Abstract
In Poland’s vegetable production, based on 2022 data, cabbage has the largest production volume at 688kt, making it the country’s main cultivated vegetable. Over the past few years, Poland has seen a boom in the cultivation of cabbage, carrots, tomatoes, and other crops, with cabbage in particular providing a major source of domestic demand due to its high production volume. In terms of land use, cabbage and carrots are cultivated on a large area, indicating a stable supply. When it comes to tomato production, the production volume by use is clear, with tomatoes for processing tending to account for a high share. Tomatoes in particular are produced in large quantities for domestic processors and are often used in products such as ketchup, juice, and sauces, so stability of supply and demand is important. Overall, Polish vegetable production not only meets domestic demand, but also provides a significant supply for export, with vegetables for processing playing a particularly important role.
Production (by vegetables)
Polish vegetable production has shown notable fluctuations between 1961 and 2022. In particular, cabbage production peaked at 2.08 Mt in 1984 and has since declined gradually. Current production volume has fallen to about 33% of its peak. This decline is thought to be due to structural changes in agriculture and fluctuations in market demand, as well as advances in agricultural technology and changes in the labor force. At its peak in the 1980s, cabbage and many other vegetables were widely cultivated as Poland’s main agricultural products. However, economic transformation since the 1990s and increased market competition after joining the EU have led to a change in agricultural direction and a reduction in the area devoted to cabbage production. On the other hand, there is a trend towards expanding production of other vegetables and crops, especially tomatoes and potatoes. Additionally, although cabbage cultivation remains important in Poland, mainly for domestic consumption and processing, the area under cultivation is being adjusted to accommodate imports from other countries and fluctuations in demand. Overall, vegetable production in Poland is characterised by increasing diversification and market-oriented crop selection.
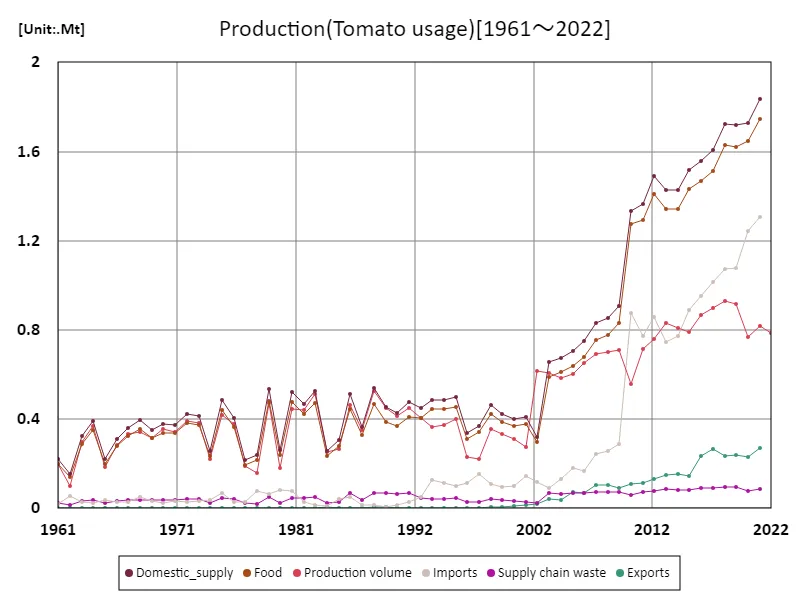

The maximum is the latest one, 1.83Mt of Domestic_supply
Yield(by vegetable)
Among vegetable production in Poland, the tomato is a particularly noteworthy crop. The tomato yield of 117t/ha recorded in 2022 is the highest ever vegetable production in Poland and is a very high figure compared to previous production volumes. In recent years, as demand for tomatoes has increased, the area under cultivation has expanded and productivity has improved. As a result, we have seen growth with yield reaching 100% compared to its peak. This trend is due to an expansion in demand for tomatoes for domestic consumption as well as for the processing industry. In Poland, processed products made from tomatoes such as ketchup, sauces and juices are widely consumed, and the growth of this market contributed to the increase in production. In particular, since joining the EU, advances in processing technology and greater efficiency in tomato cultivation have also contributed to the increase in yields. Improvements in tomato cultivation techniques have also led to a significant increase in yields. This has enabled Poland to become more competitive in tomato cultivation, enabling it to focus not only on the domestic market but also on exports to other countries. Overall, tomato has become an important crop in Polish agriculture and its productivity continues to increase.
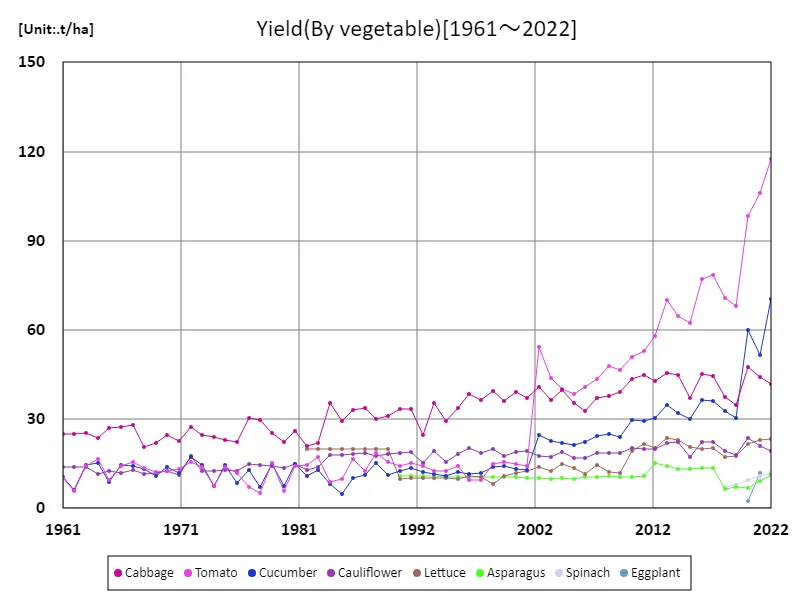

The maximum is the latest one, 117t/ha of Tomato
Land use (by vegetables)
In terms of land use for vegetable production in Poland in 2022, cabbage occupies the largest area, reaching 16.4 kha. This shows the importance of cabbage in Poland and reflects the fact that it has been in steady production for many years. The area under cabbage cultivation has remained constant as it is mainly used for domestic demand and processing. On the other hand, the average area under vegetable cultivation across Poland is 6.56 kha, with a total area of 45.9 kha. These figures also show how large a proportion cabbage makes up. The crops that follow cabbage are tomatoes and potatoes, and their cultivation areas also remain at a certain level, but there are few crops that occupy areas as large as cabbage. In recent years, agricultural efficiency has improved in Poland, and technologies have been introduced that enable higher yields on smaller areas. As a result, even though the area cultivated with cabbage is large, it can be said that the efficiency of land use across the entire farmland has improved. Furthermore, the cultivation area for each vegetable is expected to continue to fluctuate as it is influenced by market demand, agricultural policies, and even climatic conditions.

The maximum is 787kt of Production volume, the average is 787kt, and the total is 787kt
Tomato usage
Regarding tomato production by use in Poland, the maximum recorded in 1961 was 1.83 Mt, which represents a large share of the domestic supply at that time. During this period, Poland’s tomato production was mainly focused on domestic consumption, especially as a fresh vegetable. Tomato production was likely carried out on a large scale to meet the demand for fresh vegetables for home and market use. In recent years, there has been a trend towards a shift in tomato production in Poland towards processing, with demand for processed products such as ketchup, sauces and juices increasing. This change is due to increased domestic consumption as well as increased demand for processing industries as a result of Poland becoming part of the EU market. As exports to the EU market in particular have increased, Poland has established a stable supply system by producing tomatoes for processing. On the other hand, the proportion of tomatoes supplied domestically has been gradually decreasing, with processing now the mainstream, but there is still a certain level of supply to the domestic market. In this way, the uses of tomato production in Poland have changed over the years, and production has been adjusted to meet the needs of both domestic and international markets.
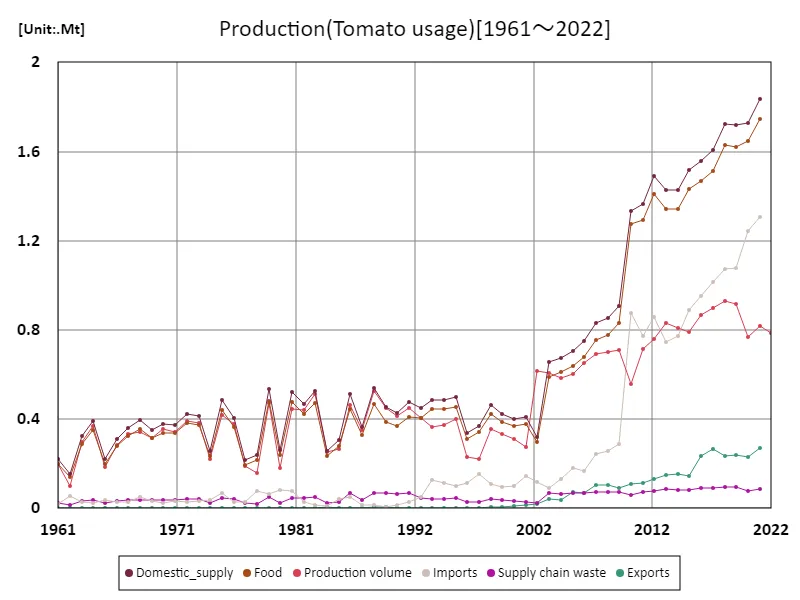

The maximum is the latest one, 1.83Mt of Domestic_supply



Comments