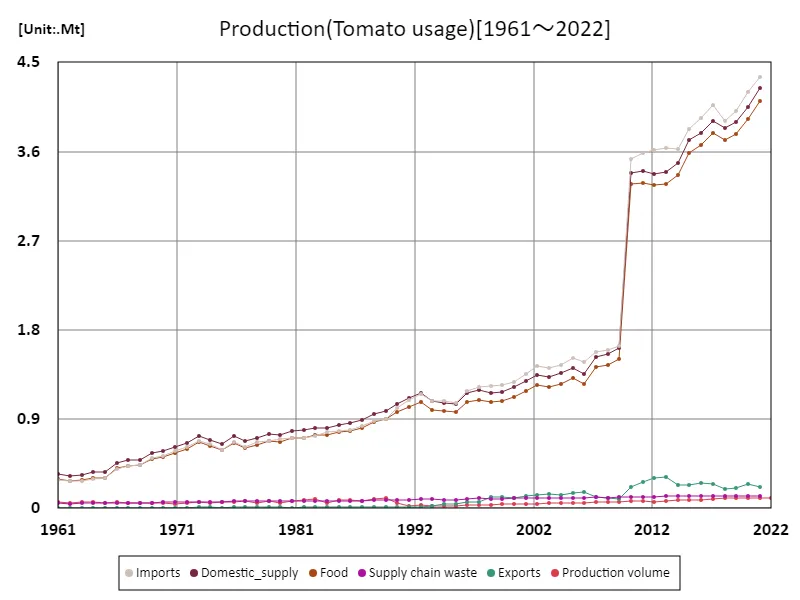

The maximum is the latest one, 4.36Mt of Imports
Yield(by vegetable)
Within vegetable production in Germany, tomato yields have shown a significant increase. In 2019, production reached a record high of 274t/ha, and has since remained at a high level of 98.3% since its peak. Tomato production is high and stable, due in particular to increased demand for processing. Growing demand for processed tomatoes, which are widely used in products such as ketchup, sauces and purees, contributed to the increase in yield. Over the past few decades, Germany has focused on improving tomato production, with advances in greenhouse cultivation techniques, improved varieties and more efficient irrigation systems contributing greatly to increased yields. In particular, due to the effects of global warming and technological innovation, tomato production in Germany has stabilized, not only meeting domestic demand but also increasing supply to the export market. In addition, the area under tomato cultivation is increasing, and consumers’ growing health consciousness and changes in food culture are also driving increased demand for tomatoes. Tomatoes play a very important role on the German diet and their high productivity is expected to continue to be maintained as agricultural efficiency improves.
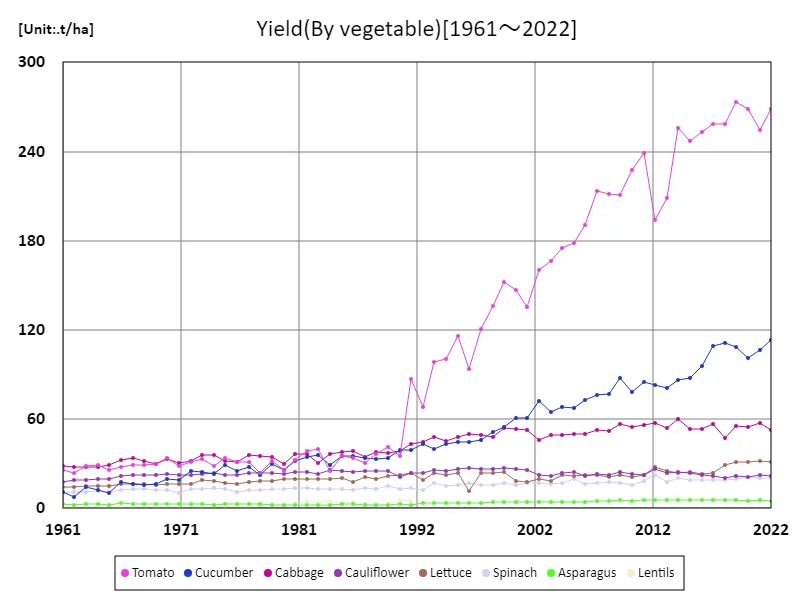

The maximum is 274t/ha[2019] of Tomato, and the current value is about 98.3%
Land use (by vegetables)
In terms of land use characteristics in German vegetable production, asparagus occupies the largest area, reaching 21.3 kha in 2022. This is the largest area of the total, reflecting the importance of asparagus demand and production. Asparagus is particularly seasonal, as it is harvested in the spring, and is deeply rooted in German food culture. For this reason, the area cultivated for asparagus is relatively large compared to other vegetables. On the other hand, the overall average area is 7.58kha, which highlights the large area taken up by asparagus. The total vegetable production area in Germany is 53.1 kha, of which asparagus accounts for the majority, making it a particularly important crop. Additionally, as asparagus cultivation continues over a relatively long period of time, the land turnover rate is lower than for other vegetables, which is also likely to have an impact on the large area. The trend so far has been an increase in demand for certain crops, such as asparagus, which has led to an increase in the area under cultivation. In addition, increased cultivation efficiency due to global warming and improvements in agricultural technology are also affecting land use. Highly seasonal crop production is expected to continue to play an important role in the future.
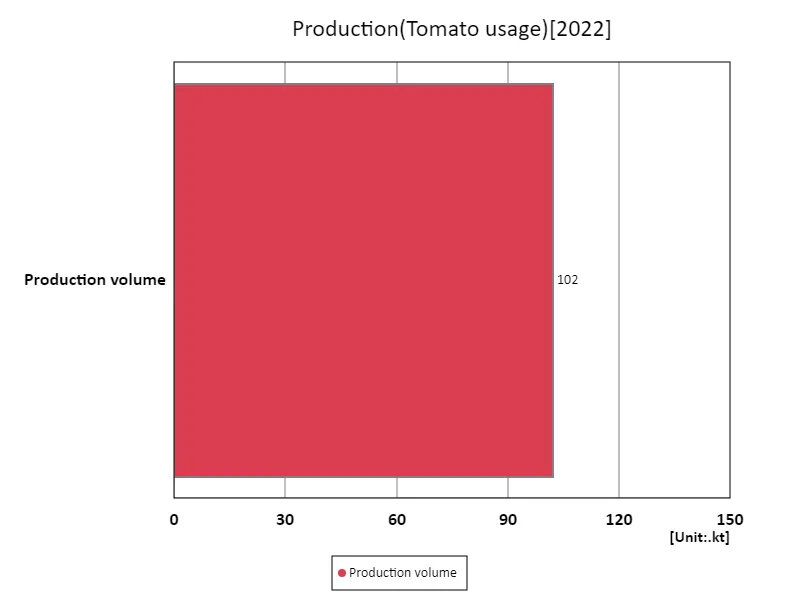

The maximum is 102kt of Production volume, the average is 102kt, and the total is 102kt
Tomato usage
A notable trend in German tomato production is the peak volume of imported tomatoes, reaching 4.36 Mt in 1961, a value that remains at the highest level today. This highlights the German tomato market’s dependence on imports and not just on domestic production. In particular, we can see that imported tomatoes play an important role in ensuring supply to meet German consumer demand. In terms of uses, imported tomatoes are mainly used for the fresh market and for processing, and are widely consumed in Germany’s culinary and food industries. There is particularly high demand for tomatoes for processing (ketchup, sauce, etc.), and as a result, the development of the processing industry has had a major impact on tomato production. The production of tomatoes for processing requires quality and stability of supply, so while domestic production is being strengthened, imported tomatoes also play an important complementary role. From the 1960s to the present day, German tomato production has adjusted according to market fluctuations and consumer tastes. In particular, due to the high reliance on imported tomatoes, the supply of tomatoes in the domestic market is easily influenced by external factors, and attention will continue to be focused on the impact that fluctuations in import volumes have on the market.
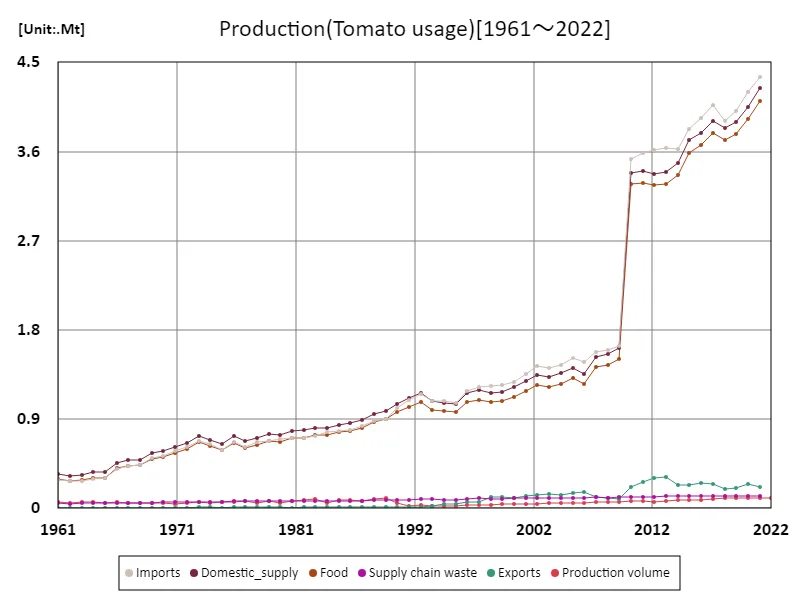

The maximum is the latest one, 4.36Mt of Imports



Comments