Abstract
In Mexico’s vegetable production, based on data for 2022, cucumber has the highest production volume, reaching 1.08 Mt. This makes cucumber an important cultivated vegetable in Mexico. The production volume of tomatoes is also very high, and by usage, most are consumed raw, with production for export also thriving. Mexico is a major exporter of tomatoes, especially to the U.S. market. In terms of land use, vegetables that require a lot of water, such as cucumbers and tomatoes, are concentrated in areas with well-developed irrigation systems. Efficient water resource management is especially needed in the arid regions of northern and western Mexico. These regions benefit from warm climates and long growing seasons, contributing to increased productivity. Additionally, Mexican vegetable production is characterized by a seasonal balance of supply and demand. For example, cultivation is active in warm climates during the winter months, ensuring a stable supply not only for domestic consumption but also for the export market. Thus, Mexican vegetable production has diverse characteristics in terms of production volume, land use, and strategic areas for different applications.
Production (by vegetables)
In Mexico’s vegetable production, based on data from 1961 to 2022, cucumber recorded its highest ever production volume of 1.19 Mt in 2019. However, production volume has since gradually decreased, and currently stands at 90.5% of its peak level. This declining trend may be due to factors such as climate change, water resource constraints, and fluctuations in market demand. Cucumbers are mainly produced in the arid regions of northern and western Mexico, where productivity has been ensured by improvements in irrigation techniques. However, the depletion of water resources and environmental issues in recent years are thought to be affecting production volumes. In addition, production of other vegetables such as tomatoes and avocados is increasing in Mexico, and investments and market shifts in these crops may also be affecting cucumber production. On the other hand, Mexico remains a world-class vegetable producing country, with many vegetables, including cucumbers, supplied not only to domestic consumption but also to export markets. Future challenges will require the introduction of sustainable production methods and the development of new markets, which will lead to the recovery and stabilization of production volumes.
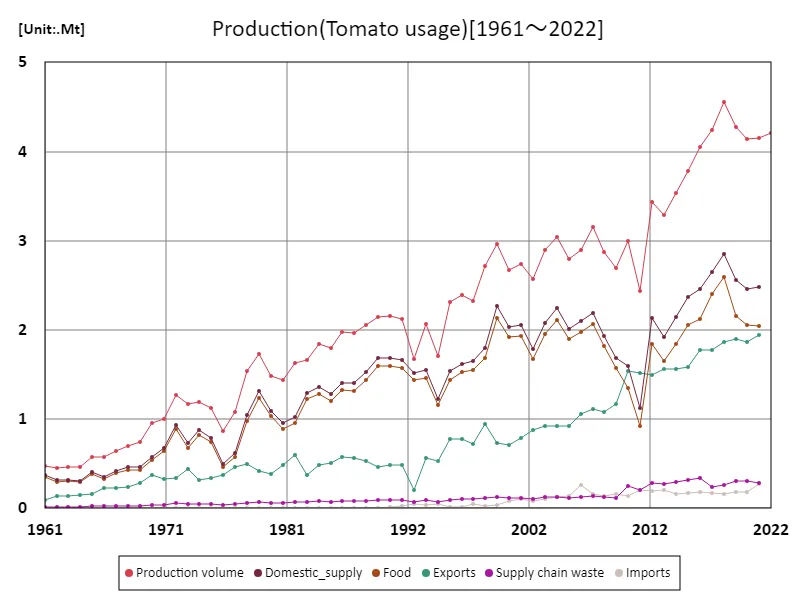

The maximum is 4.56Mt[2018] of Production volume, and the current value is about 92.3%
Yield(by vegetable)
In Mexico’s vegetable production, eggplant yield reached an all-time high of 88.4t/ha in 2012. However, current yields are only 64.5% of their peak, and this downward trend is likely due to a number of factors. Eggplant is produced in warm climate regions, particularly in Mexico, but recent climate change, water shortages, and soil degradation may be affecting it. Another factor is that while agricultural technology and cultivation methods have improved, the area cultivated with eggplant has decreased due to increased demand and improved profitability of other crops. Additionally, consumption trends for eggplant are changing, leading to increased competition in both domestic and export markets. Other vegetables are increasingly being chosen as alternatives to eggplant, which may have led to a decrease in production. However, Mexico remains a major eggplant producing country and there continues to be a certain level of demand in the domestic market. In the future, technological innovation to improve eggplant productivity and the introduction of environmentally friendly and sustainable agricultural methods will be important, and it is expected that this will contribute to a recovery in production volumes.
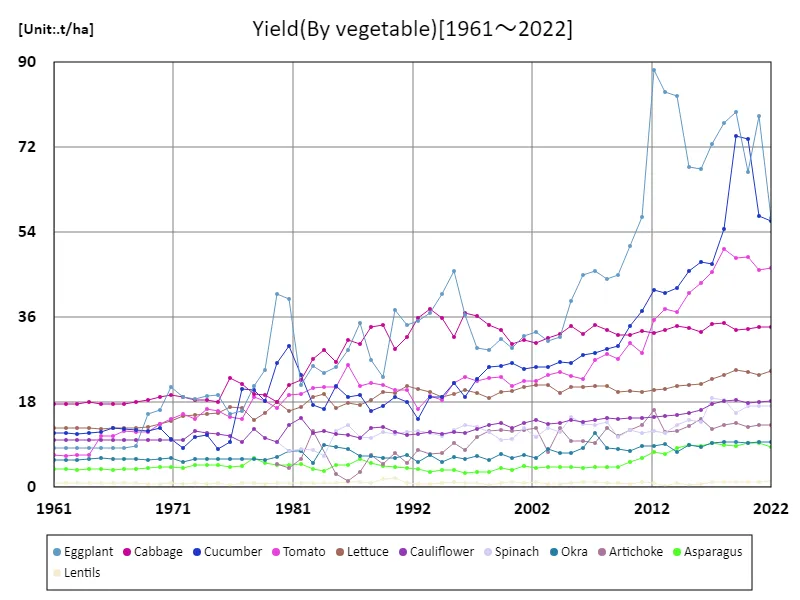

The maximum is 88.4t/ha[2012] of Eggplant, and the current value is about 64.5%
Land use (by vegetables)
Looking at 2022 data on land use in vegetable production in Mexico, tomatoes occupy the largest area, reaching 90.7 kha. This indicates that tomatoes are a major agricultural product in Mexico and that production is particularly active for export. Tomato production is primarily in the arid regions of northern and western Mexico, where it is grown over a wide area using efficient irrigation techniques. In addition to being consumed domestically, tomatoes are also widely exported to the United States and Canada, and play an important role in Mexico’s agricultural economy. The average land use is 21.3kha with a total area of 234kha. Even at this scale, vegetable production in Mexico remains large-scale and intensive. However, for the second most important crop after tomatoes, the land use area is relatively small and tends to be more dispersed than for other vegetables. This shows that particular effort is being put into tomato production. Additionally, sustainable agricultural methods and water resource management are important issues in Mexico, and there is a demand for more efficient land use. In particular, improving irrigation management and soil protection technologies will be key to reducing the burden on the environment while maintaining productivity.

The maximum is 4.21Mt of Production volume, the average is 4.21Mt, and the total is 4.21Mt
Tomato usage
In Mexico, based on data from 1961, the tomato production volume was 4.56 Mt, which is still the largest production volume today. Tomatoes are one of Mexico’s most important agricultural products and are widely consumed, especially fresh. The increase in production is due to growing demand in the domestic market as well as increased supply to export markets. Exports, particularly to the United States, have become an important economic factor for Mexico, and tomato production has increased in response to demand. Additionally, tomato production in Mexico is supported by improvements in cultivation and water management techniques, with the development of irrigation facilities in particular contributing to improved productivity. In terms of uses, tomatoes are overwhelmingly used for eating raw, but there are also tomatoes produced for processing, and they are used as ingredients in ketchup and sauces. Tomatoes for processing are supplied not only for domestic consumption but also for export, and demand for them remains at a certain level. Tomato production occurs primarily in the arid regions of northern and western Mexico, which benefit from a warm climate and irrigation. In order to maintain stable production in the future, it will be necessary to address environmental issues and introduce sustainable agricultural methods.
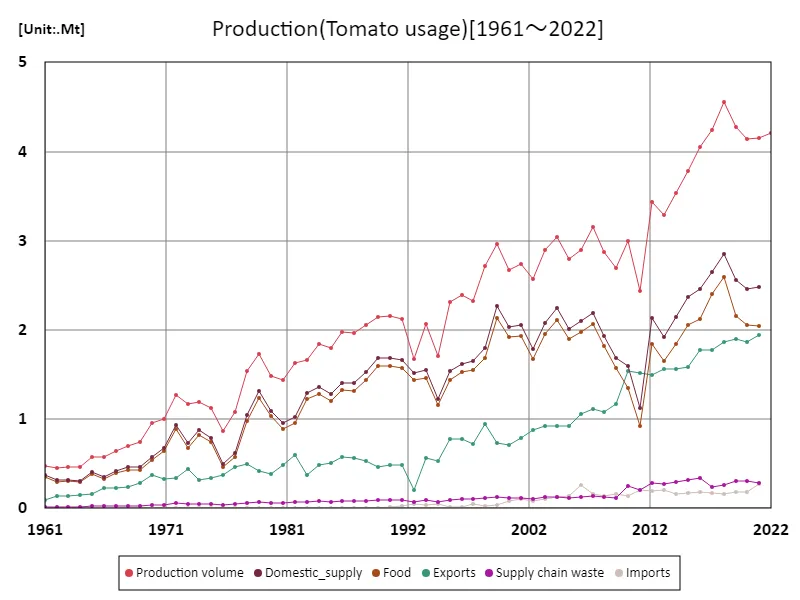

The maximum is 4.56Mt[2018] of Production volume, and the current value is about 92.3%



Comments